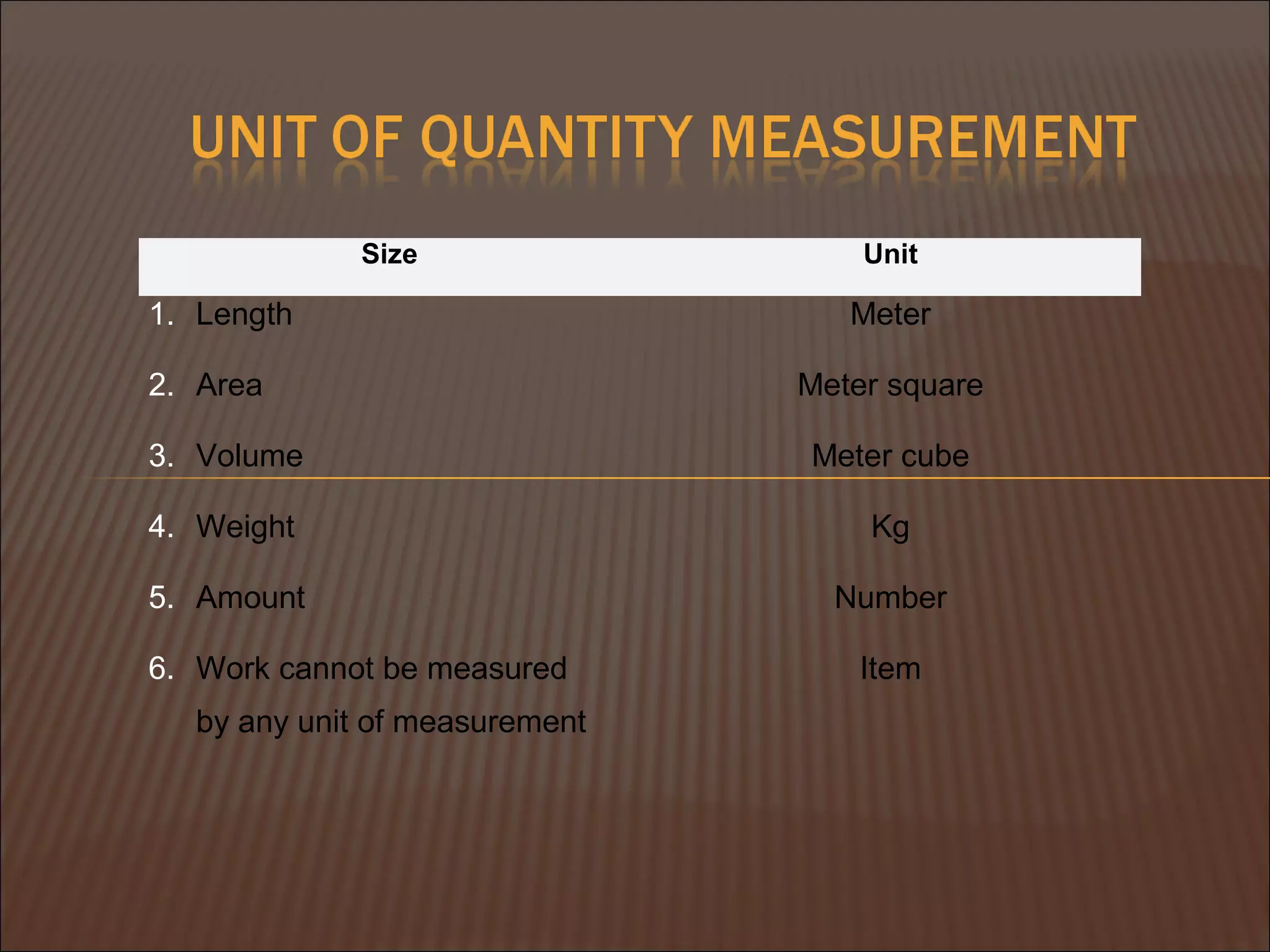
