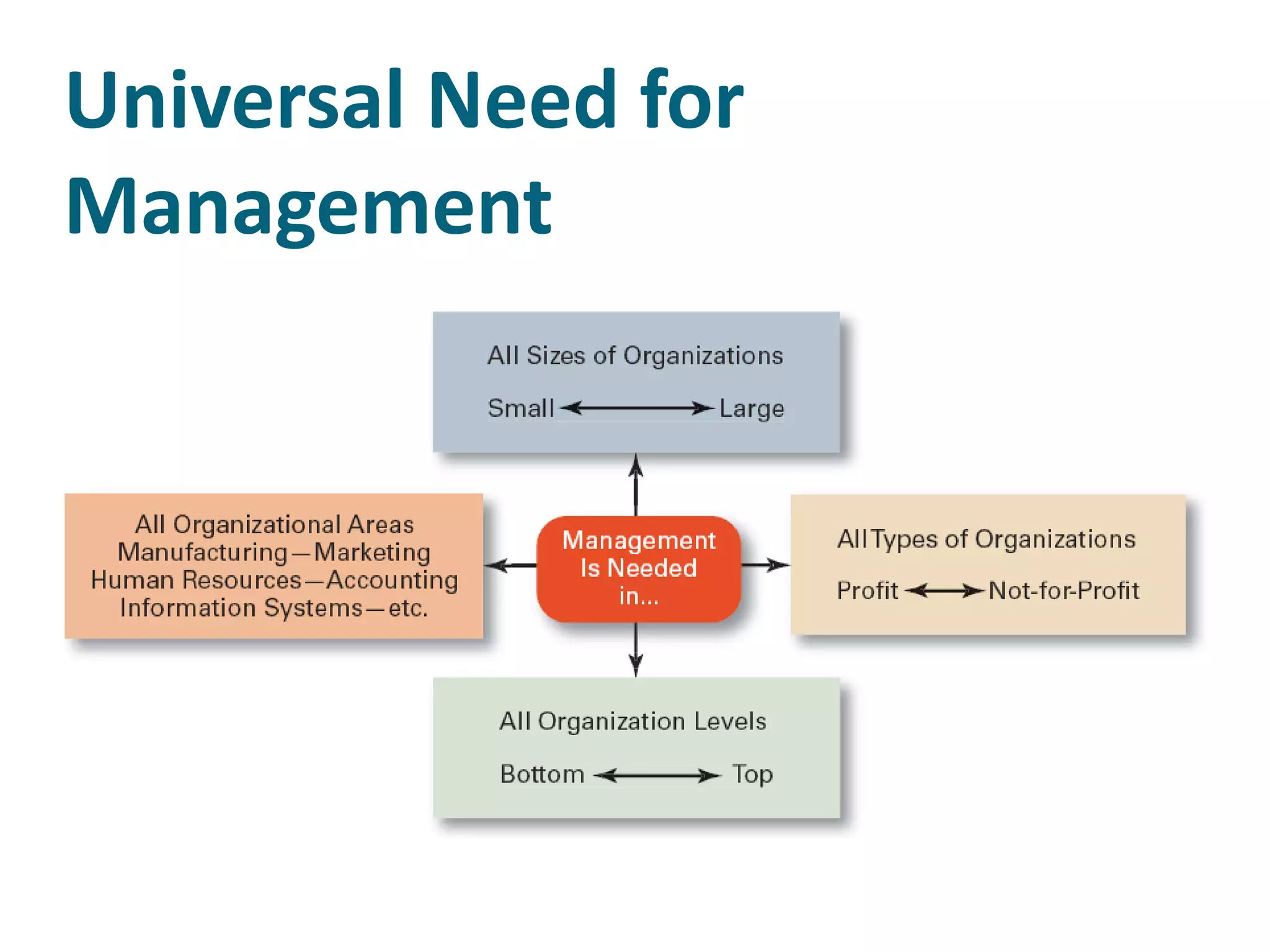
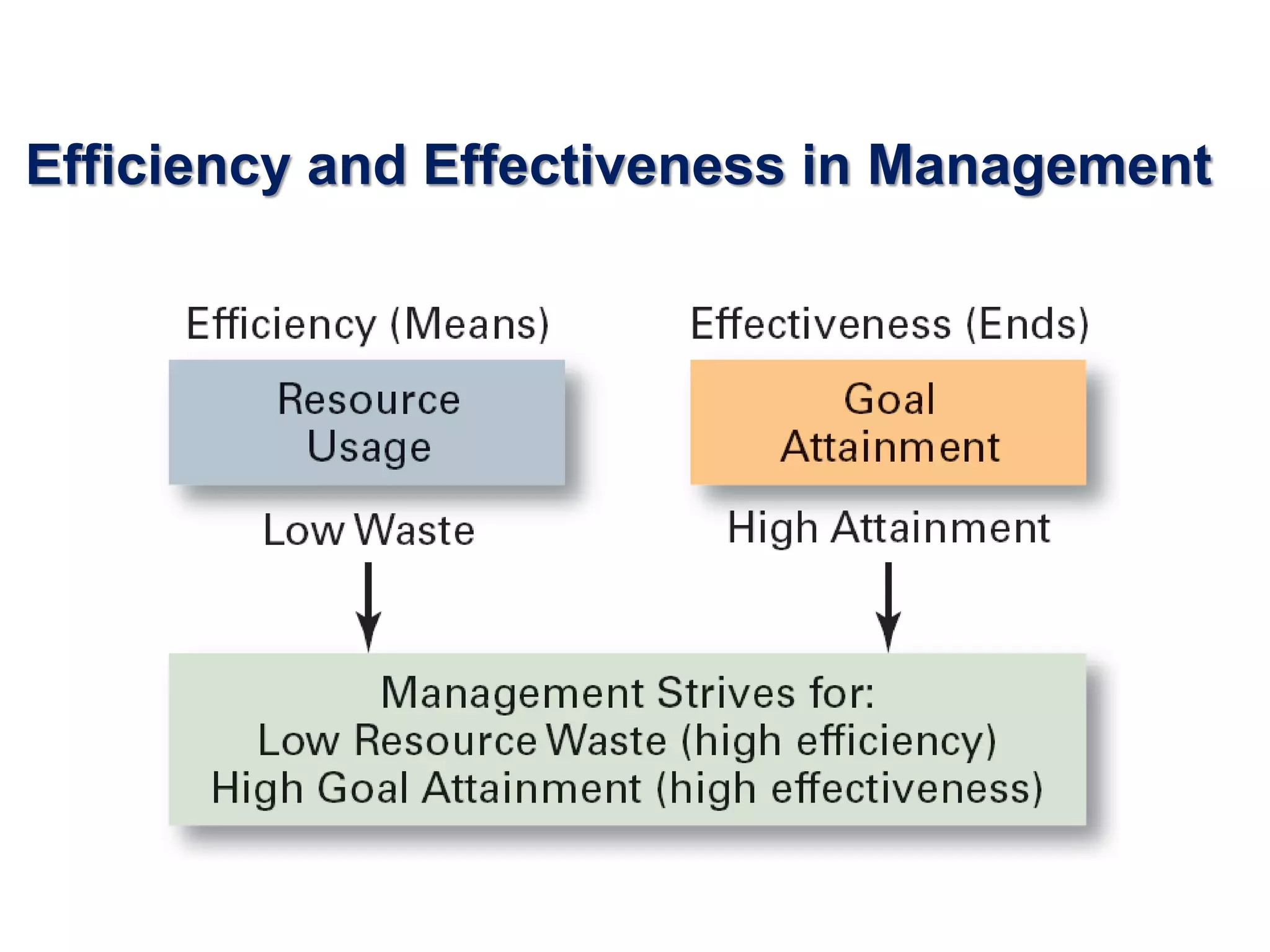
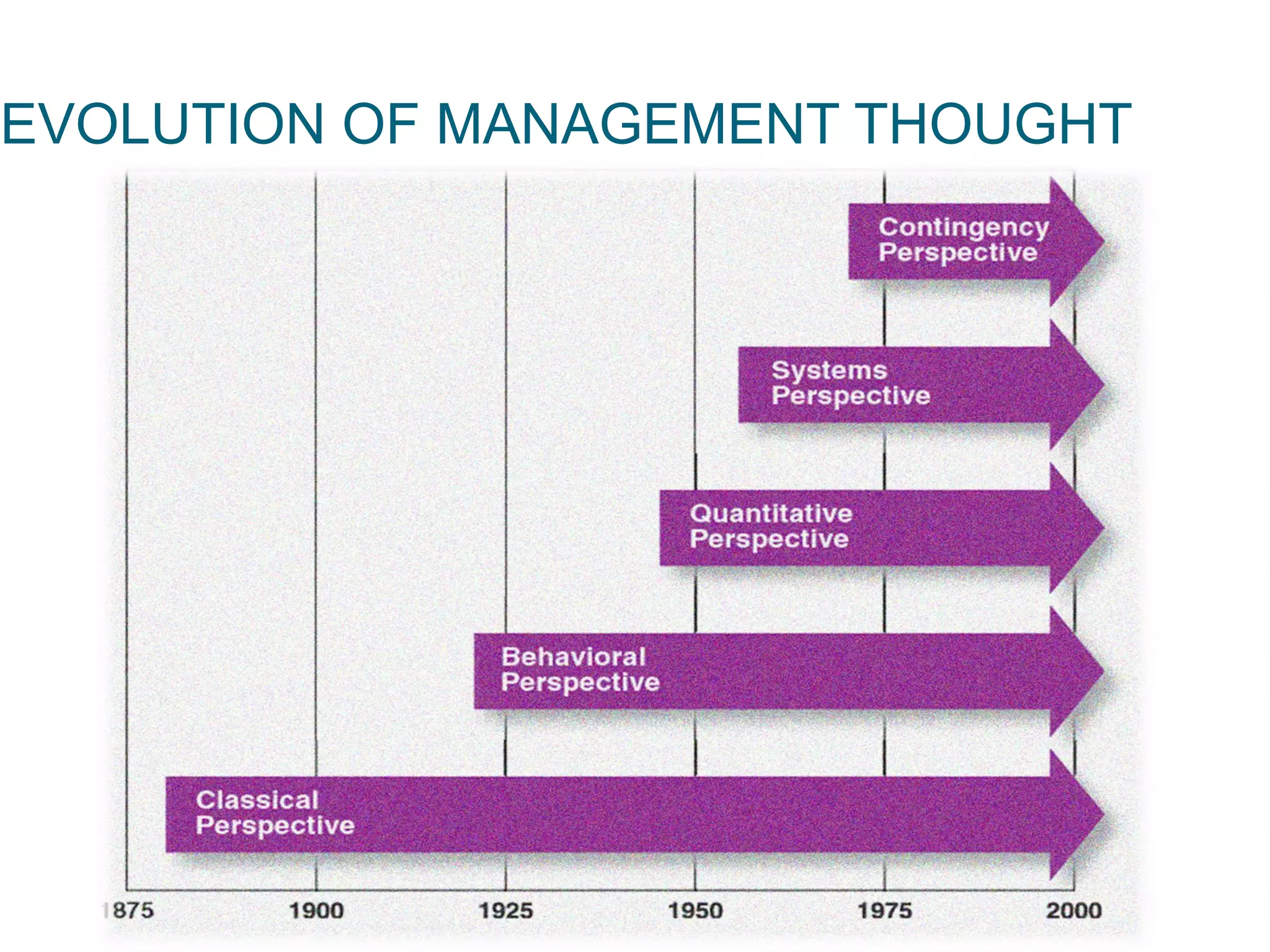
