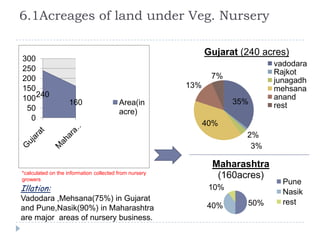
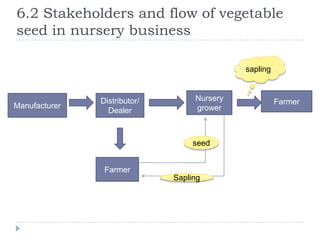
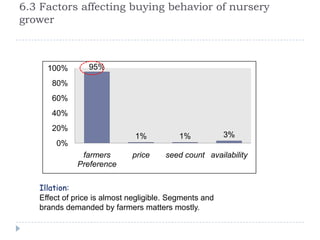
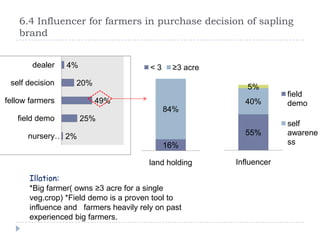
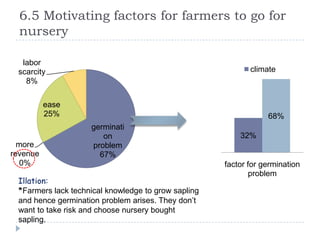
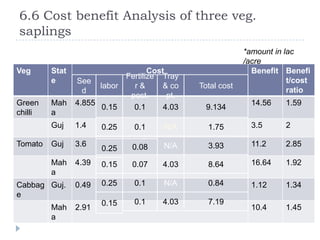
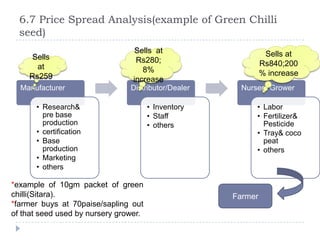
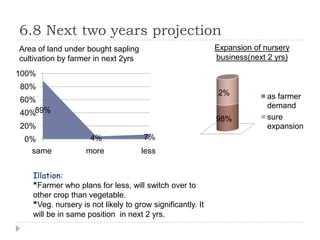
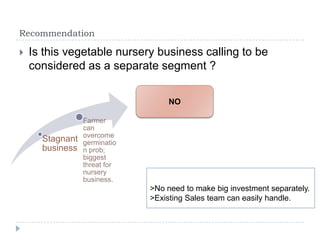
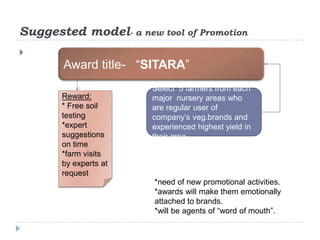
The document summarizes a research project on the vegetable nursery business in Gujarat and Maharashtra, India. The research was conducted to understand the current market scenario and identify business opportunities for Monsanto in the nursery segment. Key findings include that nursery culture is dominant in specific areas of the two states, and farmer preferences are the main influencer in the business. The research recommends strengthening relationships with nursery growers and using intensive field demonstrations as farmers are the biggest influencers for nursery growers. It also proposes a new promotional program of farmer awards to boost brand loyalty.






![5.1 Research Design
• Primary Research
Method • Survey [Questionnaire(structured)]
• Descriptive
Design • Cross-sectional
• Gujarat & Maharashtra
Area](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bidhubhushanbinit2012-copy-120926074246-phpapp02/85/Vegetable-Nursery-Business-in-Gujarat-Maharashtra-7-320.jpg)
![5.2 Research Design
• Gujarat-[ Vadodara,Junagadh,Rajkot,Mehsana]
• Maharashtra- [Pune,Nasik]
Sampling Frame
• Probabilistic Sampling(Multistage/Combination Sampling)
Sampling
Technique
• Sampling Elements: Nursery grower, Farmer & Distributor/Dealer
• Sample Size- 180 [nursery grower -35;Farmer -130;Distributor-15
Sampling
element &
Sample Size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bidhubhushanbinit2012-copy-120926074246-phpapp02/85/Vegetable-Nursery-Business-in-Gujarat-Maharashtra-8-320.jpg)