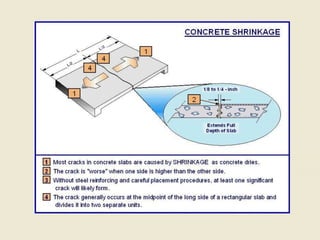
This document summarizes the effects of shrinkage and temperature changes on concrete, including:
- Shrinkage occurs as free water evaporates from concrete, causing cracks if not controlled. It can cause stresses in statically indeterminate structures and loss of pre-stress.
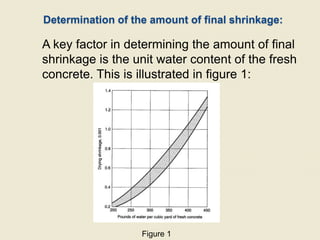
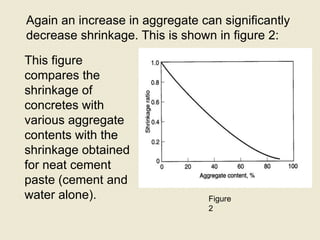
- The amount of shrinkage depends on water-cement ratio, cement content, aggregate type and content. It can be reduced by decreasing water, increasing aggregate, and proper curing.
- Temperature changes cause expansion and contraction that can also cause cracks. The coefficient of thermal expansion is typically 4-7x10-6 per °F.
- Both shrinkage and temperature effects are important to consider in concrete design to