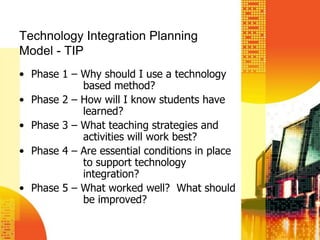
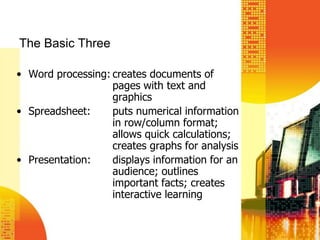
The document outlines the foundations of effective technology integration in education, emphasizing the importance of incorporating 21st-century skills and various media into learning processes. It discusses instructional technology, the use of technology to enhance motivation and productivity, and provides a planning model for technology integration in classrooms. Additionally, it highlights different types of educational software and practical applications for word processing, spreadsheets, and presentations.