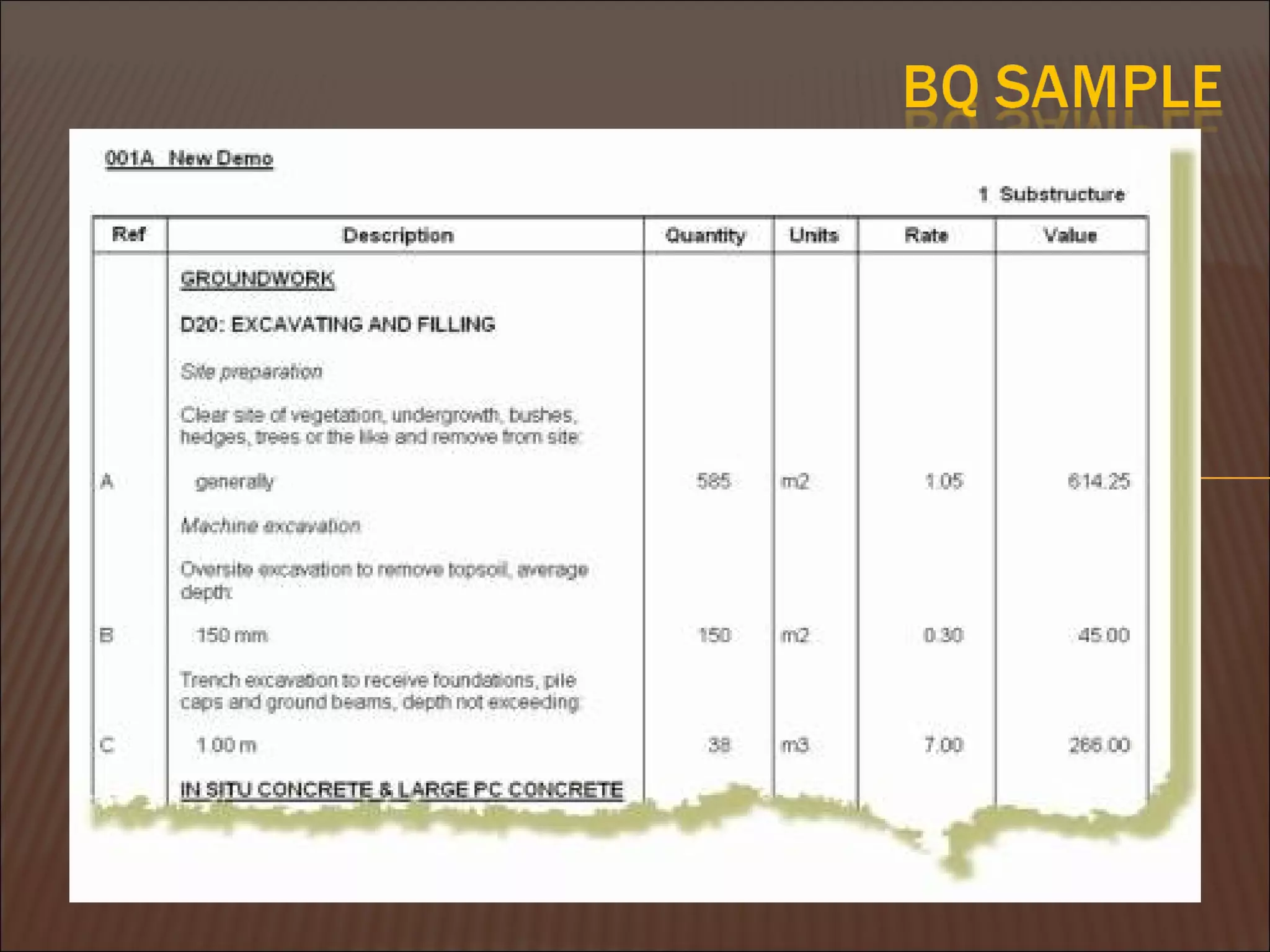
