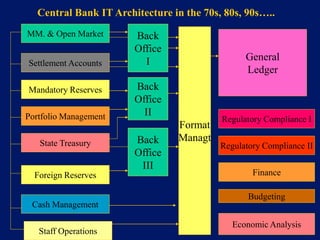
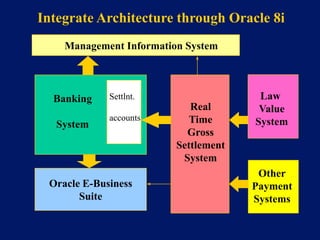
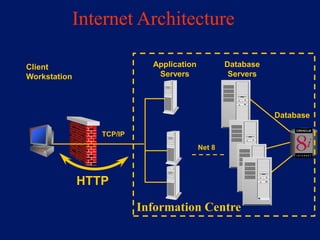
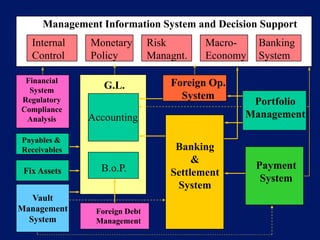
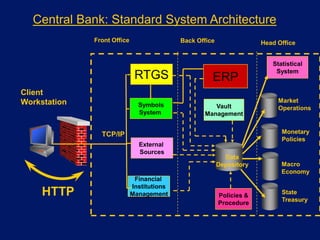
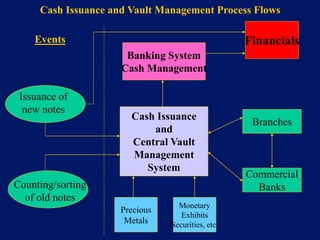
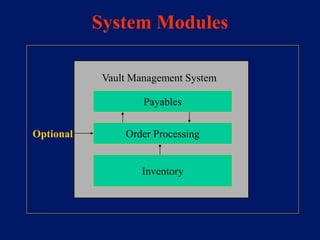
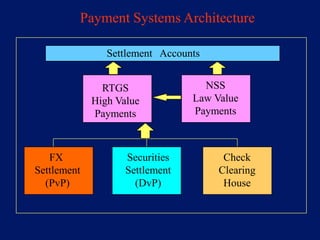
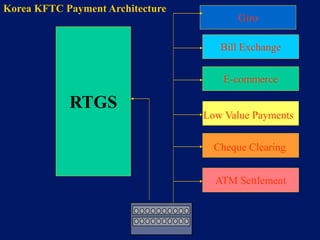
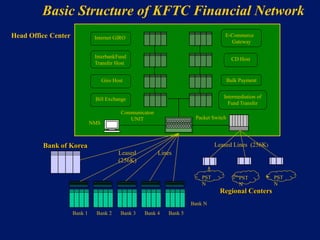
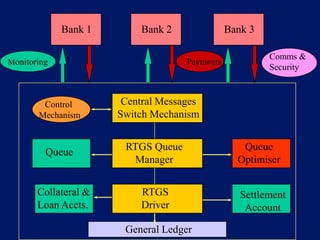
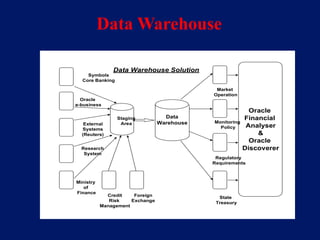
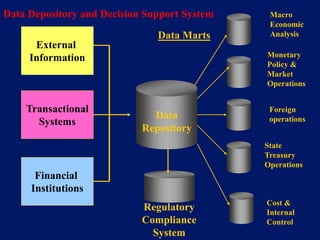
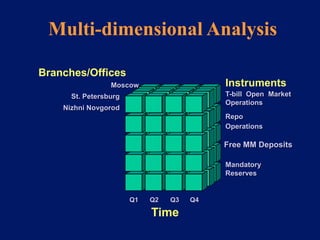
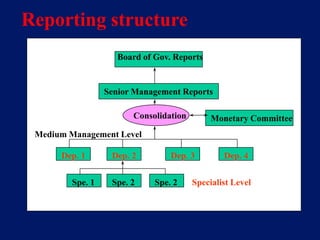
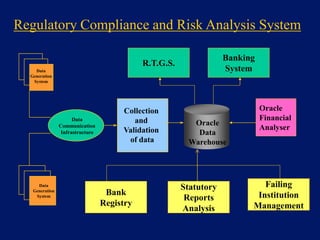
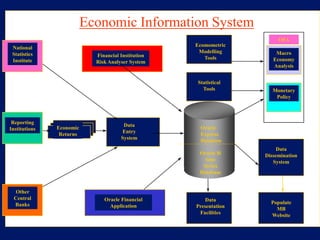
This document discusses system architecture for central banks. It proposes an integrated Oracle ERP system to consolidate various applications including banking, payments, general ledger, cash management, and regulatory reporting. A data warehouse would store transactional and external data to power decision support tools for monetary policy, risk management, and economic analysis. Standardizing on Oracle applications and a web-centric architecture allows centralization of information and reduces costs.