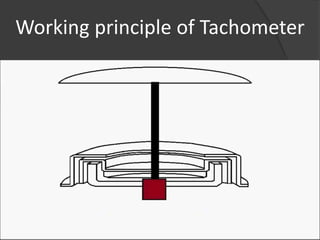
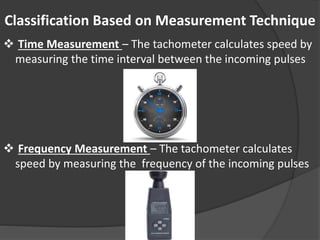
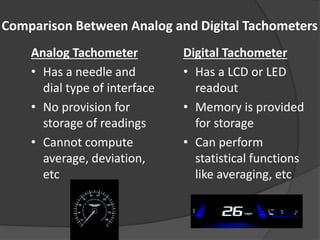
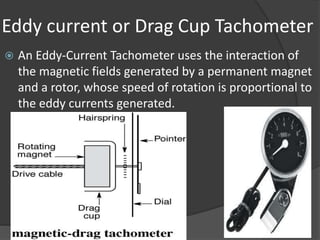
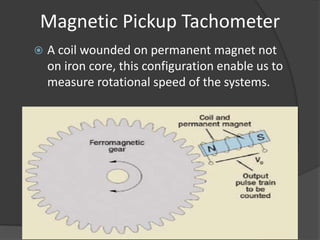
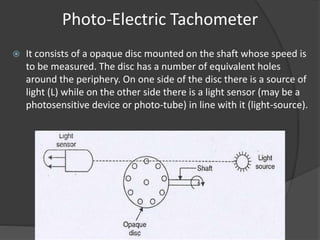
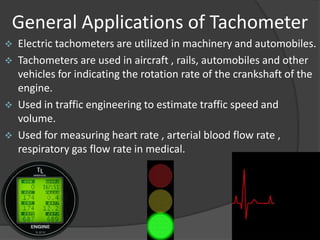
The document outlines the history, principles, types, and applications of tachometers, instruments designed to measure speed. It details various classification methods such as data acquisition (contact vs. non-contact) and measurement techniques (time-based vs. frequency-based), as well as differences between analog and digital tachometers. The document also lists multiple types of tachometers and their specific applications in sectors like automotive, medical, and industrial machinery.