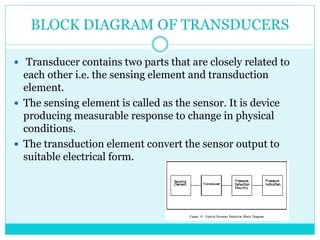
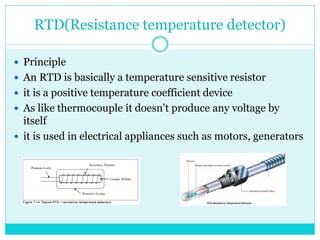
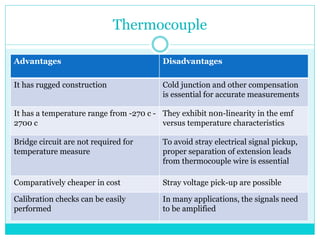
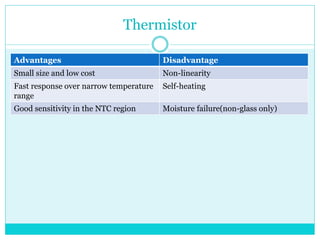
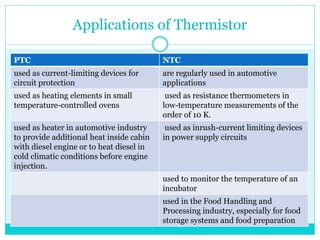
This document provides information about temperature transducers. It discusses that a temperature transducer is a device that converts a temperature measurement into another form of energy, such as an electrical signal. It then describes different types of temperature transducers, including resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), thermocouples, and thermistors. For each type, it explains the basic principle of operation, common applications, and advantages and disadvantages. The document aims to inform readers about how temperature transducers work and their various uses in fields like manufacturing, heating/cooling systems, and more.