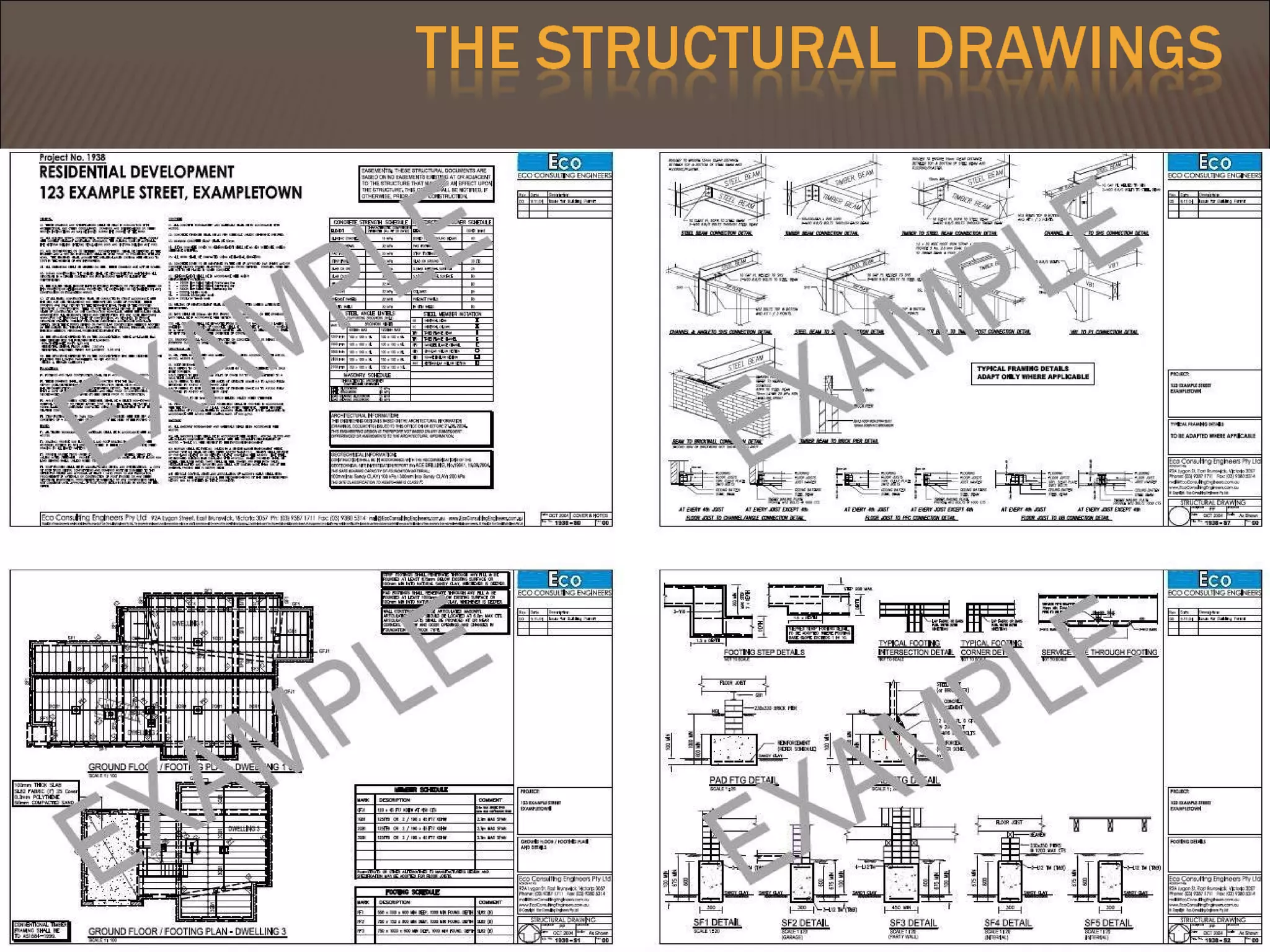
