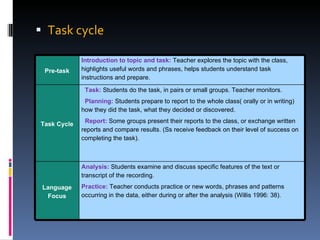
This document outlines the theory and techniques of task-based language instruction. It discusses the roles of the teacher and students, types of tasks, task cycles, modes of interaction, language areas addressed, error correction approaches, advantages and disadvantages. The key aspects are that tasks provide opportunities for meaningful communication and language use, the teacher facilitates while students actively work together to complete tasks using their linguistic resources.