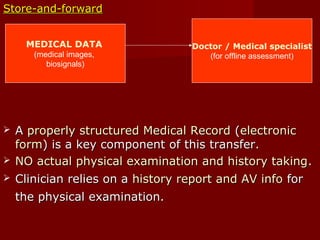
Telemedicine is a rapidly evolving field that employs electronic communication for clinical care delivery, including consultations and examinations. It encompasses various modalities like interactive and store-and-forward telemedicine, and has applications in remote monitoring and specialty consultations, particularly beneficial for isolated populations. Despite its advantages, such as improved access and cost-effectiveness, challenges include potential system abuse, diminished patient-doctor relationships, and the need for expensive equipment.








![TELEMEDICINE INTERACTIONSTELEMEDICINE INTERACTIONS
SimplestSimplest ::
• optical disk system at hospital transmits images, text andoptical disk system at hospital transmits images, text and
other data to a physician’s home. (physician requires littleother data to a physician’s home. (physician requires little
bandwidth and specialized equipment).bandwidth and specialized equipment).
LecturesLectures ::
medical student education course given from hospitalmedical student education course given from hospital
location to students in another region.location to students in another region.
One-way videoOne-way video [students can only view the lecture].[students can only view the lecture].
2-way video2-way video [students can also take part].[students can also take part].
Instructor can transmit sound , video, text and images toInstructor can transmit sound , video, text and images to
multiple classrooms.multiple classrooms.
Minimum bandwidth required (moderate to high).Minimum bandwidth required (moderate to high).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telemedicine-150930072308-lva1-app6891/85/Telemedicine-10-320.jpg)

![BENEFITS & USESBENEFITS & USES
Most beneficial for populations living inMost beneficial for populations living in isolated communities andisolated communities and
remote regions.remote regions.
Currently being appliedCurrently being applied in virtually all medical domainsin virtually all medical domains..
[Teleradiology, telecardiology, etc].[Teleradiology, telecardiology, etc].
Useful as a communication tool b/n aUseful as a communication tool b/n a general practitioner and ageneral practitioner and a
specialistspecialist available at a remote location.available at a remote location.
Monitoring a patient at homeMonitoring a patient at home (using devices like B.P. monitors) and(using devices like B.P. monitors) and
transferring the information to a caregivertransferring the information to a caregiver is a fast growing emergingis a fast growing emerging
service.service.
Primary Remote Diagnostic VisitsPrimary Remote Diagnostic Visits
• In developing countries;In developing countries;
• A doctor uses devices to remotely examine and treat a patient.A doctor uses devices to remotely examine and treat a patient.
• holds big promises to solving major health care delivery problems.holds big promises to solving major health care delivery problems.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telemedicine-150930072308-lva1-app6891/85/Telemedicine-12-320.jpg)