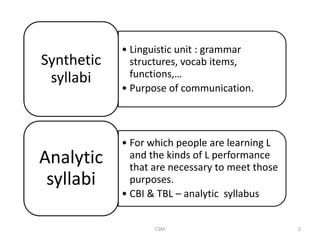
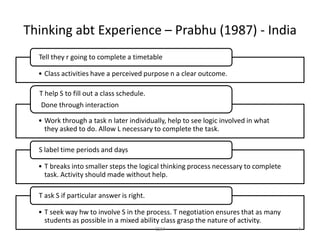
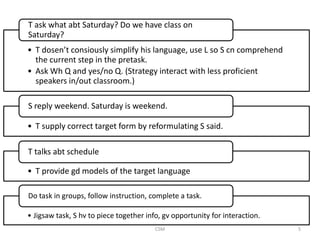
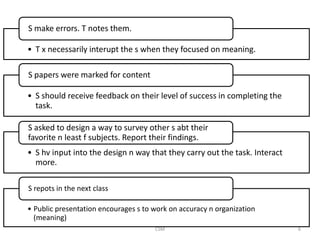
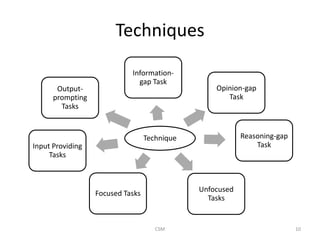
Task-based language teaching focuses on having students complete meaningful tasks using the target language. There are two types of syllabi - synthetic which focuses on grammar structures, and analytic which focuses on the purposes of communication. Effective tasks have clear outcomes, require students to communicate, and involve planning or problem solving like creating a travel itinerary. Tasks should allow students to complete them through negotiation and interaction without direct help from the teacher. Teachers observe students, note errors, and design new tasks to address problems. The goal is to engage students in purposeful communication through task-based activities.