The document discusses various topics related to concrete structures including:
- Concrete is the second most used construction material after water due to its durability and ability to be molded into different shapes. Reinforcement is added to concrete to improve tensile strength.
- Types of cement used in concrete structures including Type K and Type M cement.
- Reinforced concrete uses steel reinforcement bars to improve tensile strength. Prestressed concrete applies stress before external loads to increase load capacity.
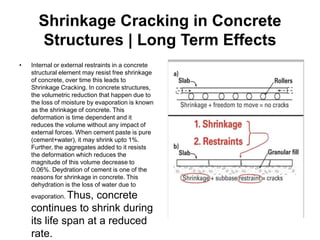
- Advantages of concrete structures include availability/cost of materials and ability to take compressive/bending forces. Disadvantages include cracking from shrinkage and weakness in tension.
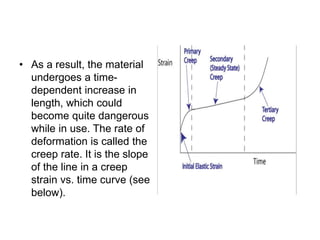
- Concrete creep is a permanent deformation over time under load. Cre