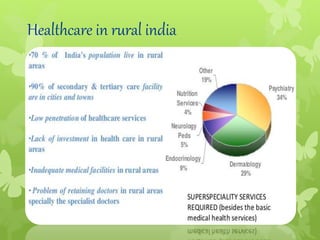
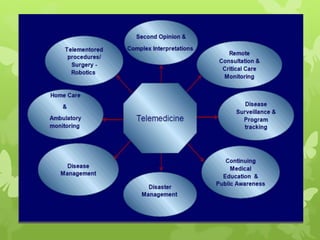
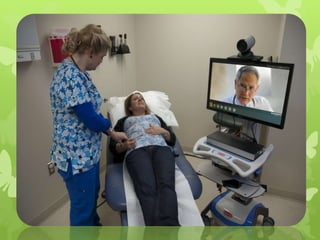
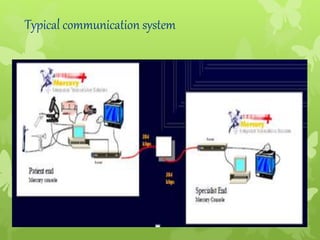
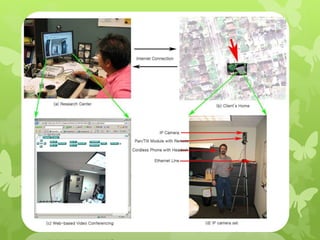
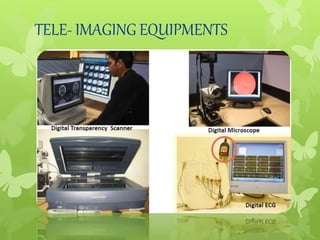
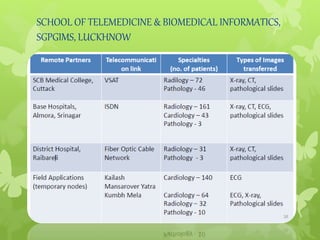
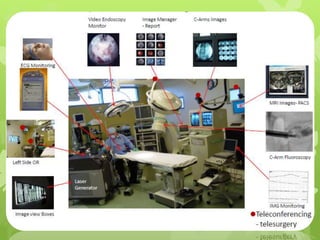
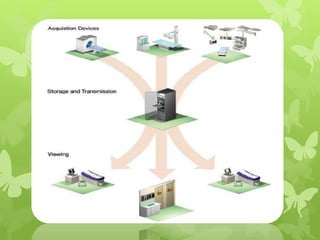
Telemedicine provides healthcare access in rural areas through technology. It involves transmitting medical information like test results, records, and real-time video conferences between patients and doctors. This allows specialists to consult on remote cases. The document discusses the types of telemedicine like synchronous video calls and asynchronous store-and-forward of data. Challenges include low bandwidth and lack of infrastructure in rural areas, but telemedicine can improve access to healthcare when traditional care is not available or feasible.