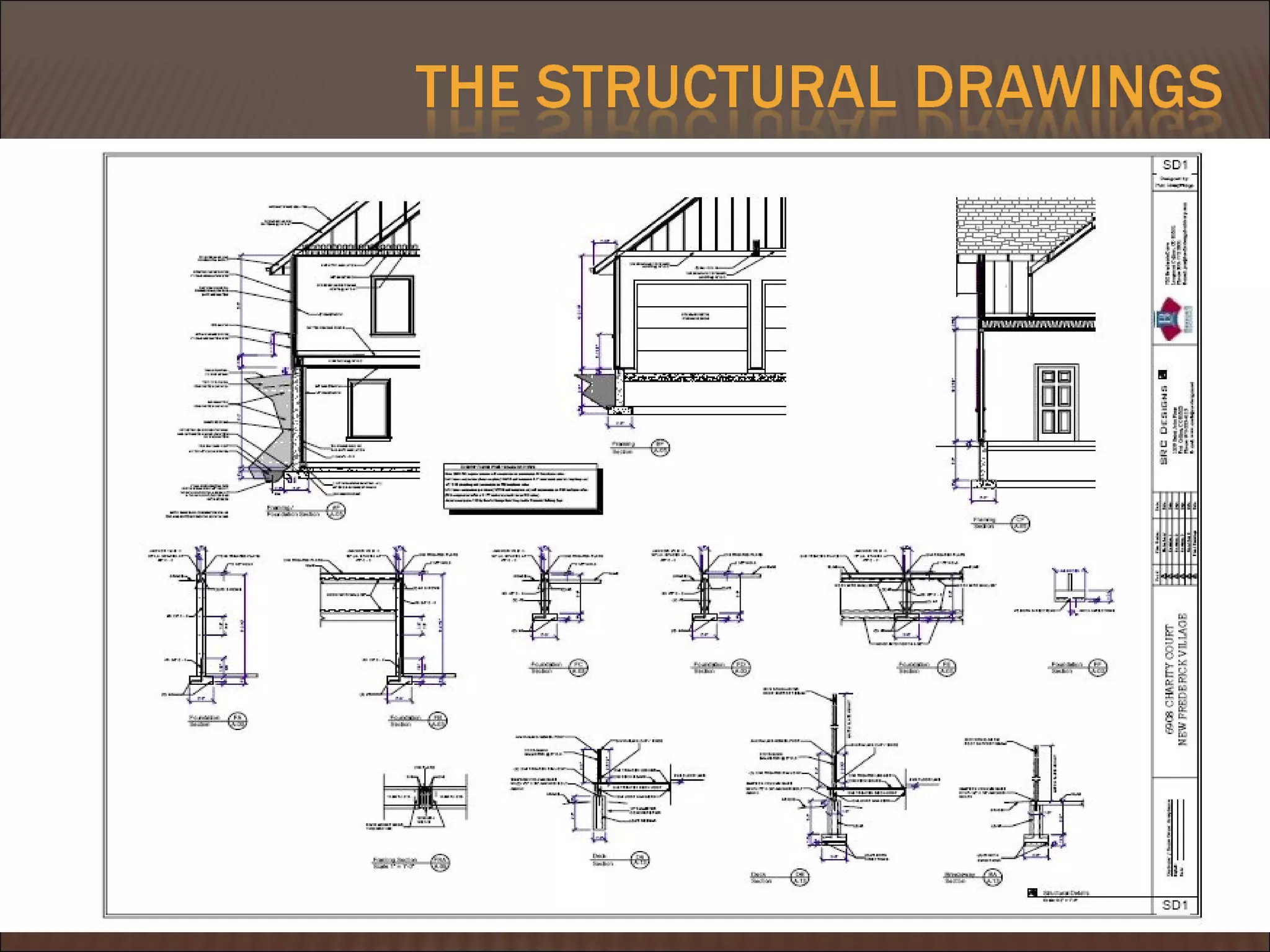
