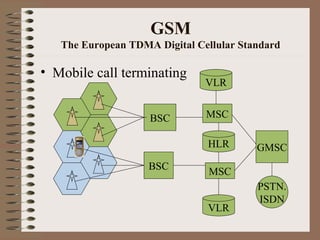
The document compares GSM and CDMA mobile technologies. It provides an overview of GSM including its architecture, services provided, and radio aspects using TDMA and FDMA. It also summarizes CDMA including its use of direct sequence spread spectrum, advantages over TDMA/FDMA, types of codes used, and formation of channels on the forward and reverse links.