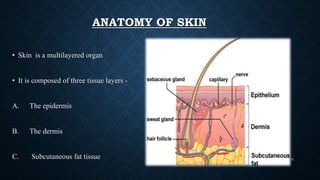
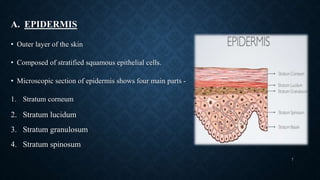
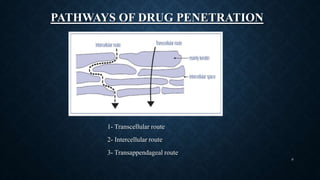
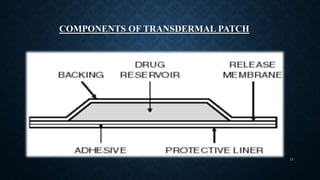
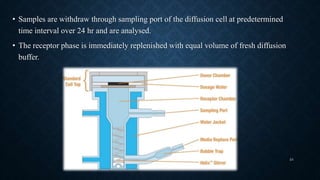
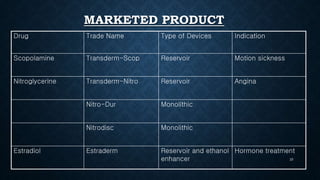
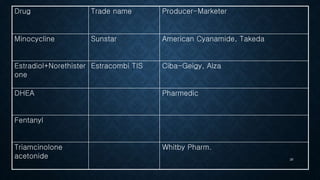
Transdermal drug delivery systems (TDDS) are patches that deliver medication through the skin for systemic effects at controlled rates, offering advantages like ease of use and improved patient compliance, although they are limited for drugs requiring high dosages. The design of TDDS involves various components such as a drug reservoir and permeation enhancers, with several classification types including reservoir, matrix, and adhesive systems. Evaluation parameters for these systems include moisture uptake, skin irritation studies, and in vitro drug release assessments.