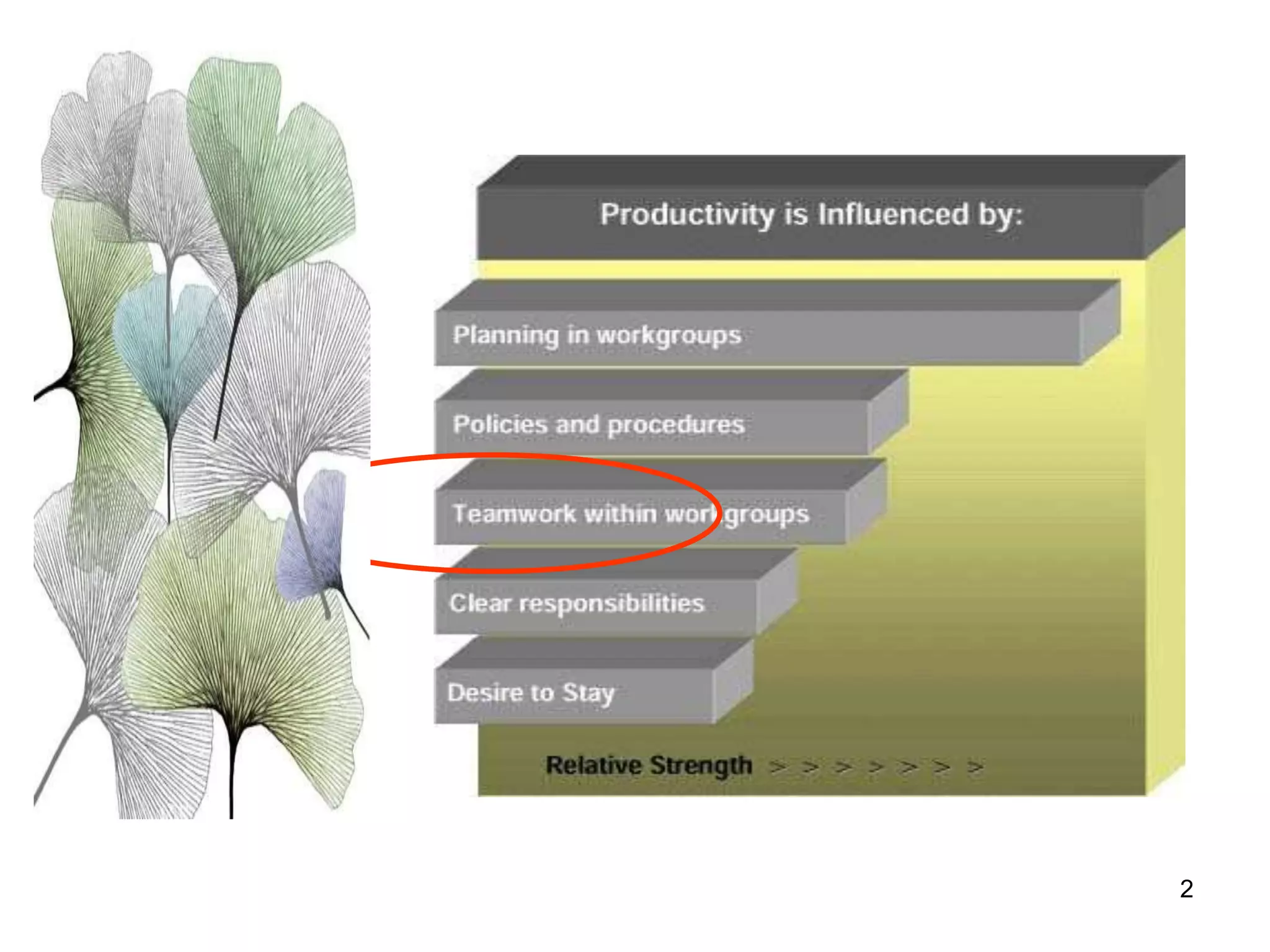
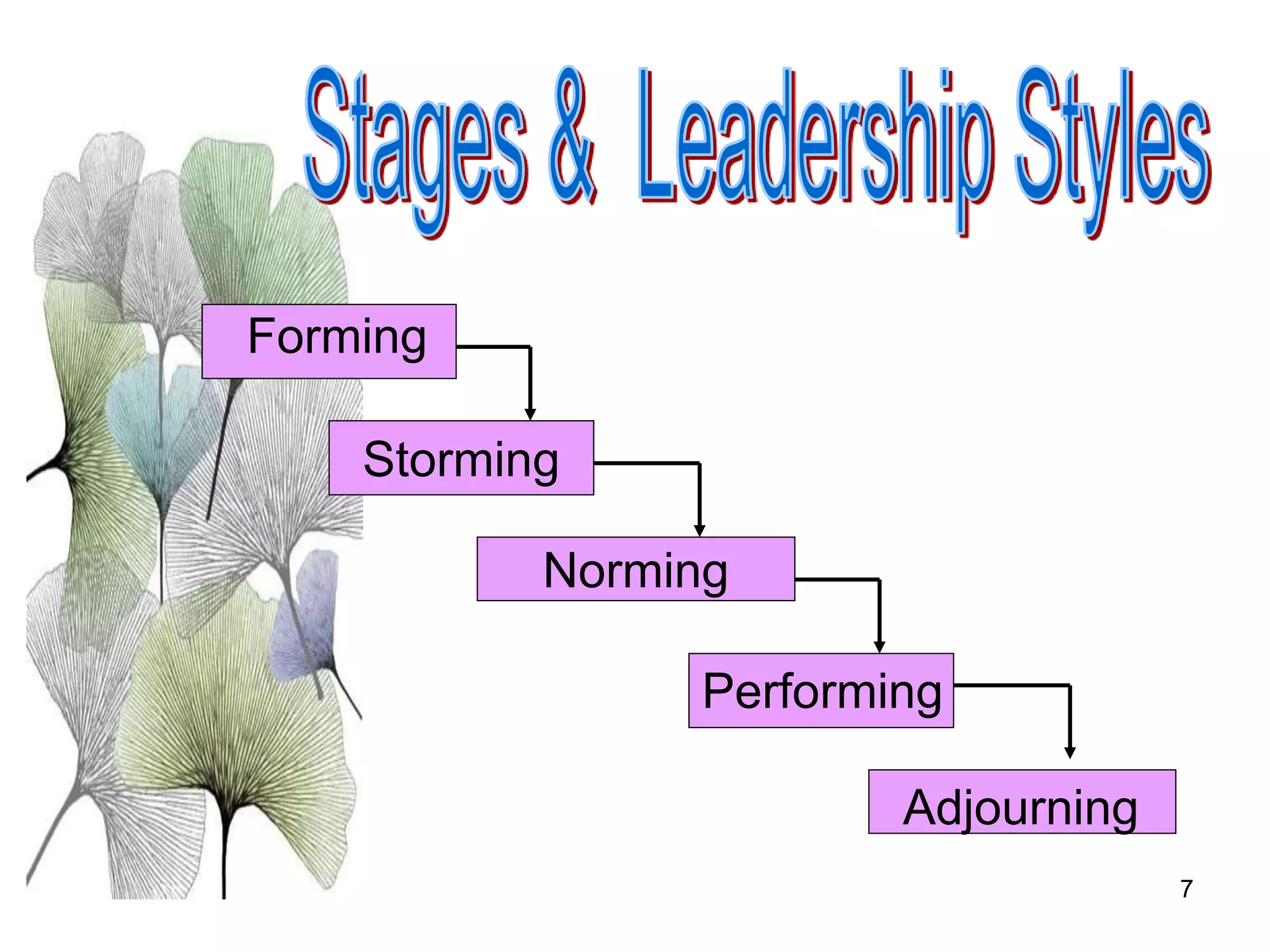
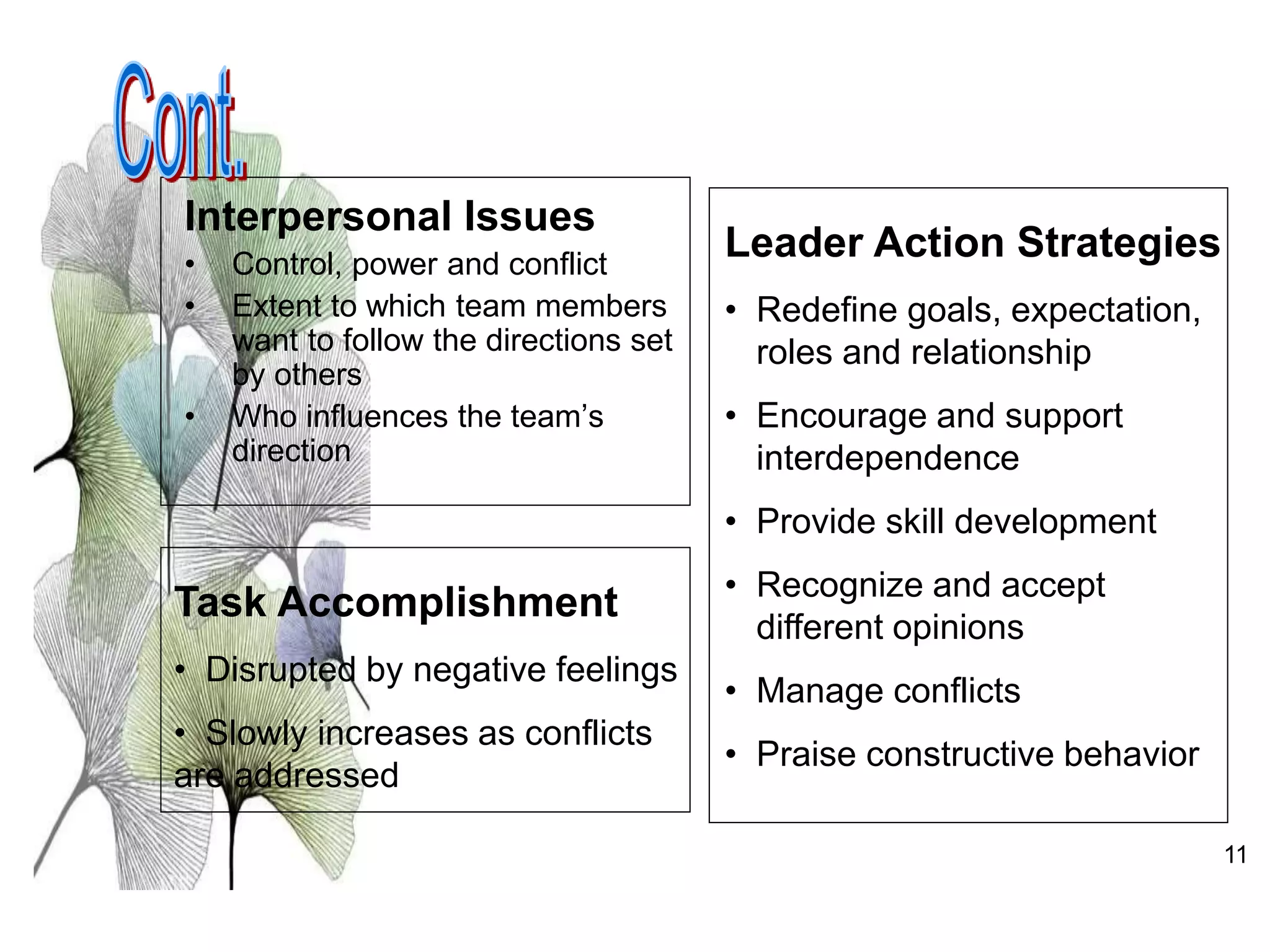
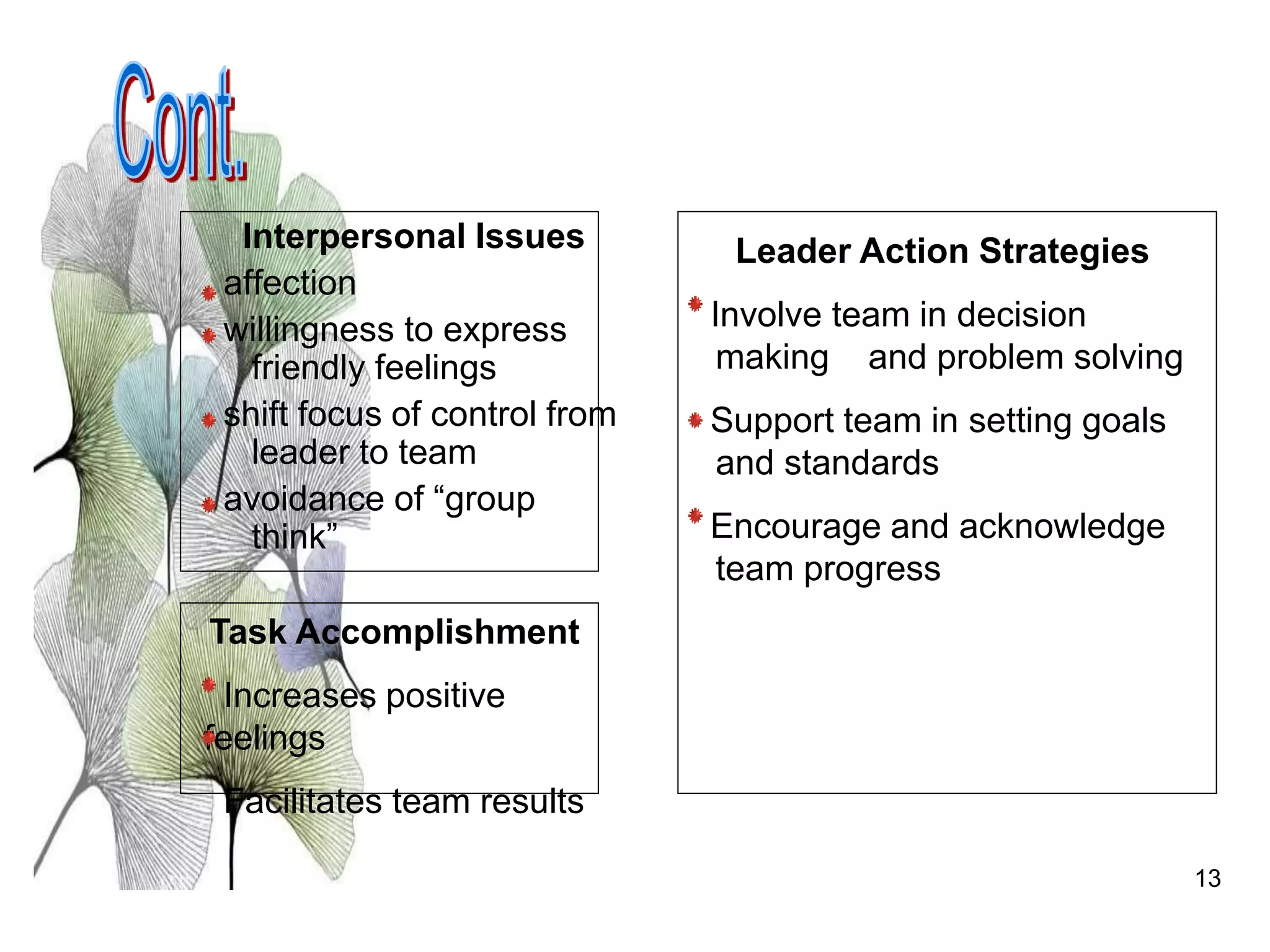
