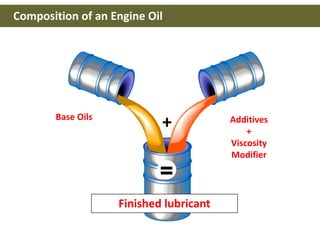
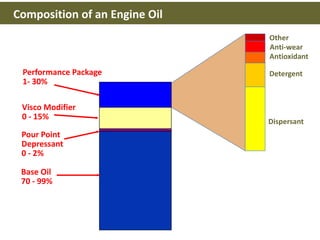
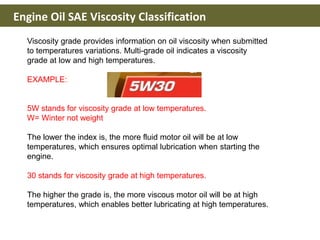
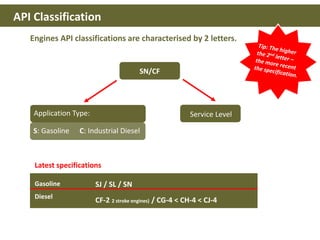
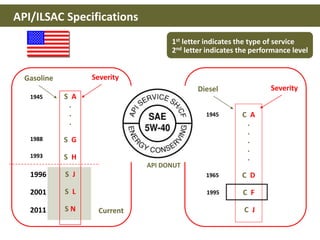
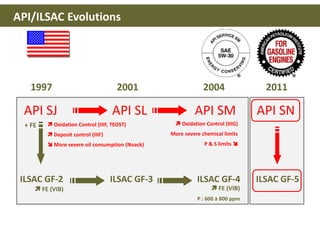
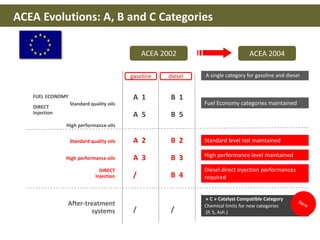
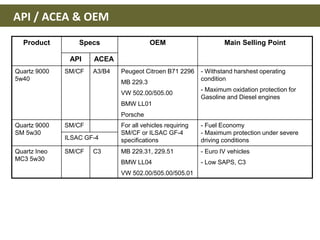
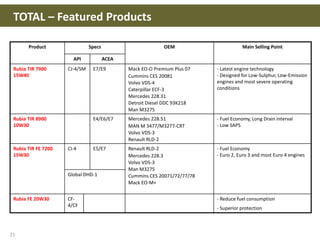
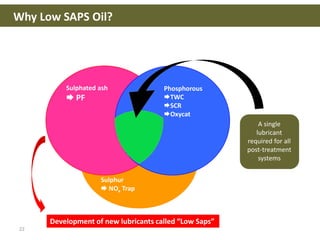
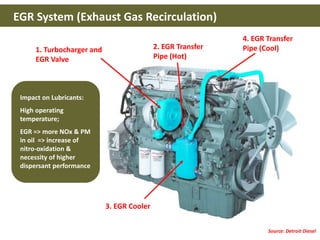
This document discusses base oils and additives used in engine oil composition. It covers the different types of base oils including mineral, synthetic and semi-synthetic oils. It also describes key base oil properties that affect lubricant characteristics and performance. Additionally, it provides an overview of common additive packages and how they contribute to properties like wear protection, viscosity and chemical stability.