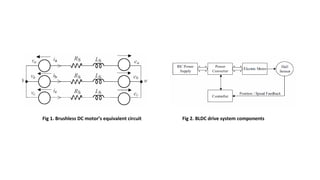
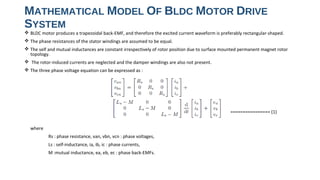
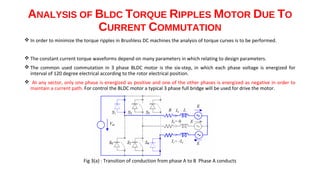
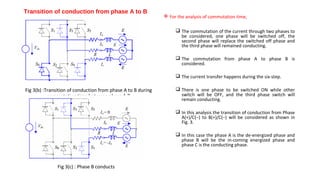
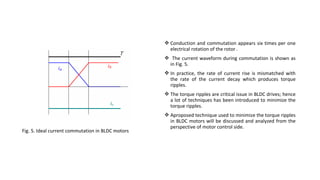
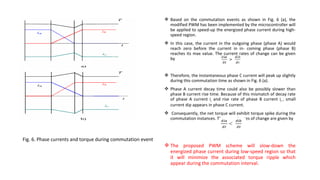
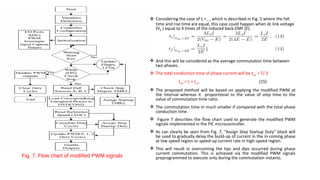
The document discusses torque ripple minimization in BLDC motors. It describes how torque ripples occur during current commutation between phases in BLDC motors due to mismatched current rise and fall times. A proposed PWM switching strategy uses modified PWM signals to speed up or slow down the energized phase current during commutation based on motor speed, minimizing torque ripples. Experimental results show that the modified PWM approach reduces current spikes and dips during commutation, resulting in lower torque ripple compared to conventional PWM control.












![RESULT
TOLIYAT, H. A.—CAMPBELL, S. : DSP-Based Electromechanical Motion Control, CRC Press, Boca Raton [Fla.], 2004.
JAHNS, T. M.—SOONG, W. L. : Pulsating Torque Minimization Techniques for Permanent Magnet AC Motor Drives – a
Review, Industrial Electronics, IEEE Transactions on 43 (1996), 321–330.
SINGH, B. : Recent Advances in Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motors, Sadhana – Academy Proceedings in Engineering
Sciences 22 (1997), 837–853.
HOLTZ, J.—SPRINGOB, L. : Identification and Compensation of Torque Ripple in High-Precision Permanent Magnet Motor
Drives, Industrial Electronics, IEEE Transactions on 43 (1996), 309–320.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/technicalseminar-130416181211-phpapp01/85/Technical-seminar-20-320.jpg)