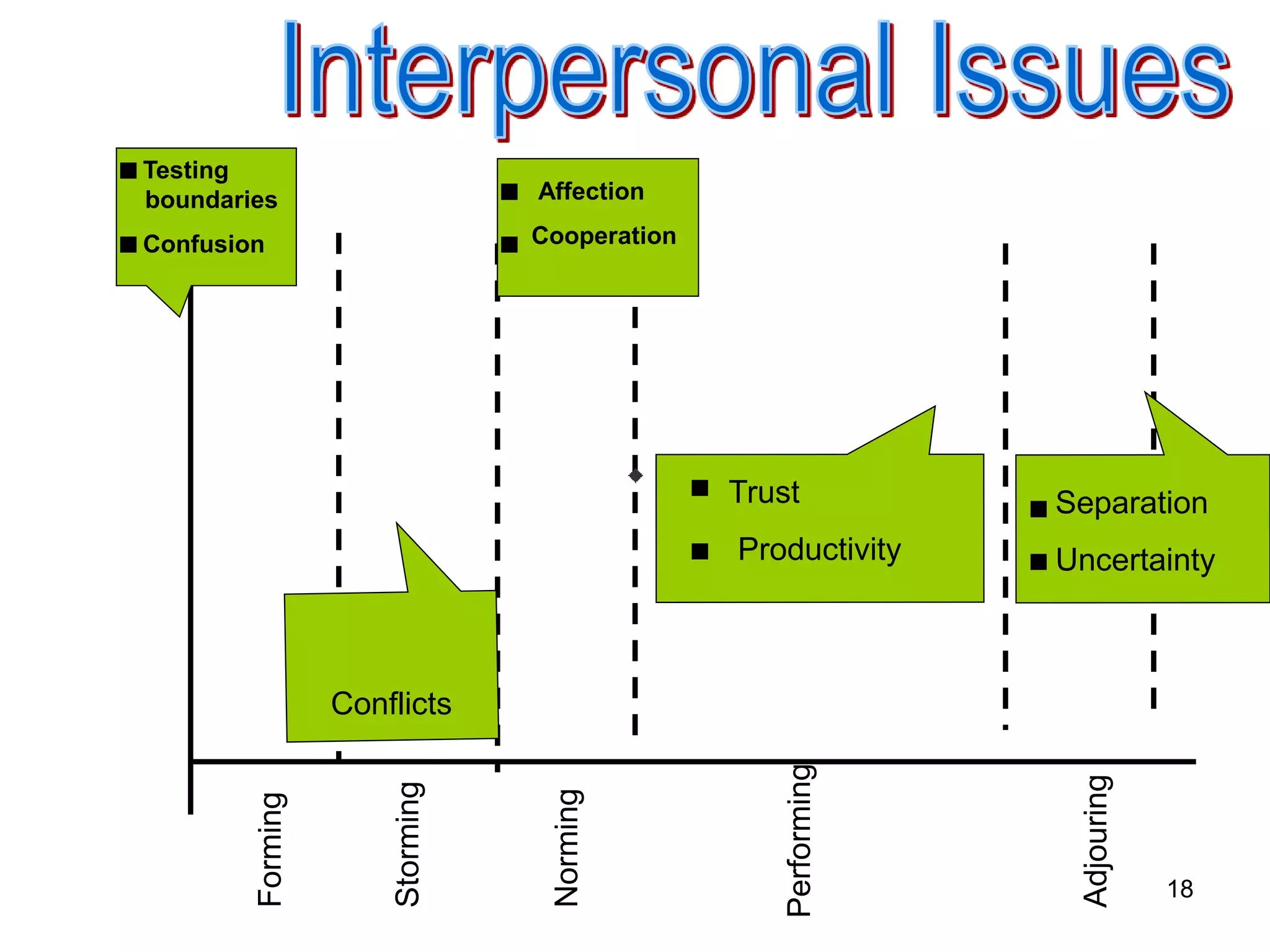
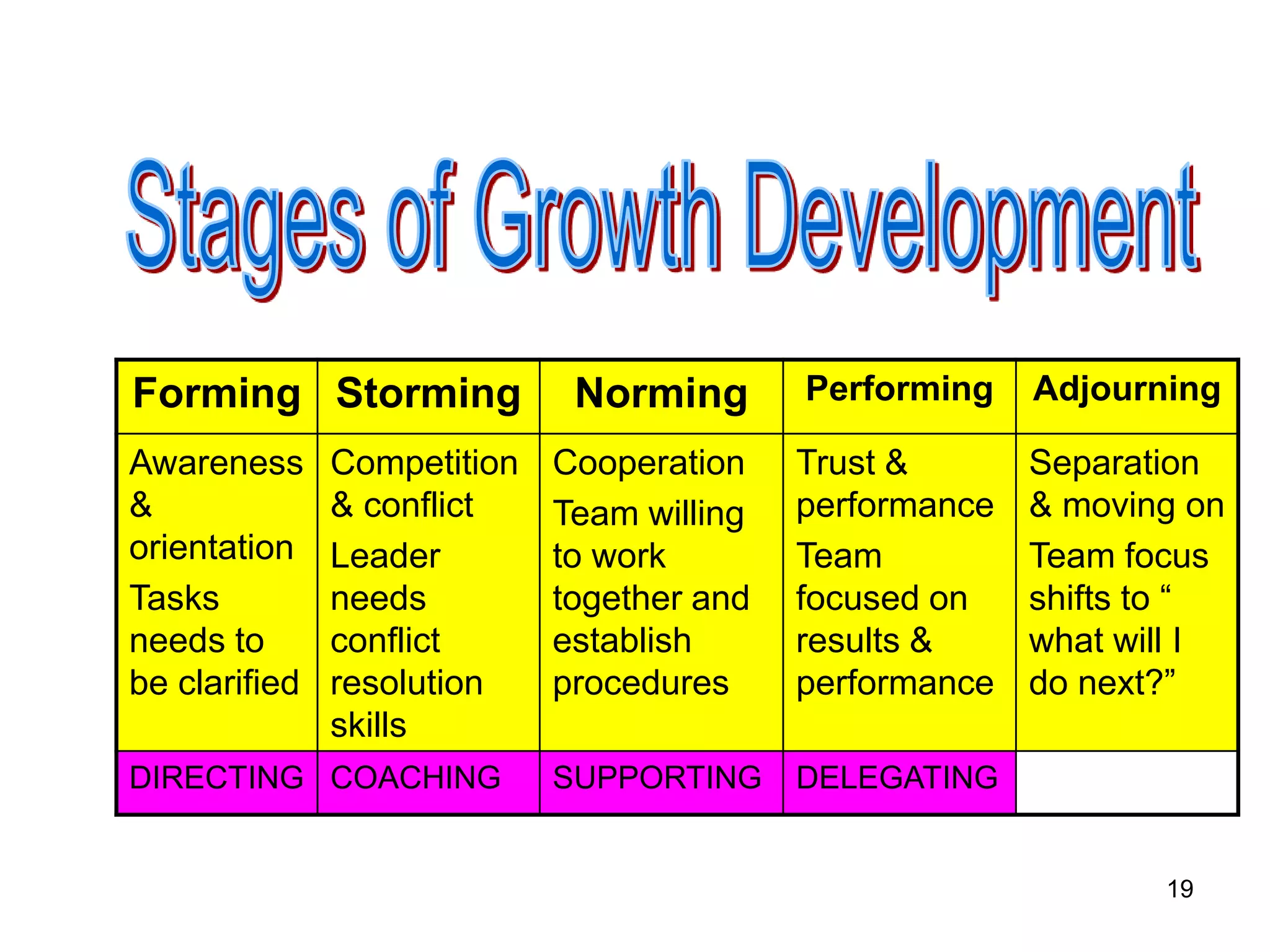
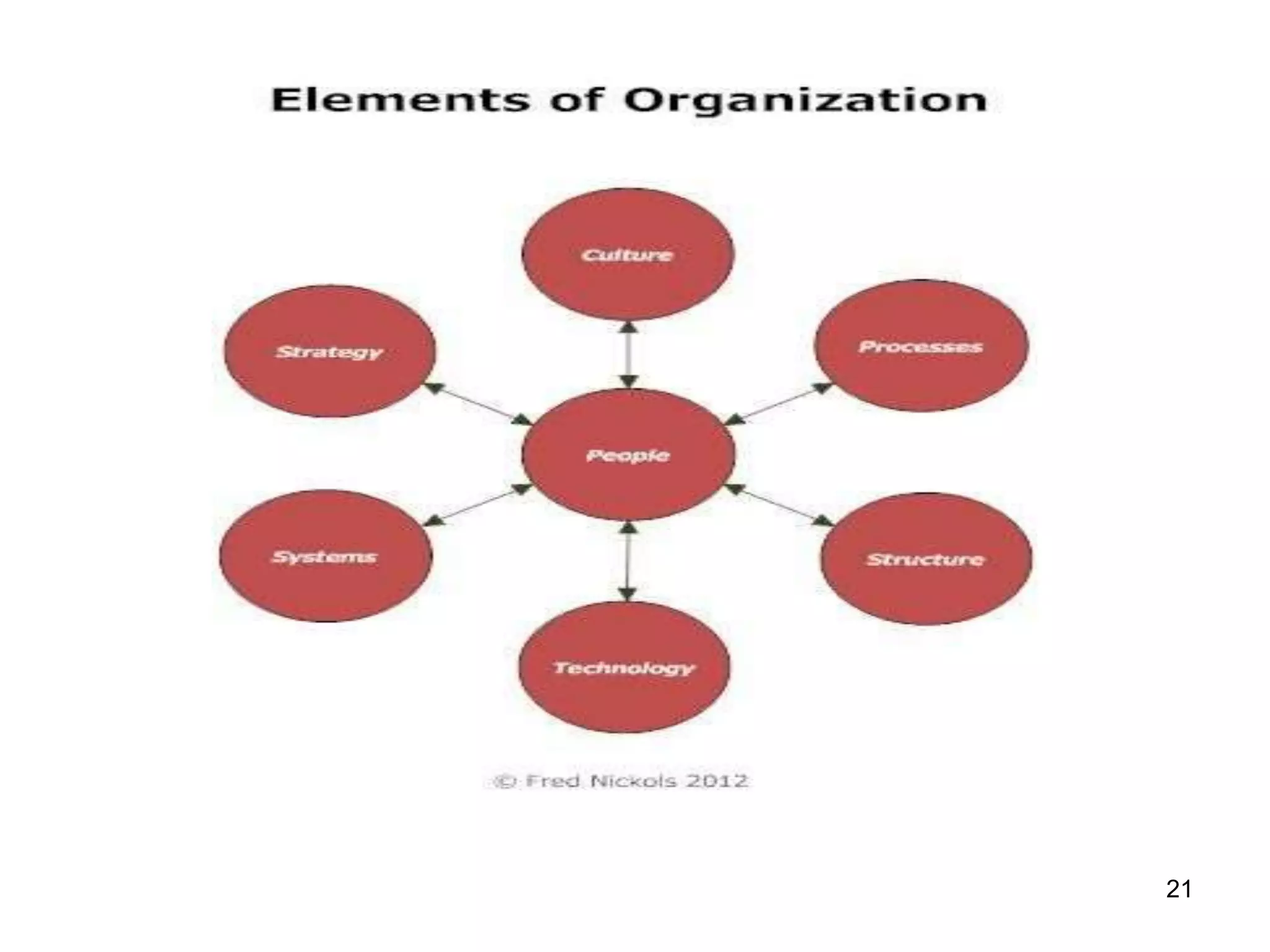
