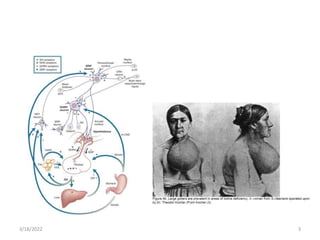
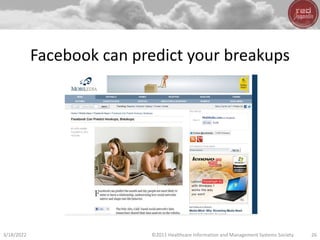
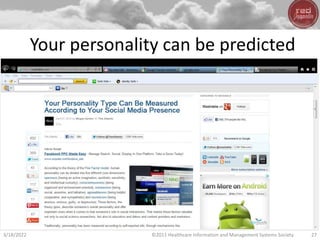
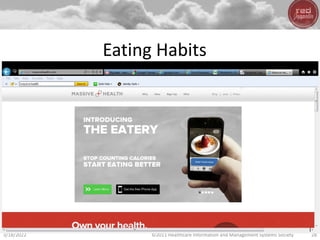
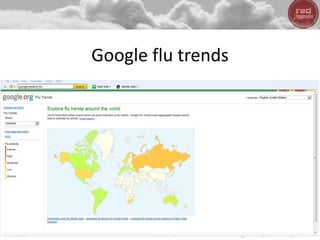
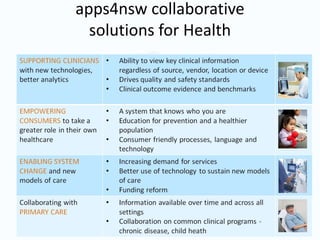
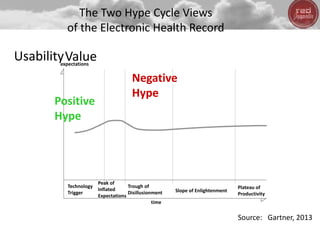
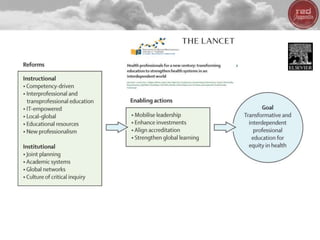
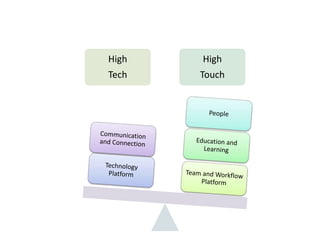
- Big data, predictive analytics, and business intelligence (BI) tools can help healthcare organizations address growing cost pressures and improve operational and financial efficiency. However, their benefits are often underappreciated in healthcare.
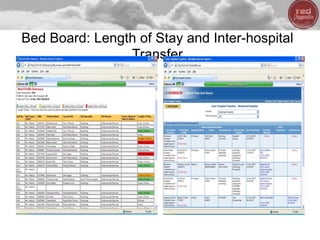
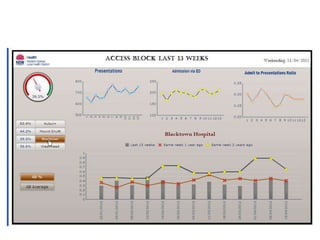
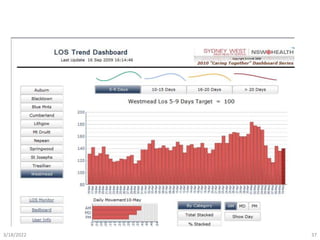
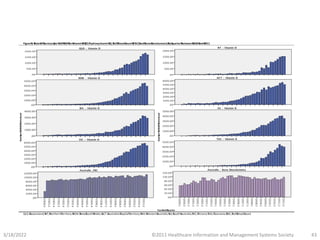
- BI can be used for both clinical and non-clinical purposes to analyze large amounts of healthcare data and gain insights. When properly implemented and governed, it allows organizations to better understand variability and optimize performance.
- The presentation will provide real-world examples of how BI is being used in healthcare to improve patient outcomes, safety, and experience as well as hospital operations and systems.