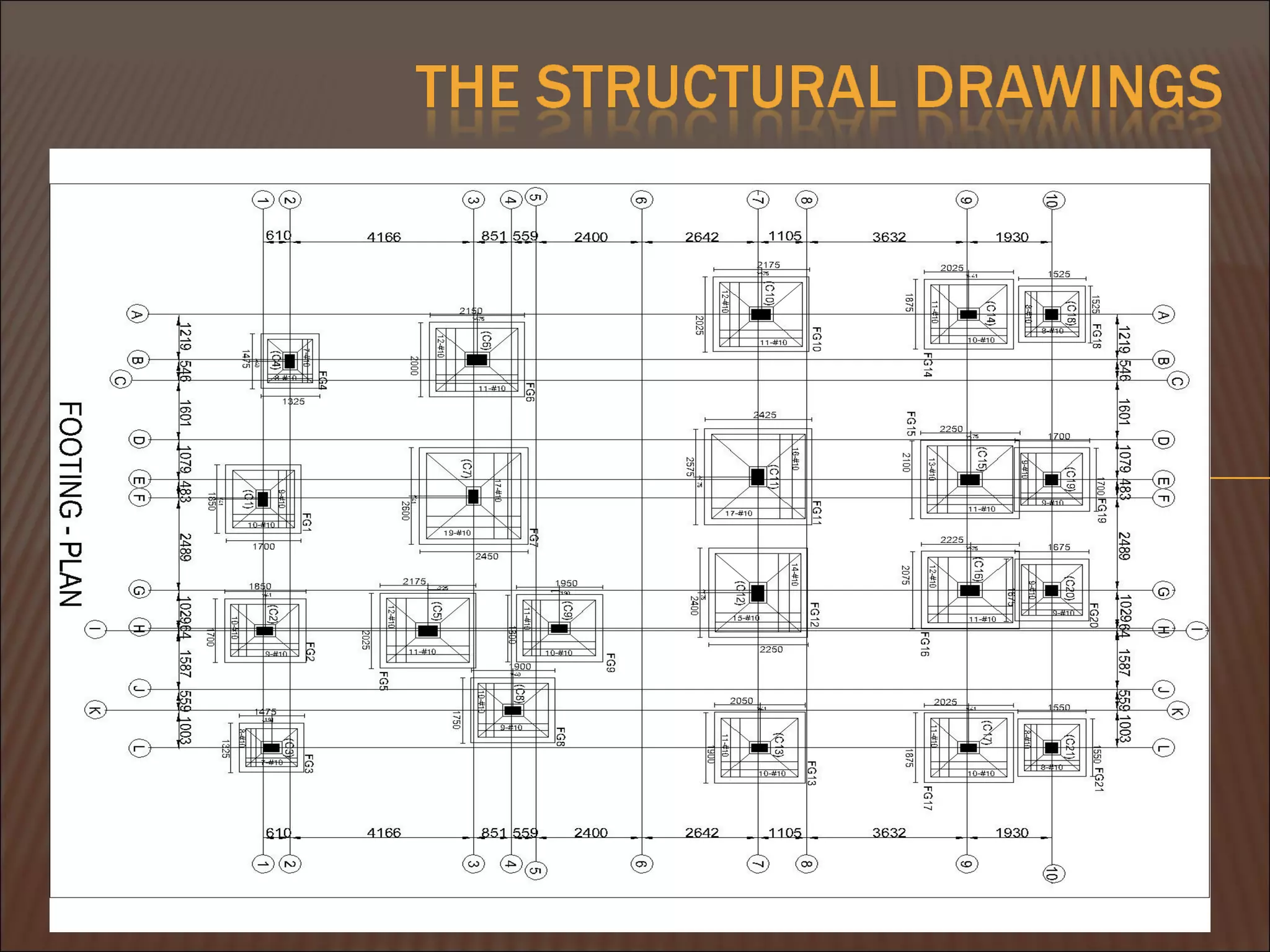