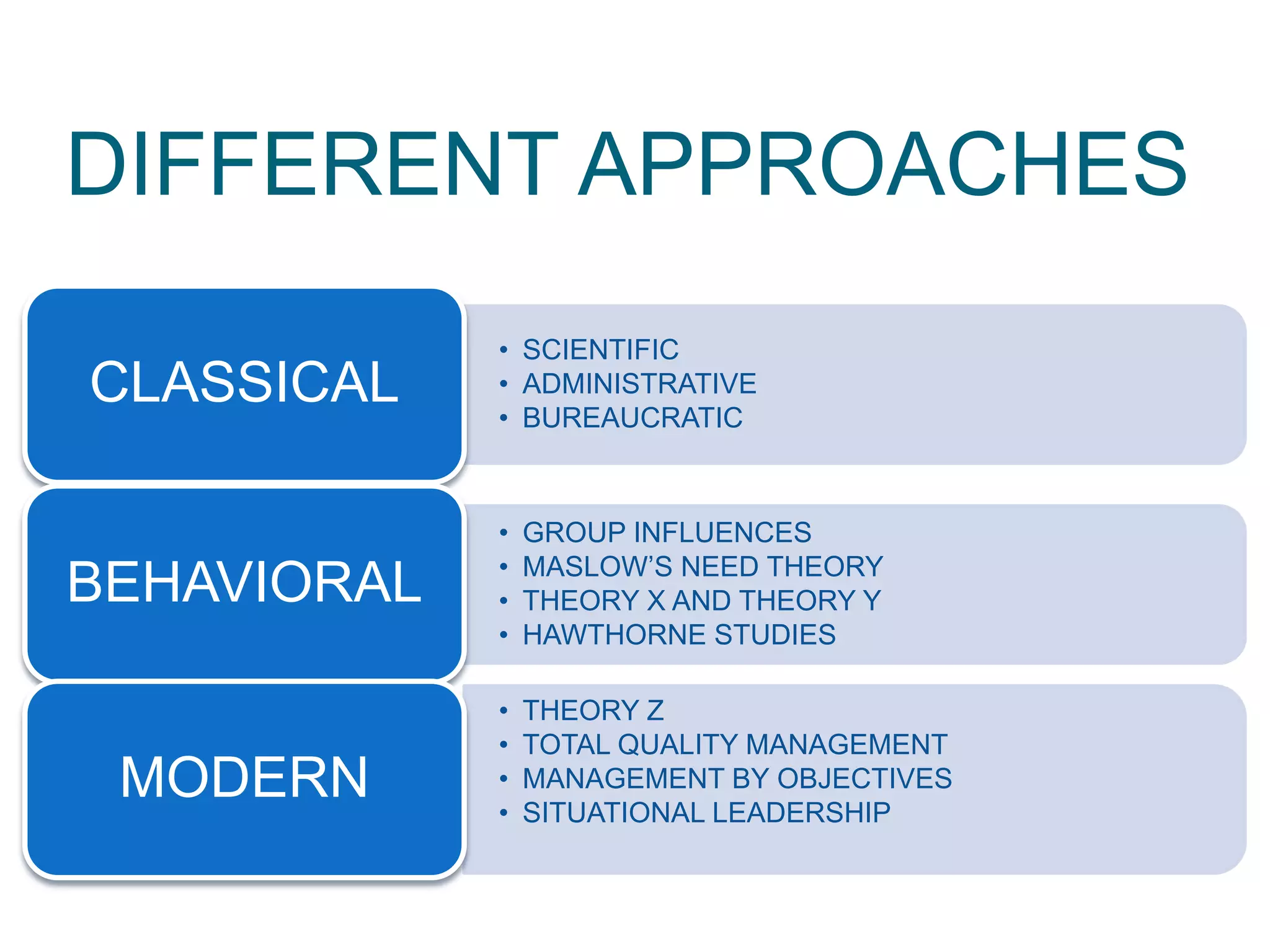
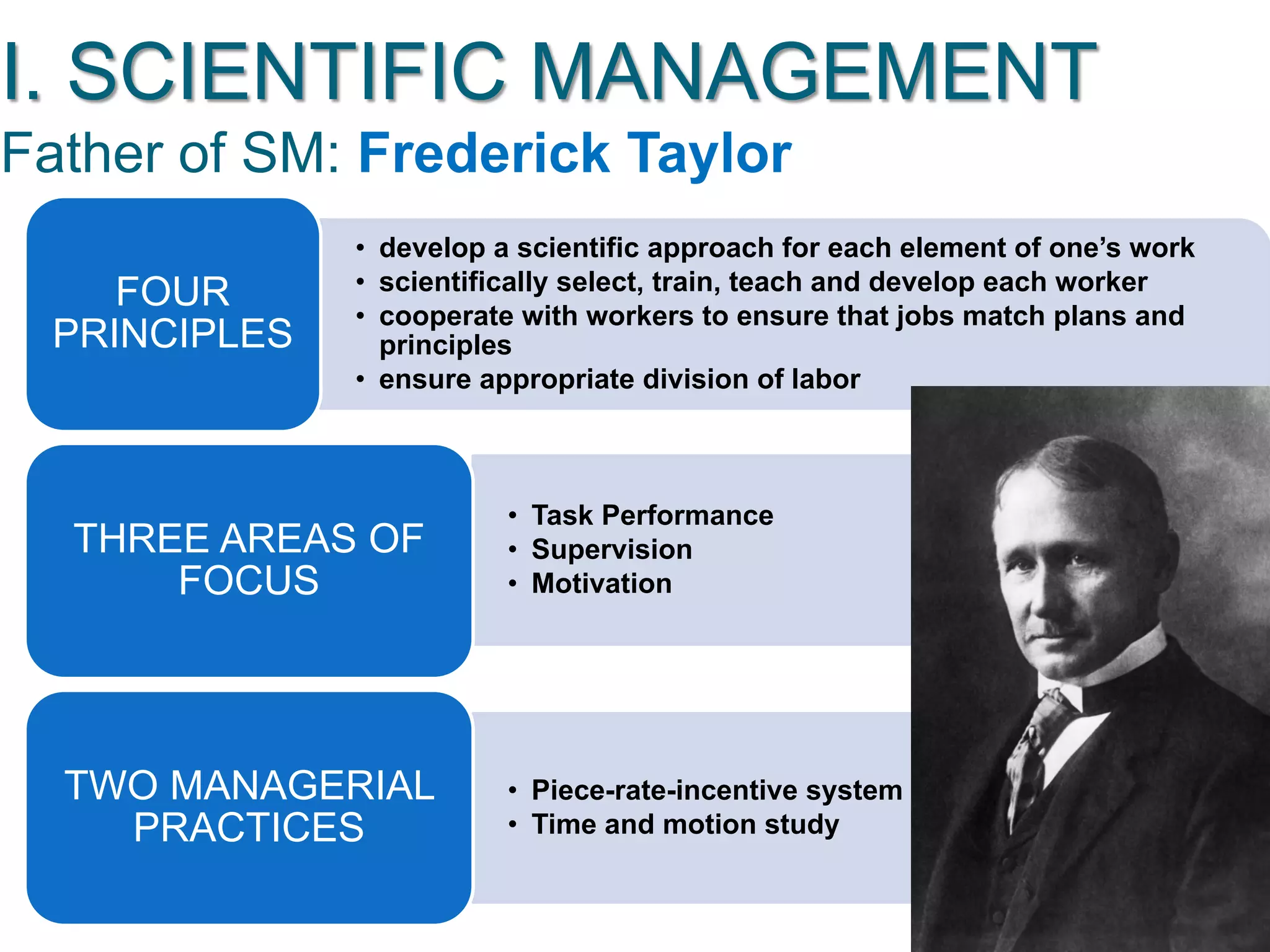
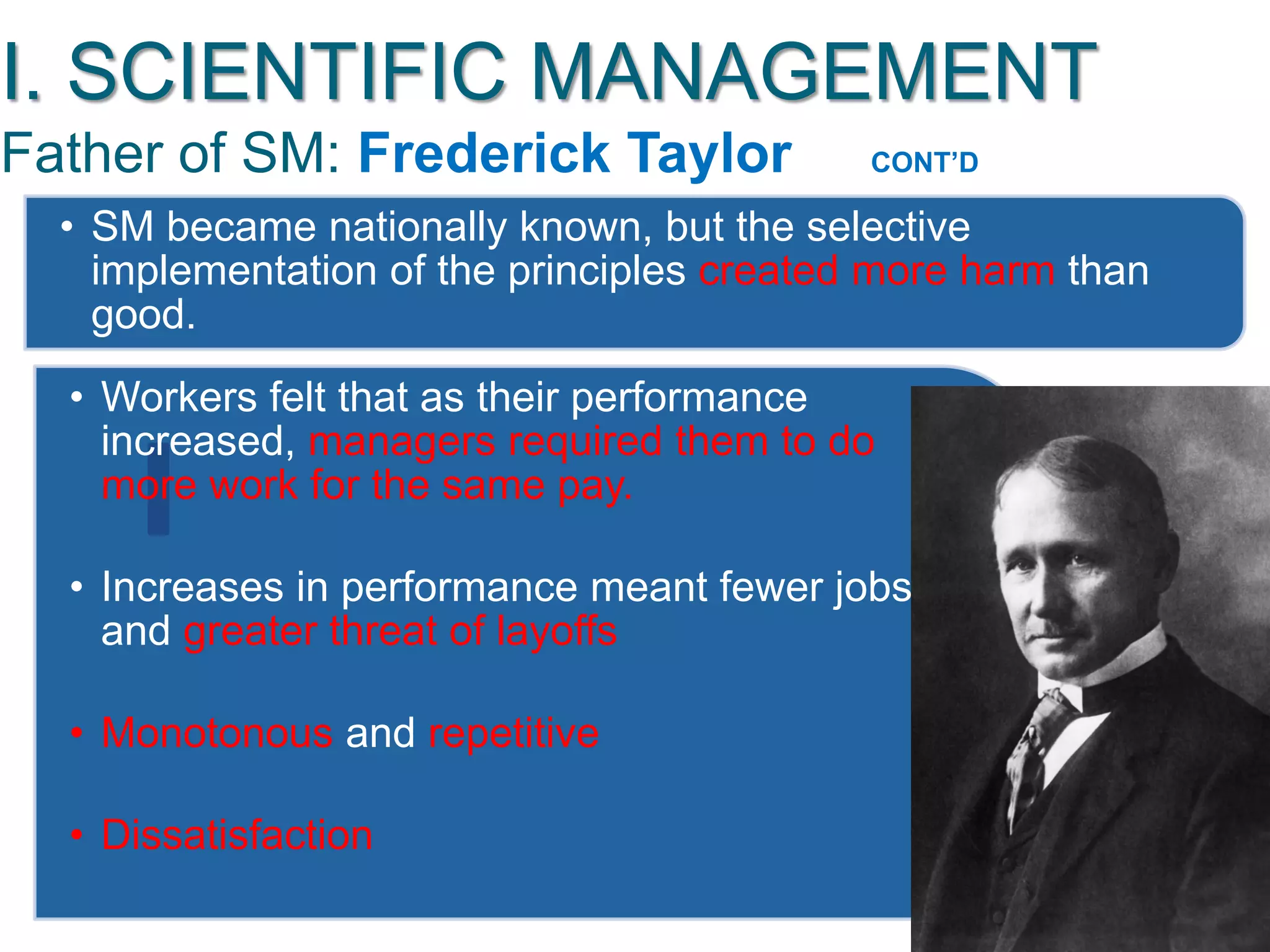