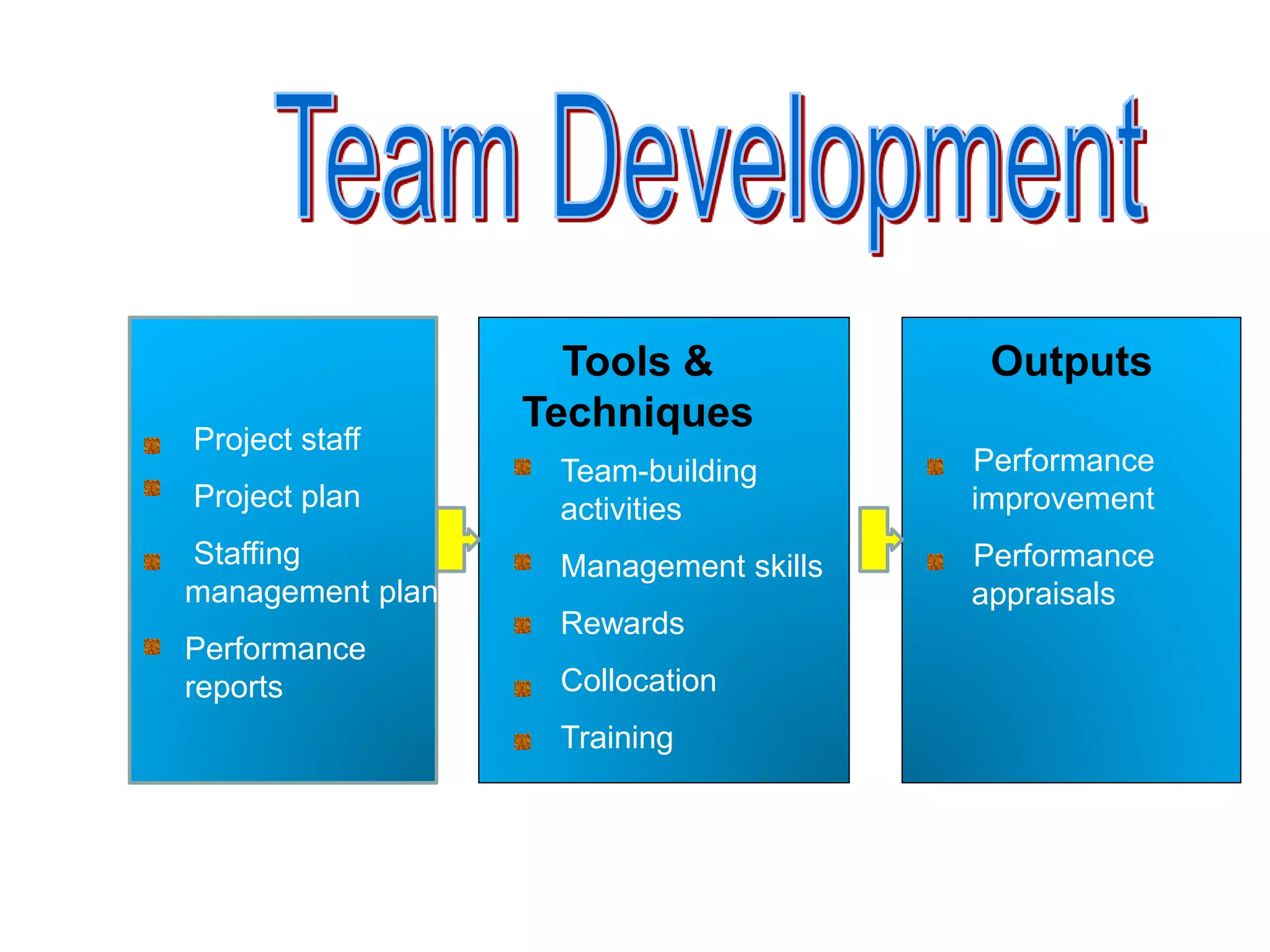
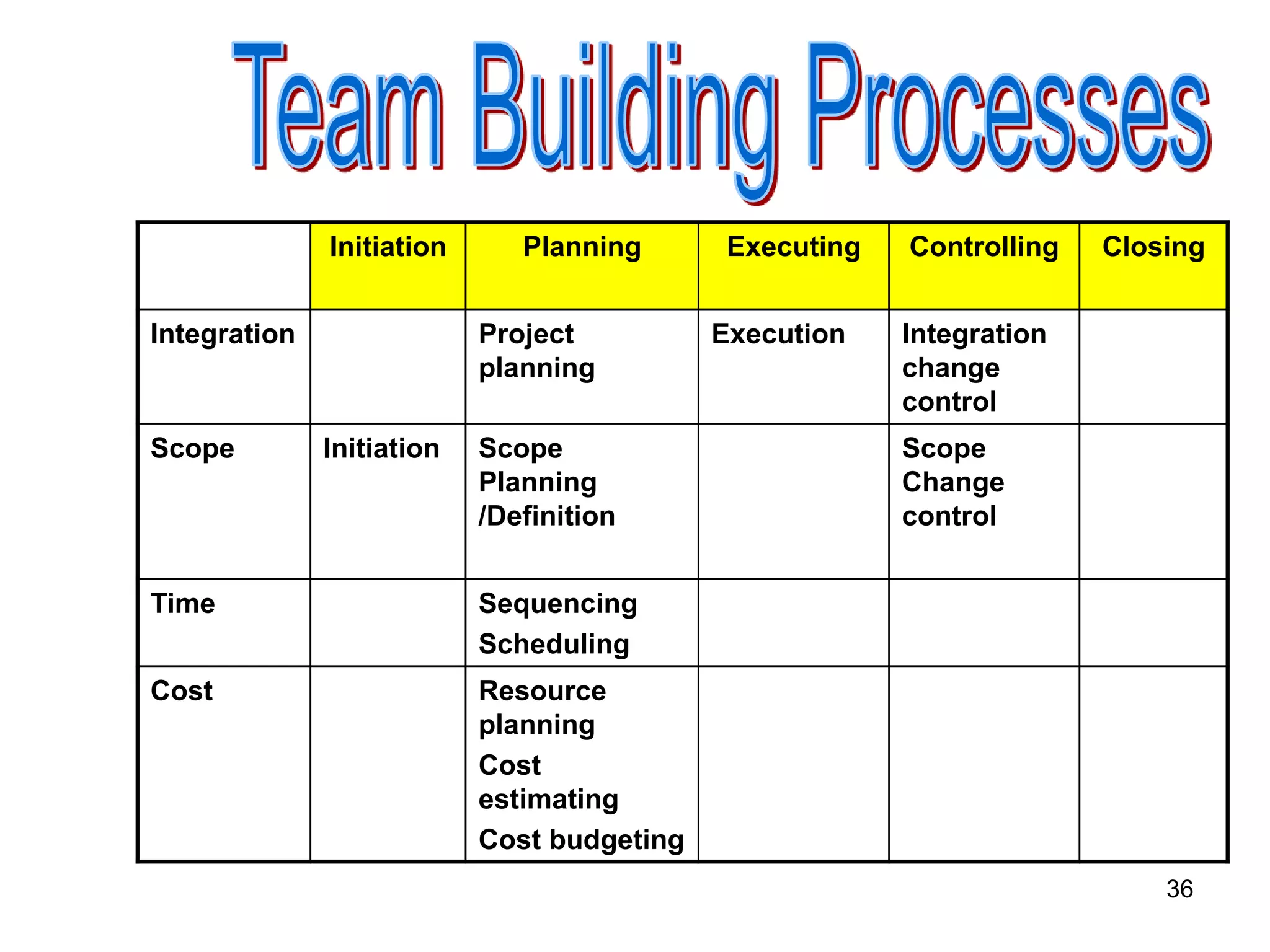
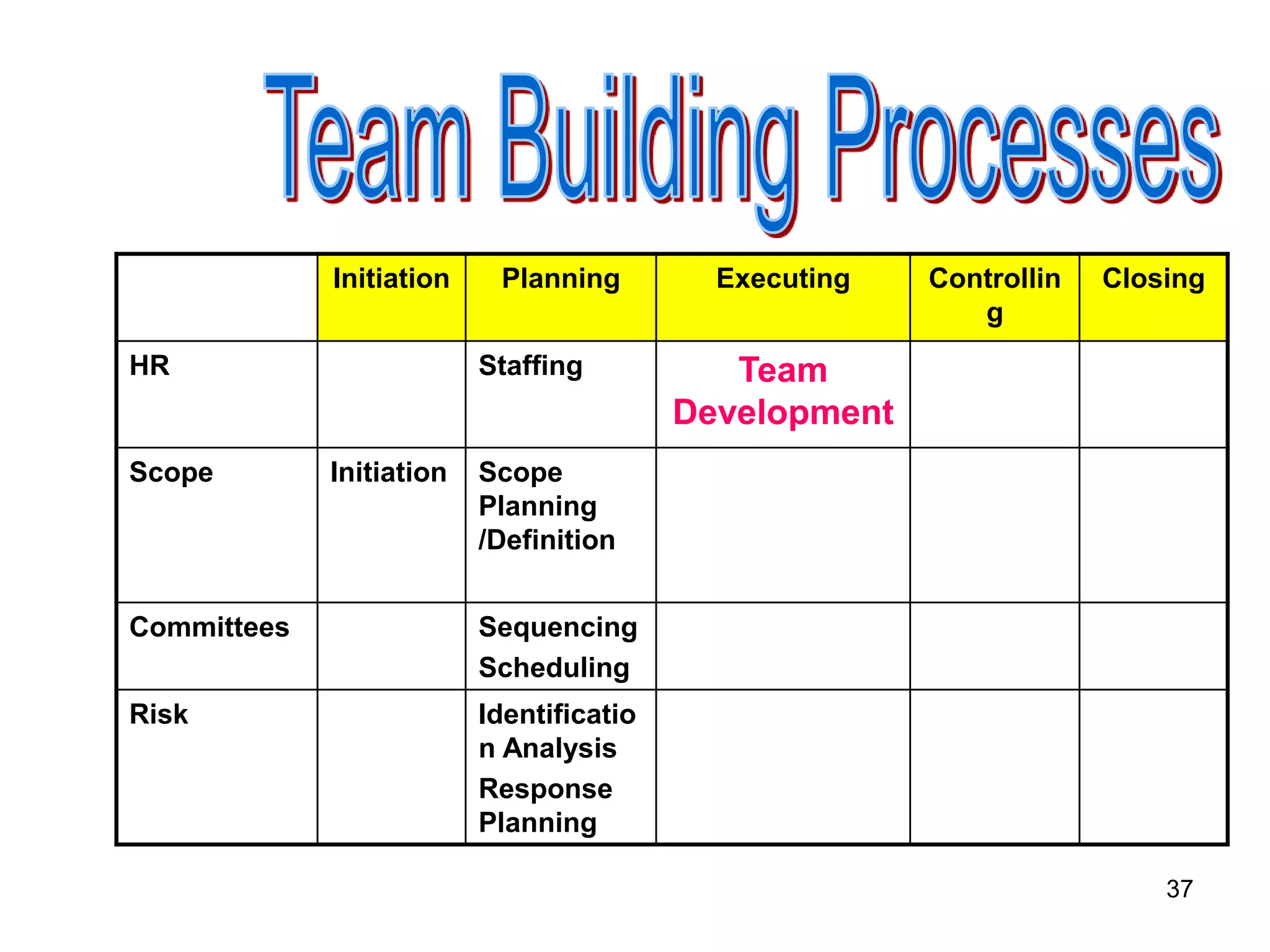
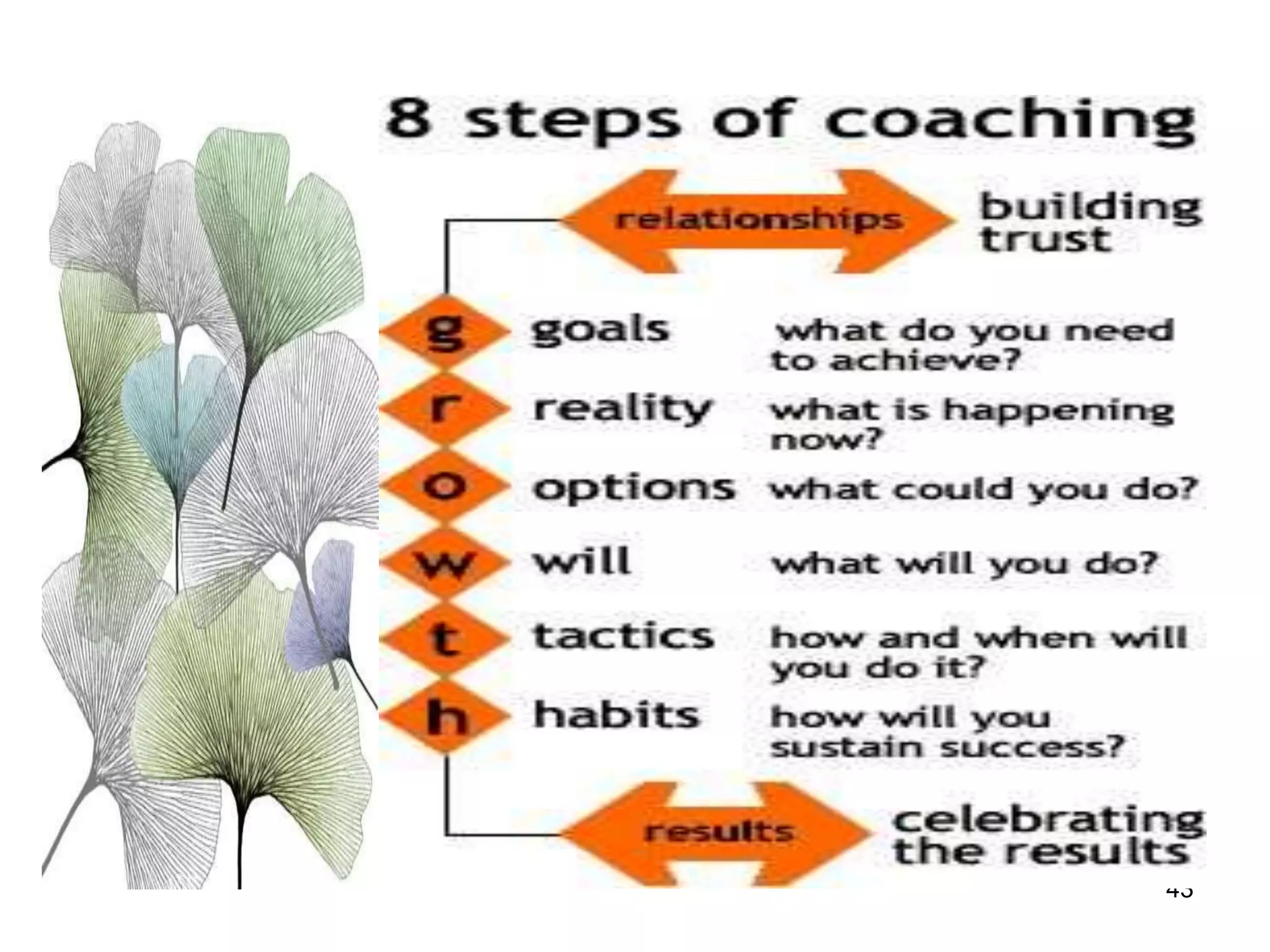