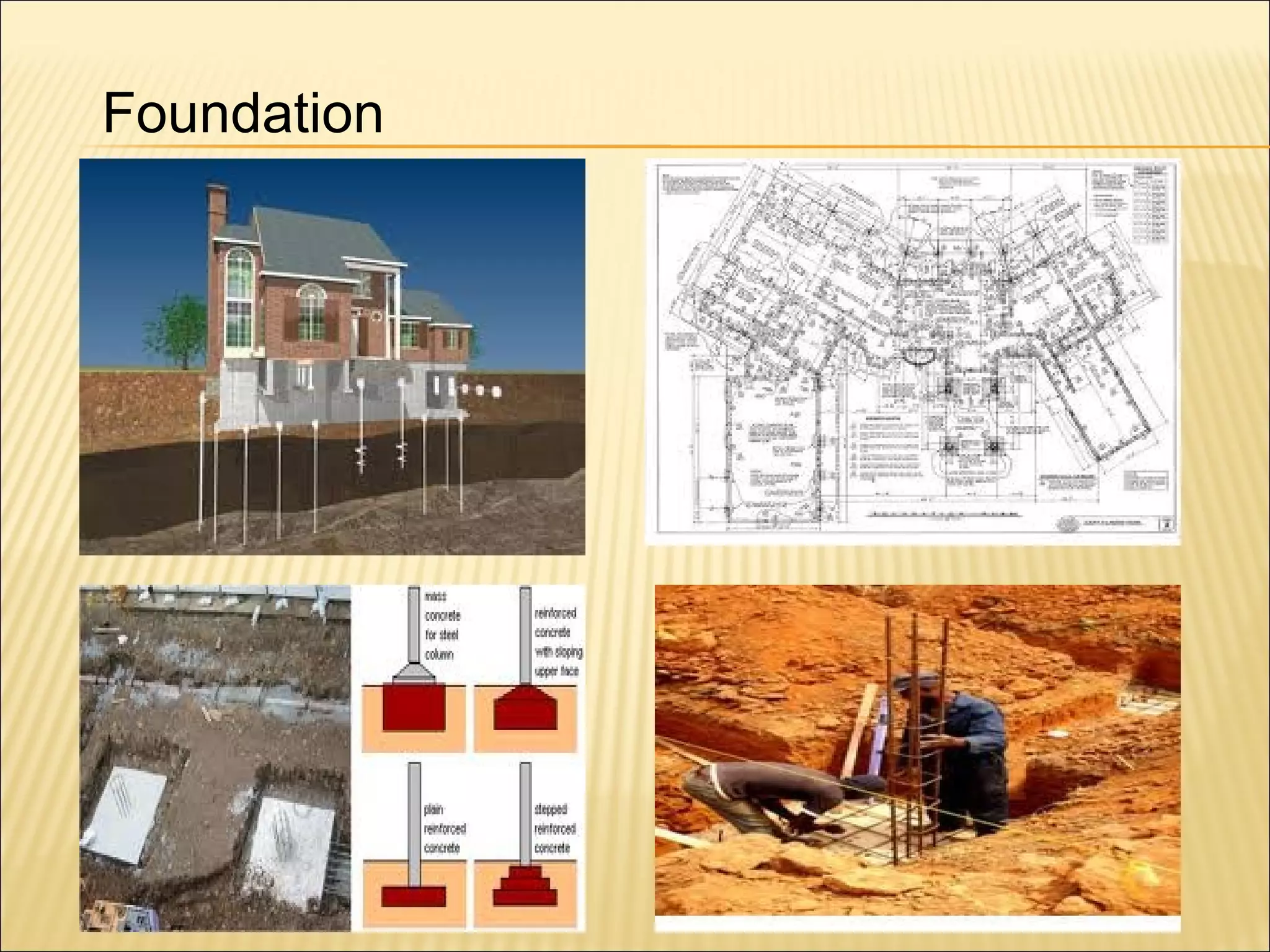