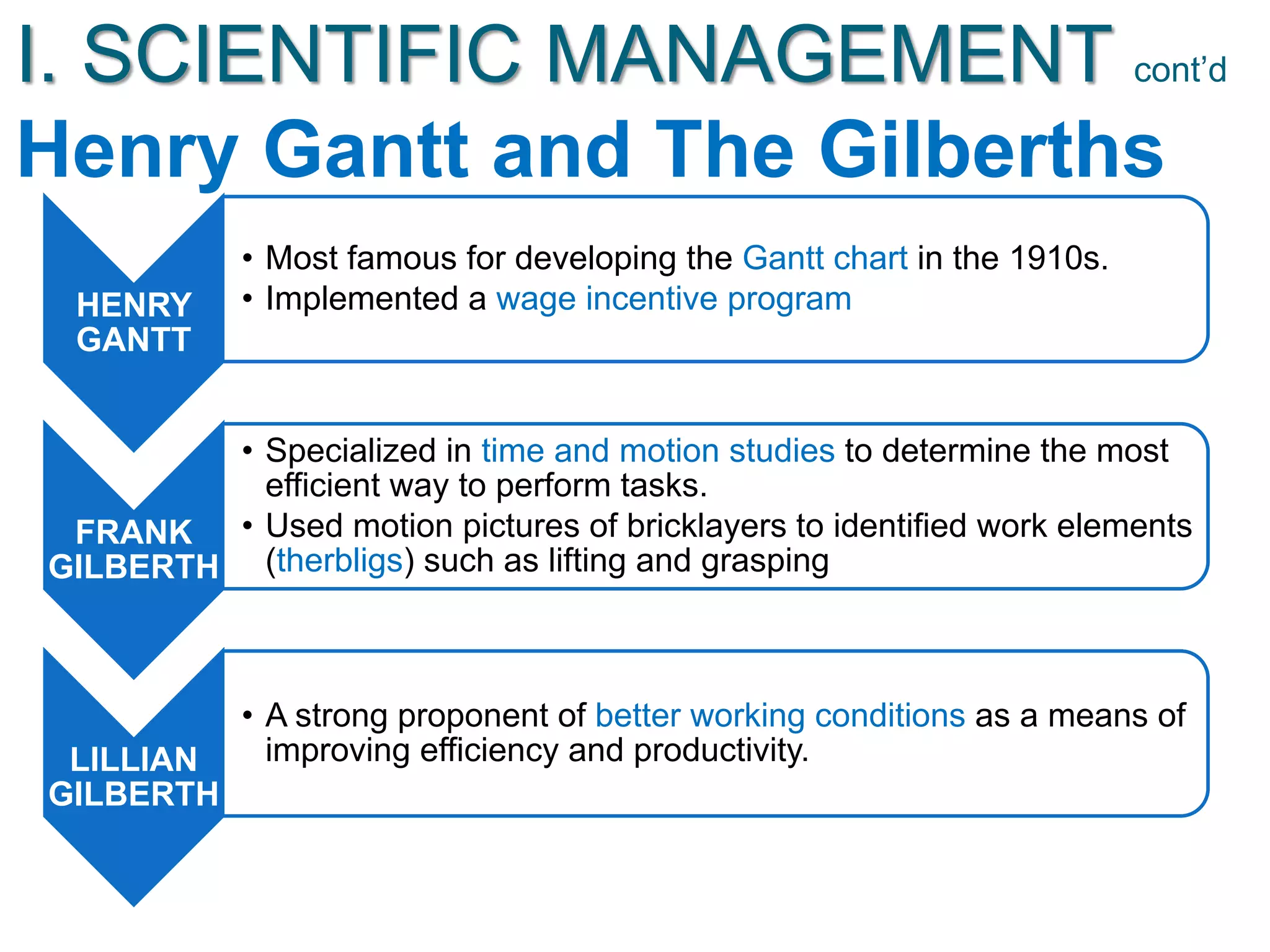
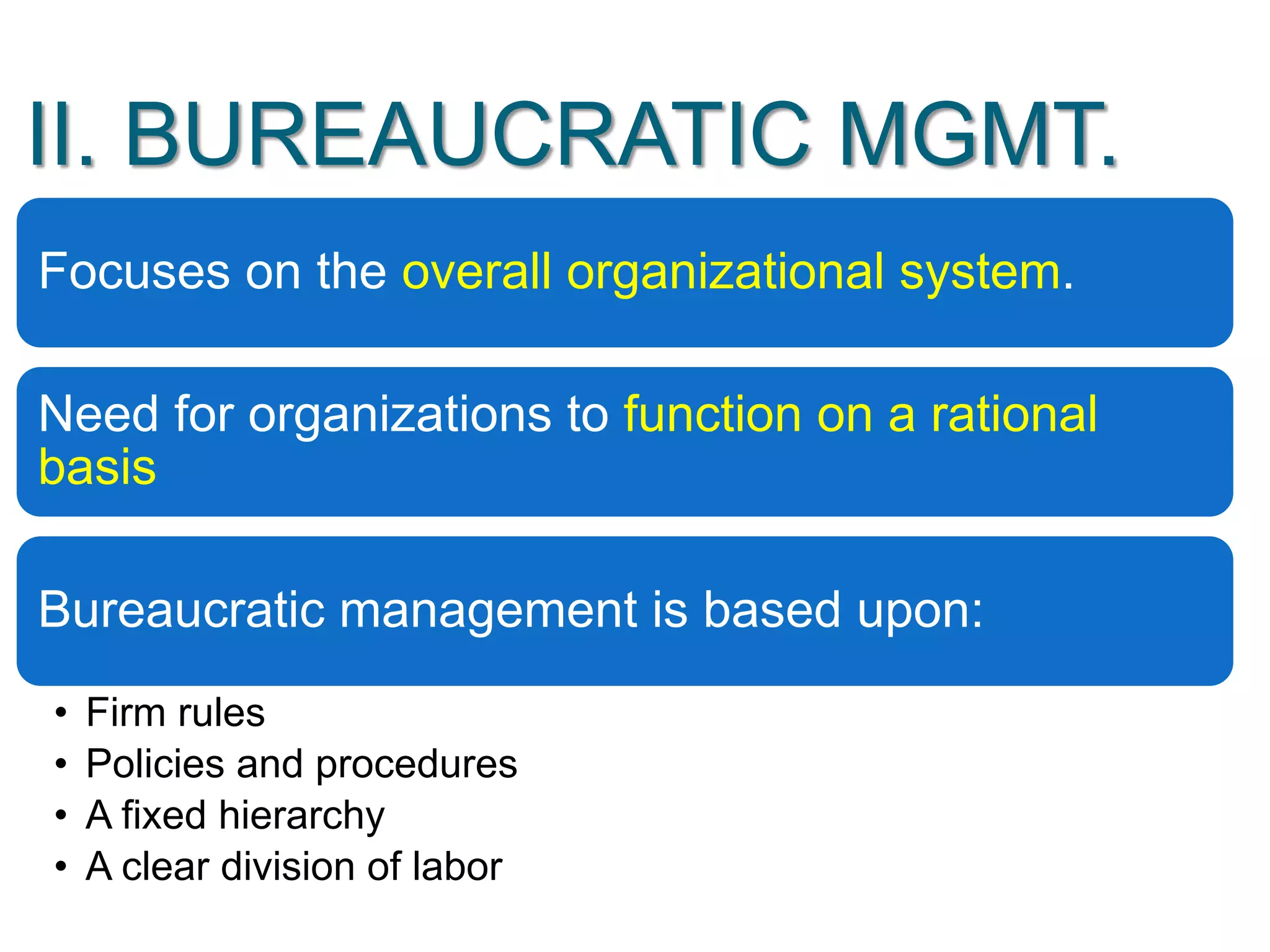
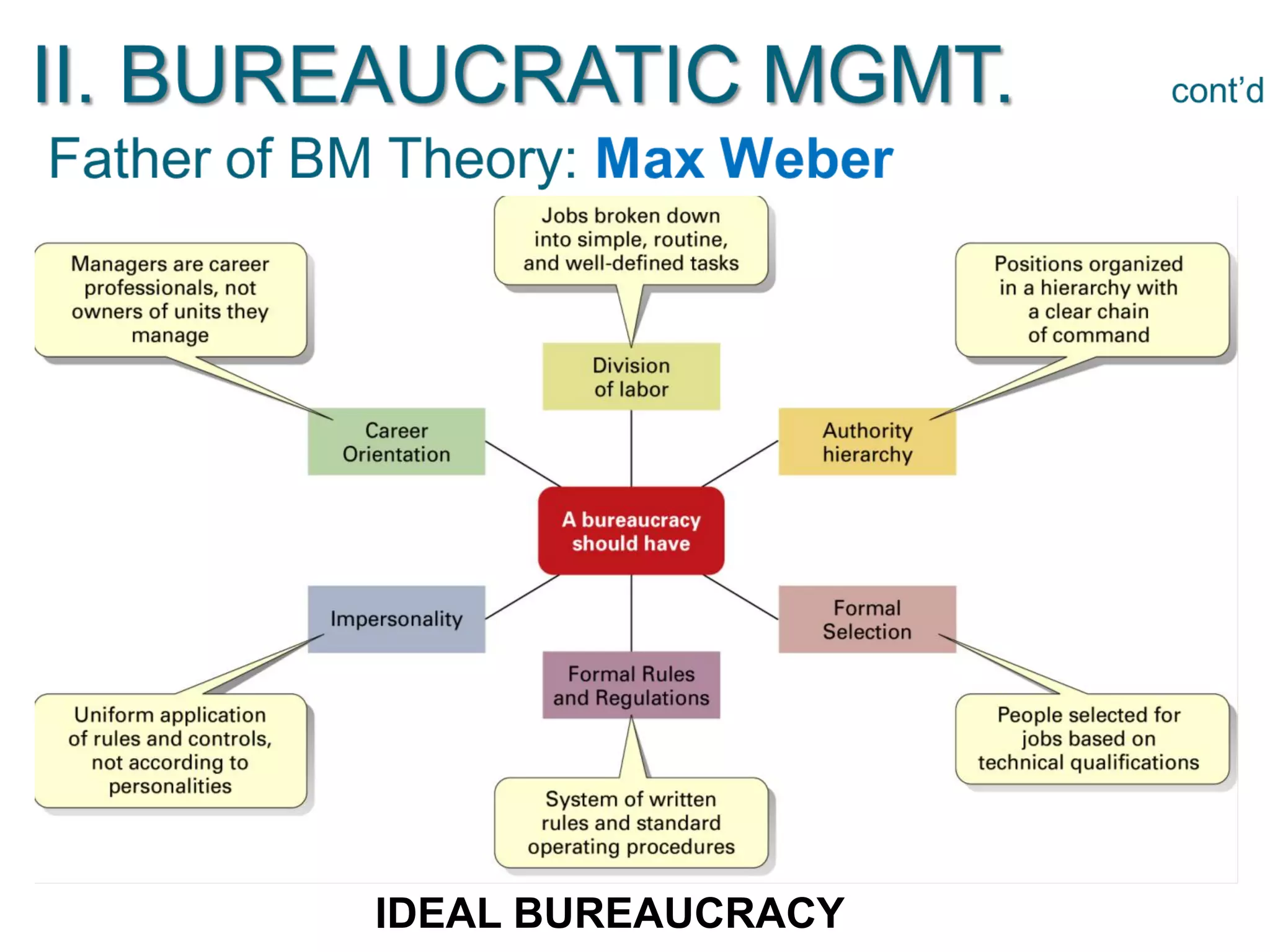