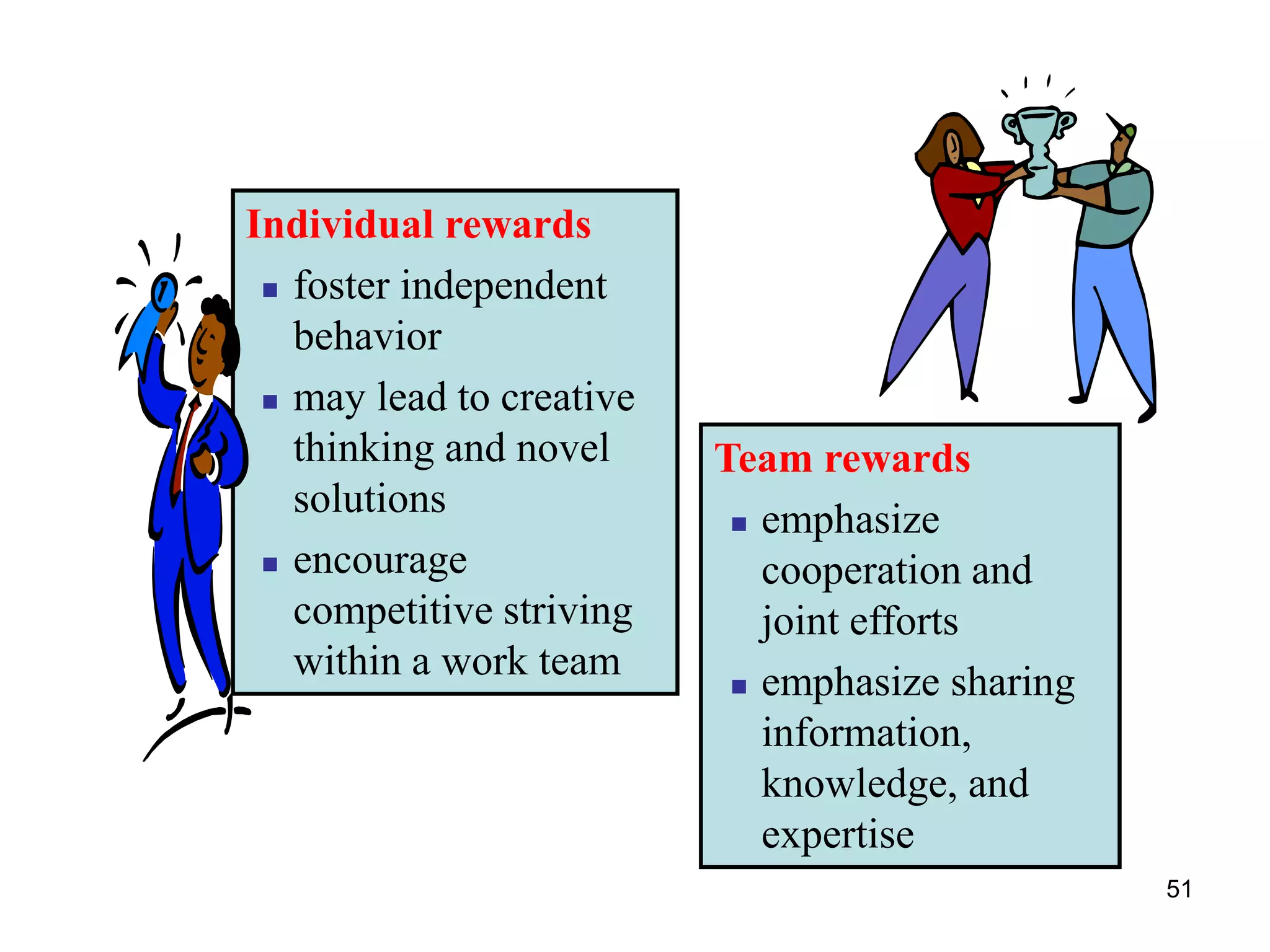
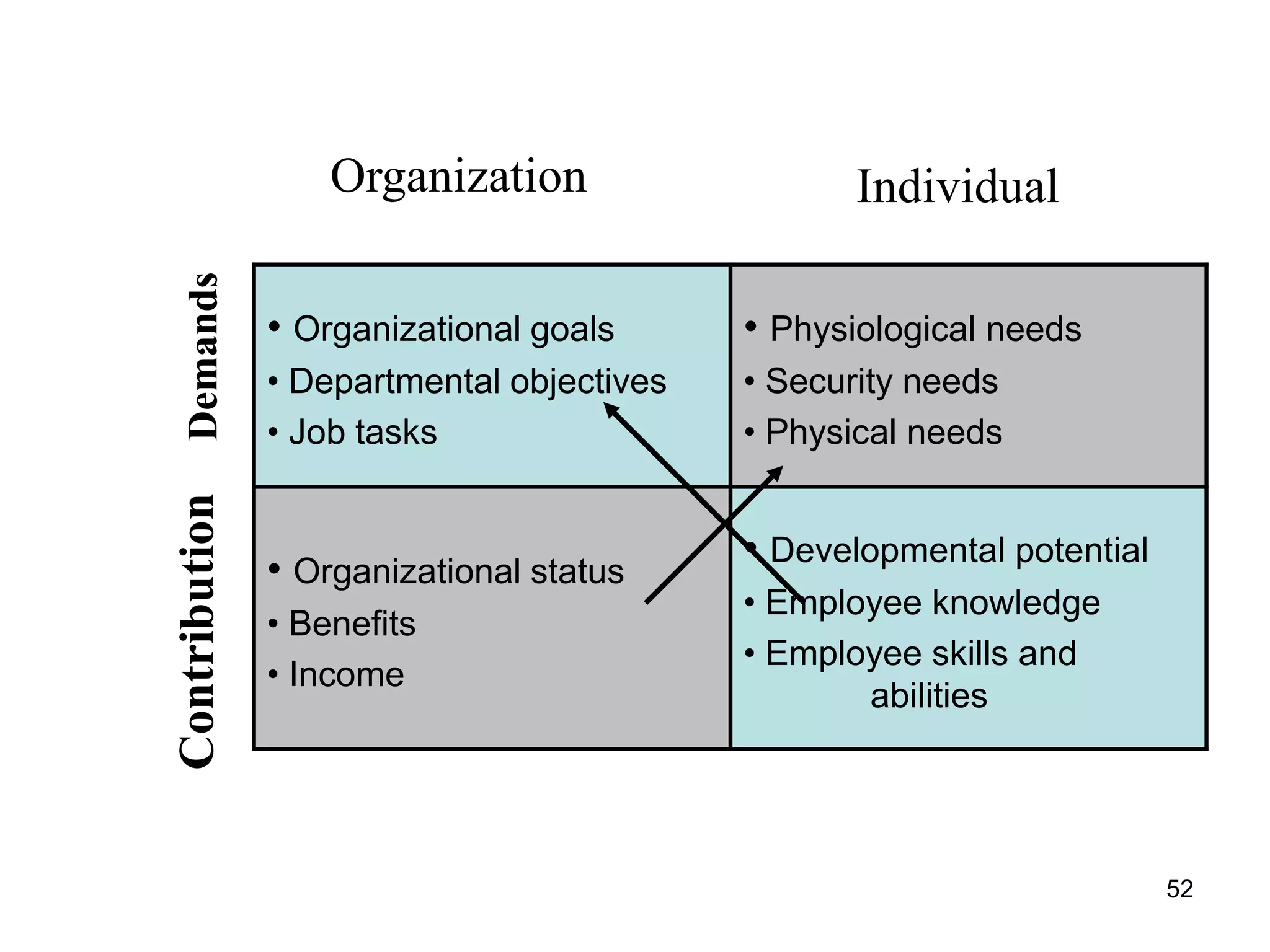
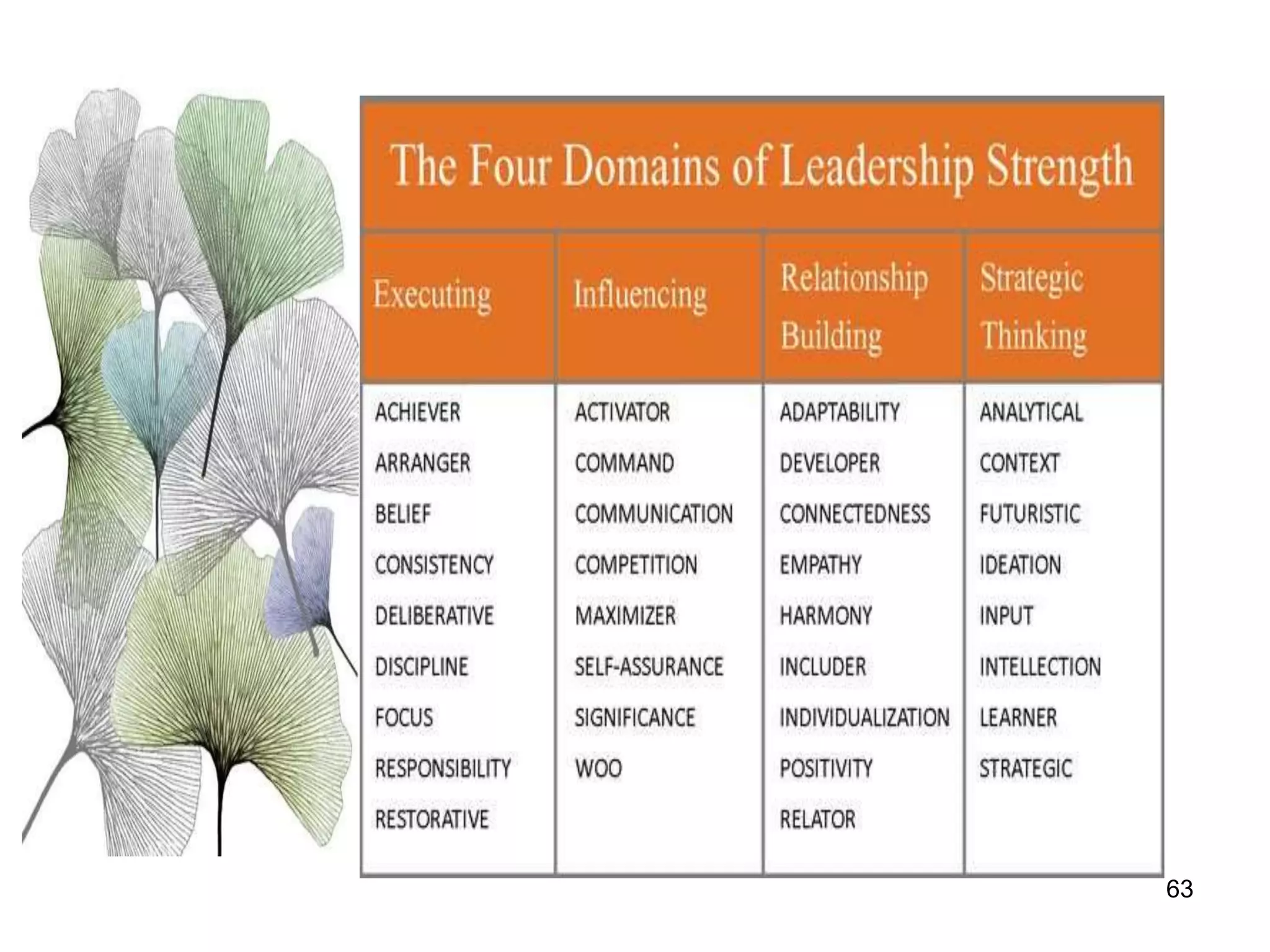
