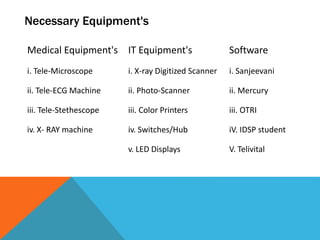
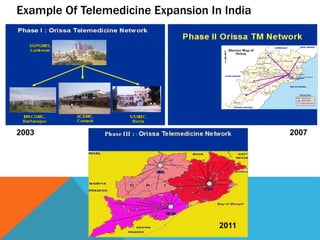
This document provides an overview of telemedicine, including its origins, definitions, types, equipment, staffing, benefits, and future directions. Telemedicine allows for the delivery of healthcare services via technology where distance is a factor, including video conferencing between patients and doctors, monitoring patient vitals remotely, and transferring medical data between hospitals. It has various applications like tele-radiology, cardiology, and psychiatry. Establishing telemedicine departments requires equipment like telescopes, ECG machines, digital cameras, and IT infrastructure. Staff typically include doctors, technicians, and administrators. Telemedicine provides benefits like increased access to expertise, cost savings, and opportunities for education and research. Its future expansion may include more robotics and remote