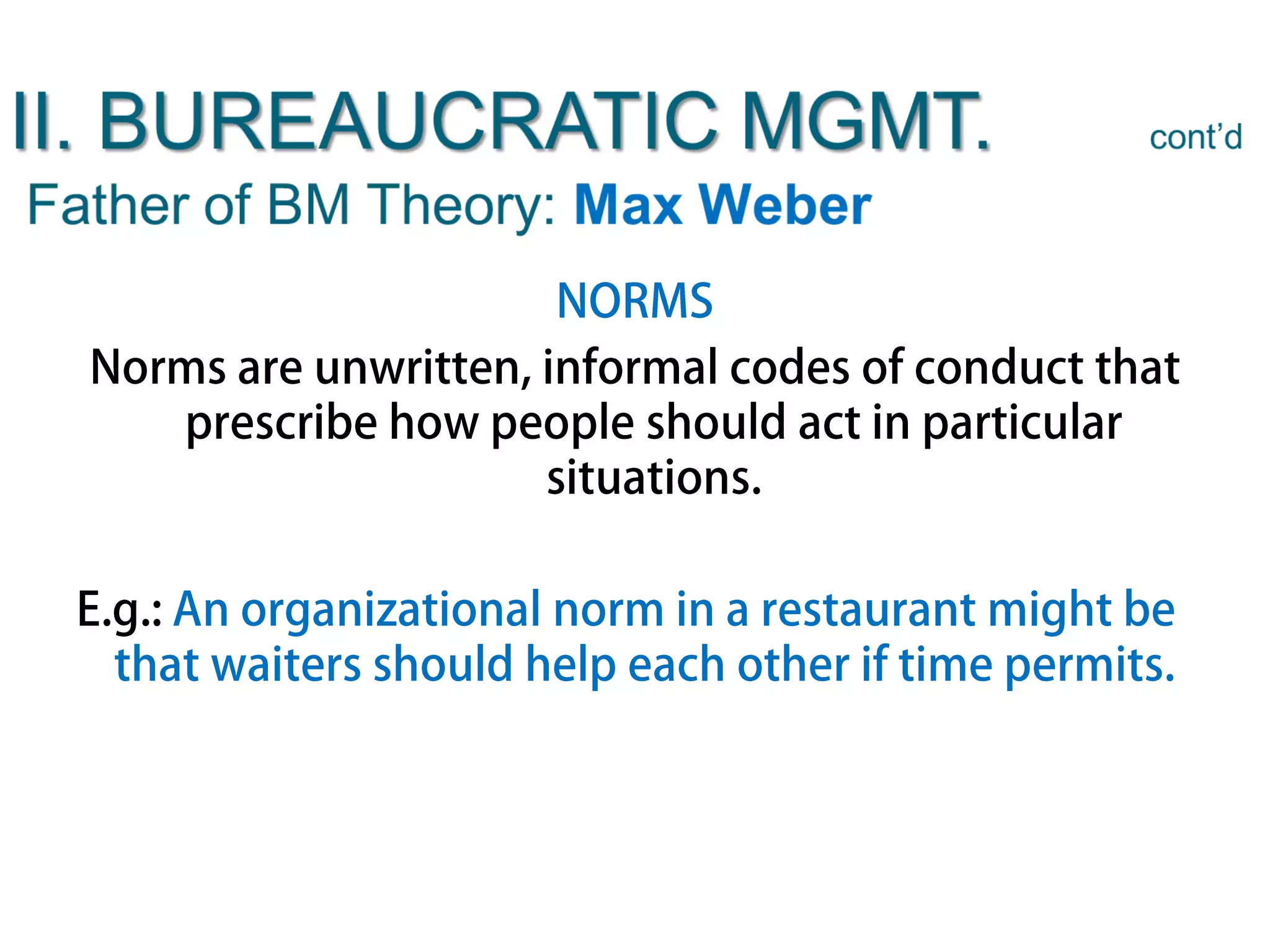
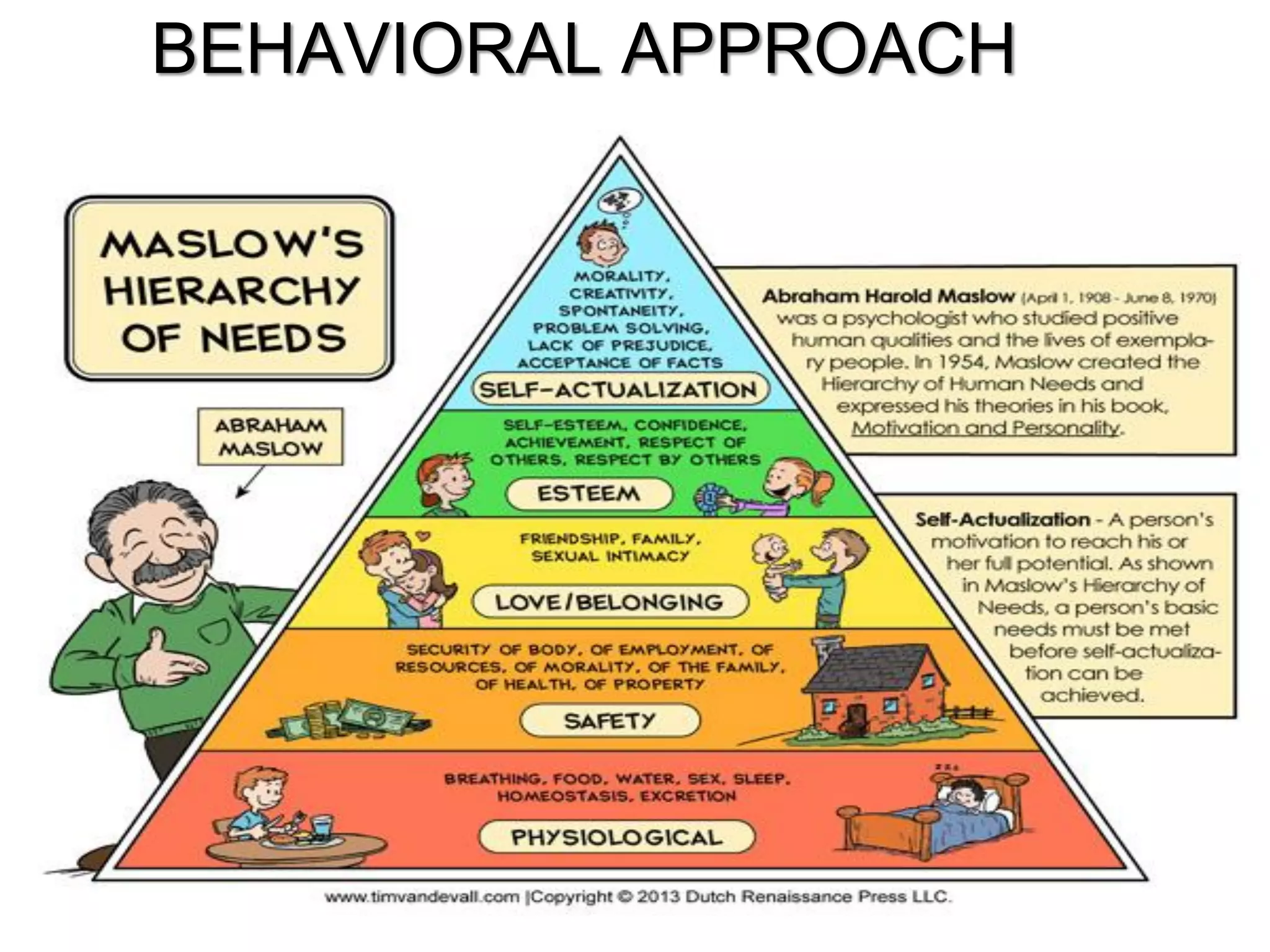
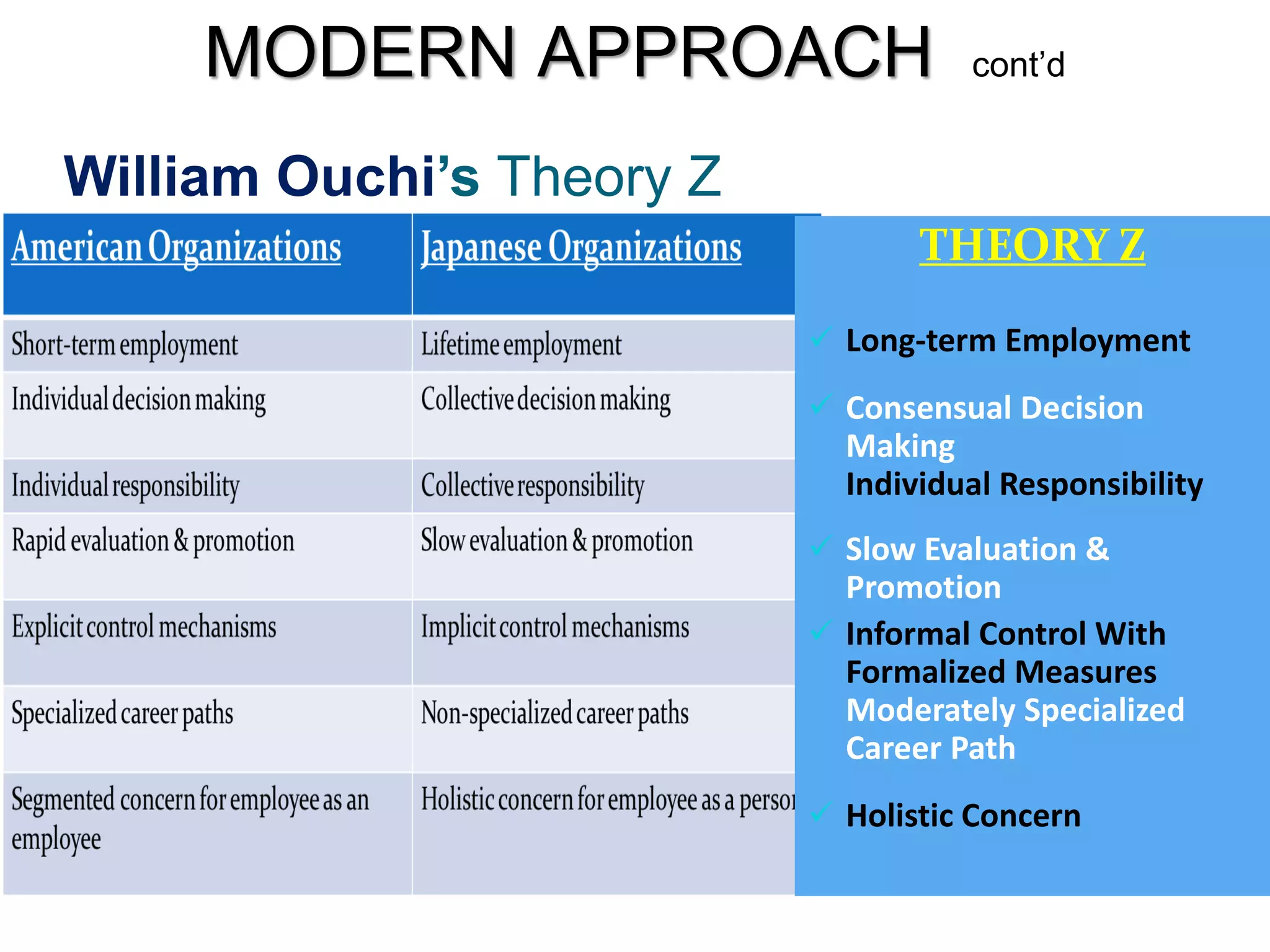