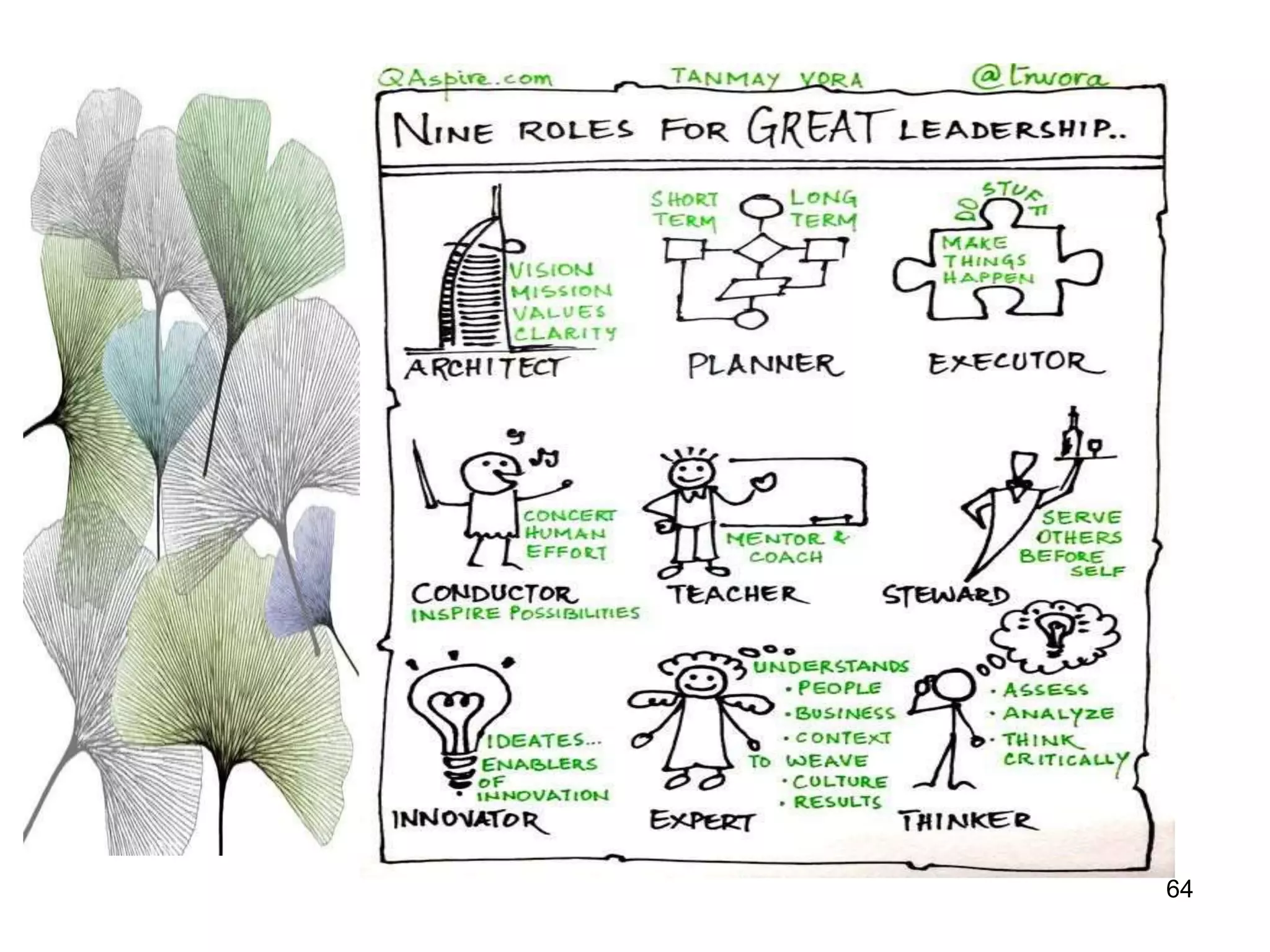
The document discusses teamwork and its benefits for organizations. It notes that teamwork increases productivity and quality, improves morale, and enhances problem-solving and creativity. It defines teams as small groups of people with complementary skills committed to a common purpose and goals. The document then outlines the typical stages a team goes through - forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. It provides strategies for leaders and issues to address at each stage to help the team progress effectively.