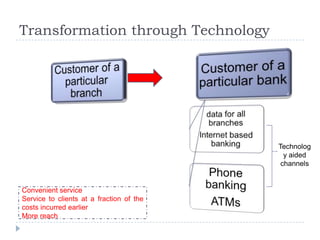
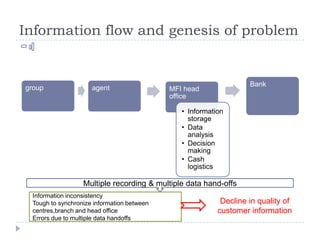
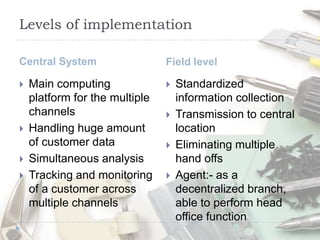
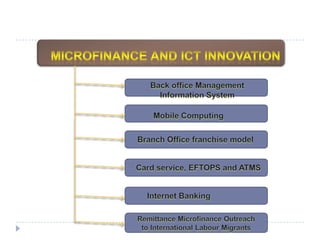
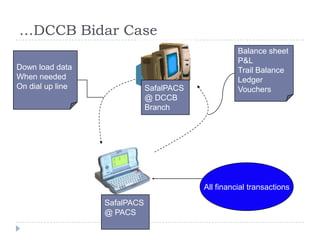
The document discusses the role of technology in transforming the microfinance sector in India, highlighting issues related to customer information systems and management. It proposes solutions such as mobile computing and branch office franchise models to enhance data accuracy and reduce transaction costs. The conclusion emphasizes that leveraging technology is essential for microfinance to support inclusive growth and address information asymmetry.