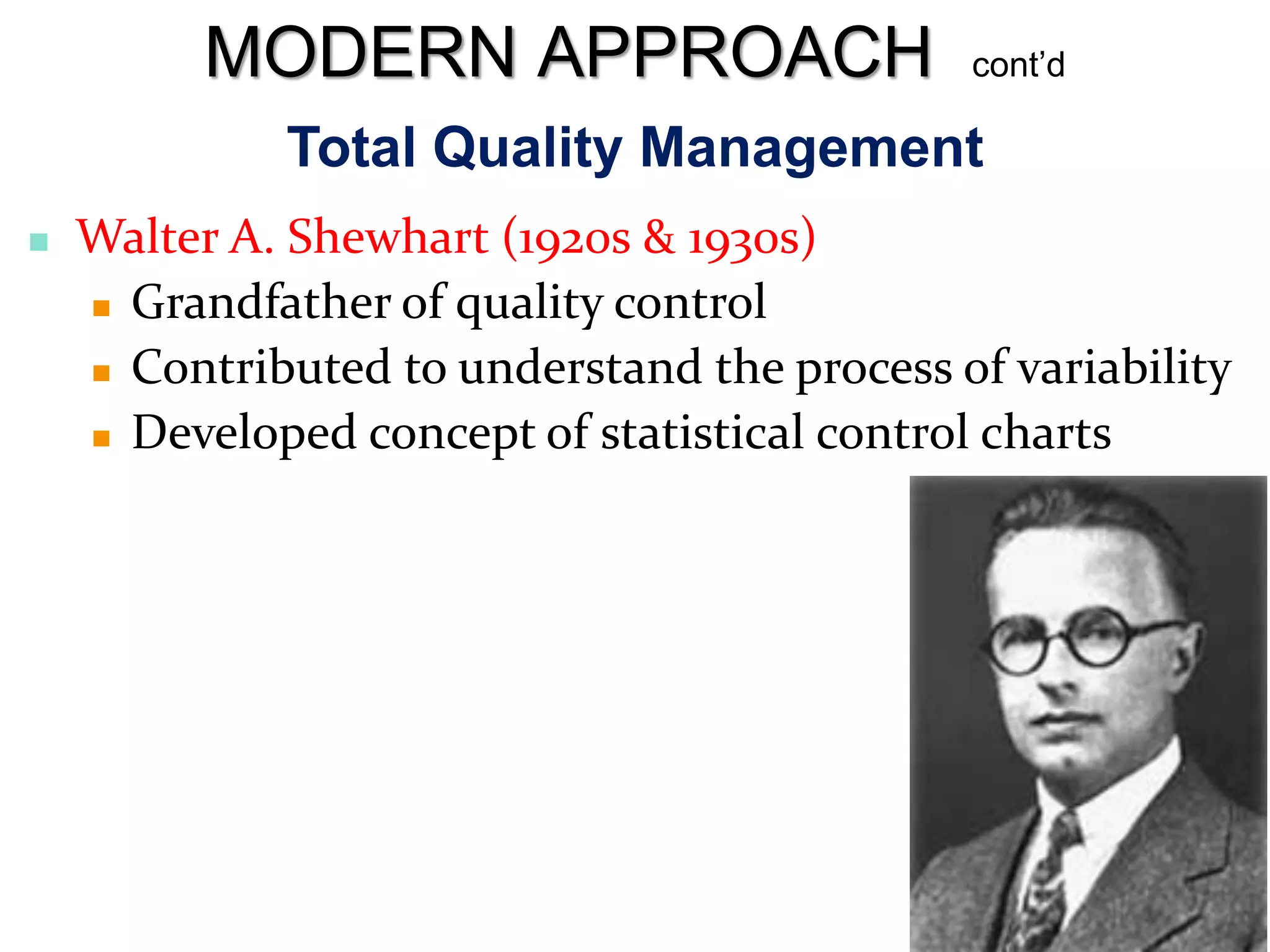
The document discusses the evolution of management thought, highlighting various approaches, including scientific management, bureaucratic management, and administrative management. It emphasizes the importance of efficiency and effectiveness in management, as well as the impact of social and economic factors. The text also explores modern management practices such as total quality management and management by objectives, showcasing influential figures and theories in the field.