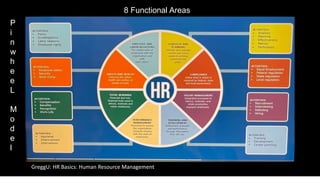
The document discusses the future direction of human resource management (HRM) in strategic, operational, and administrative terms. It outlines the role of HRM in aligning with business strategy, addressing daily operational issues, and ensuring compliance. It also discusses eight functional areas of HRM: strategy and planning, compliance, talent management, performance management, safety and health, employee and labor relations, total rewards, and developing talent pools to address skills gaps in key functions. The overall goal is to have an effective HRM system that supports the organization's vision and mission.