1. The document discusses various key concepts related to taxation in India such as direct taxes, indirect taxes, types of taxes including income tax, duty, cess, and surcharge. It provides definitions and explanations of these tax terms.
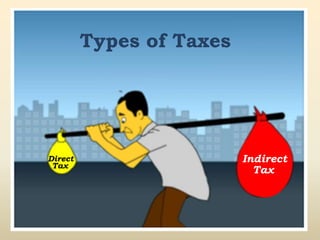
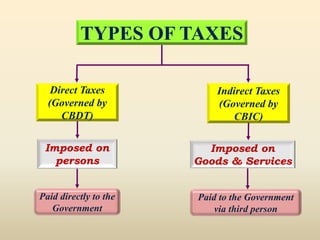
2. The key highlights are that direct taxes are imposed directly on income and wealth while indirect taxes are imposed on goods and services. Income tax is governed by the Income Tax Act of 1961 which is amended every year by the Finance Act.
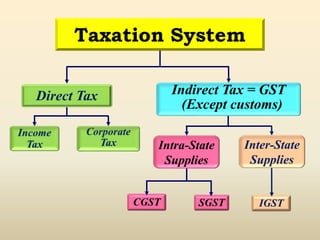
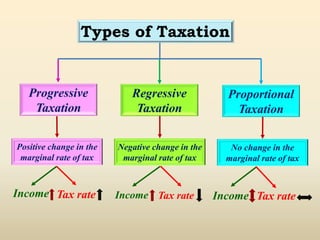
3. The document also explains the difference between direct and indirect taxes, taxation system in India, types of taxation including progressive, regressive and proportional, and income tax computation process.





























![ This means the year commencing on the
1st day of April every year and ending
on 31st march of the next year.
The current Assessment Year is 2018-19.
Assessment year [Sec.2(9)]
Previous year [Sec.3]
Previous year means the financial year
immediately preceding the assessment year.
The current Previous Year is 2017-18.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/taxbasic-181004011838/85/Basic-concepts-of-Tax-34-320.jpg)


