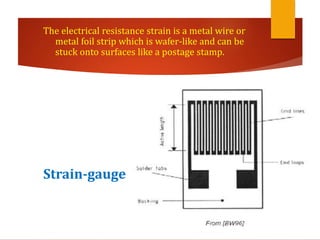
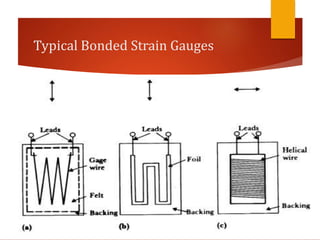
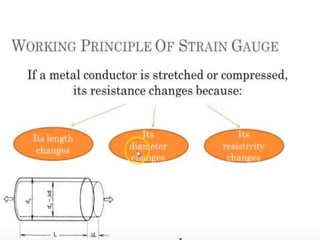
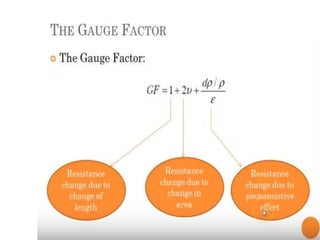
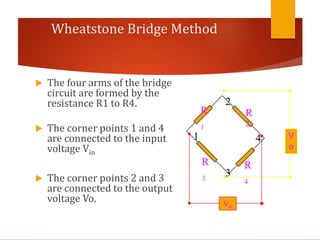
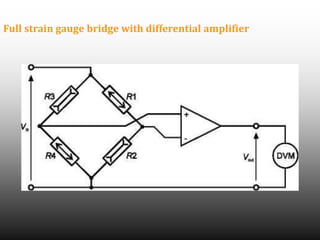
Strain gauges are devices used to measure small changes in dimensions of a structure when force is applied, based on the principle that these changes affect the electrical resistance of a metal wire or foil. Different types of strain gauges exist, including bonded, unbonded, electrical, and piezoelectric, each working on unique principles to measure strain via resistance change. The Wheatstone bridge method is commonly employed to convert changes in resistance to voltage output, which requires amplification due to the relatively small nature of the resistance changes.