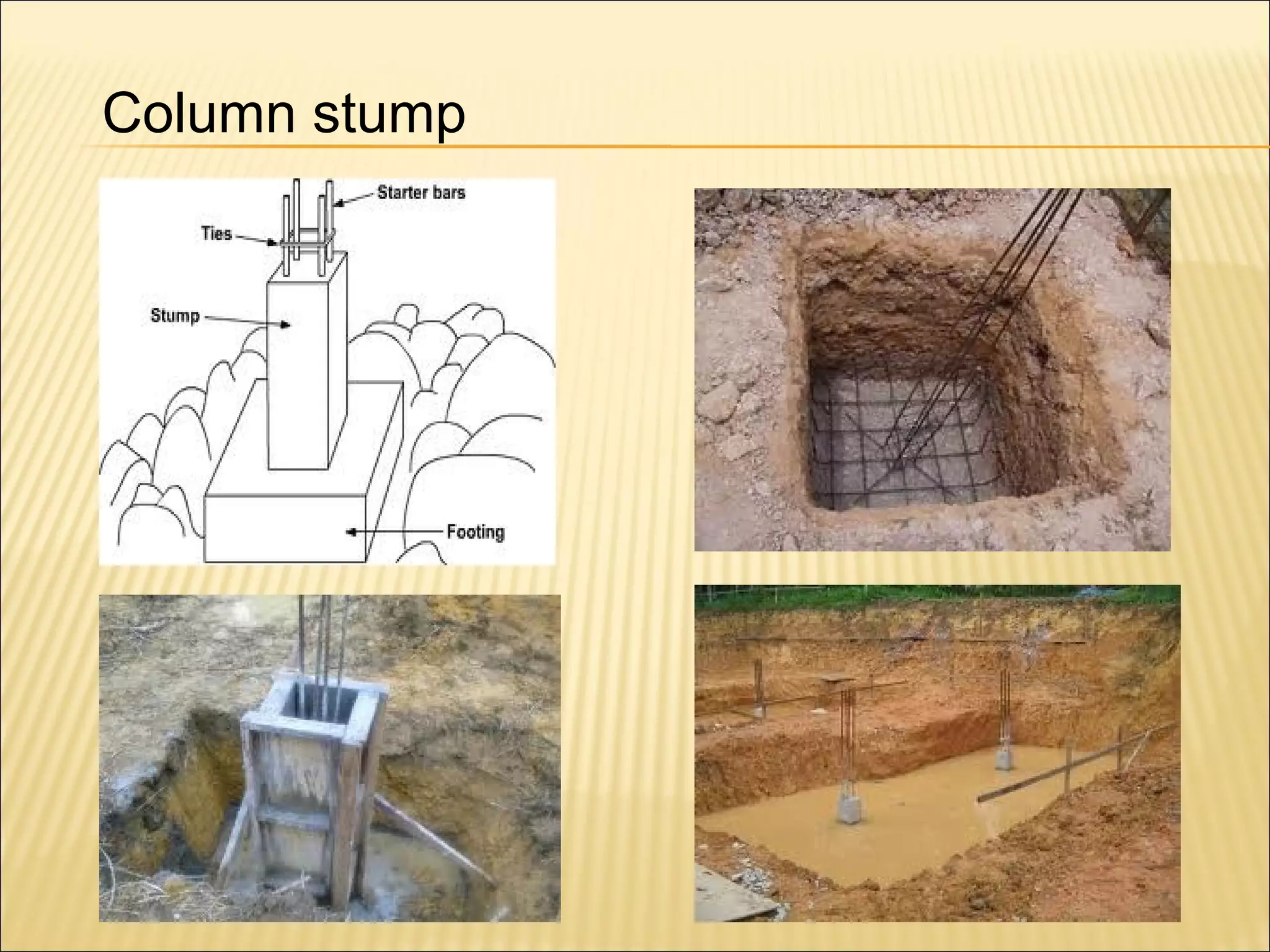
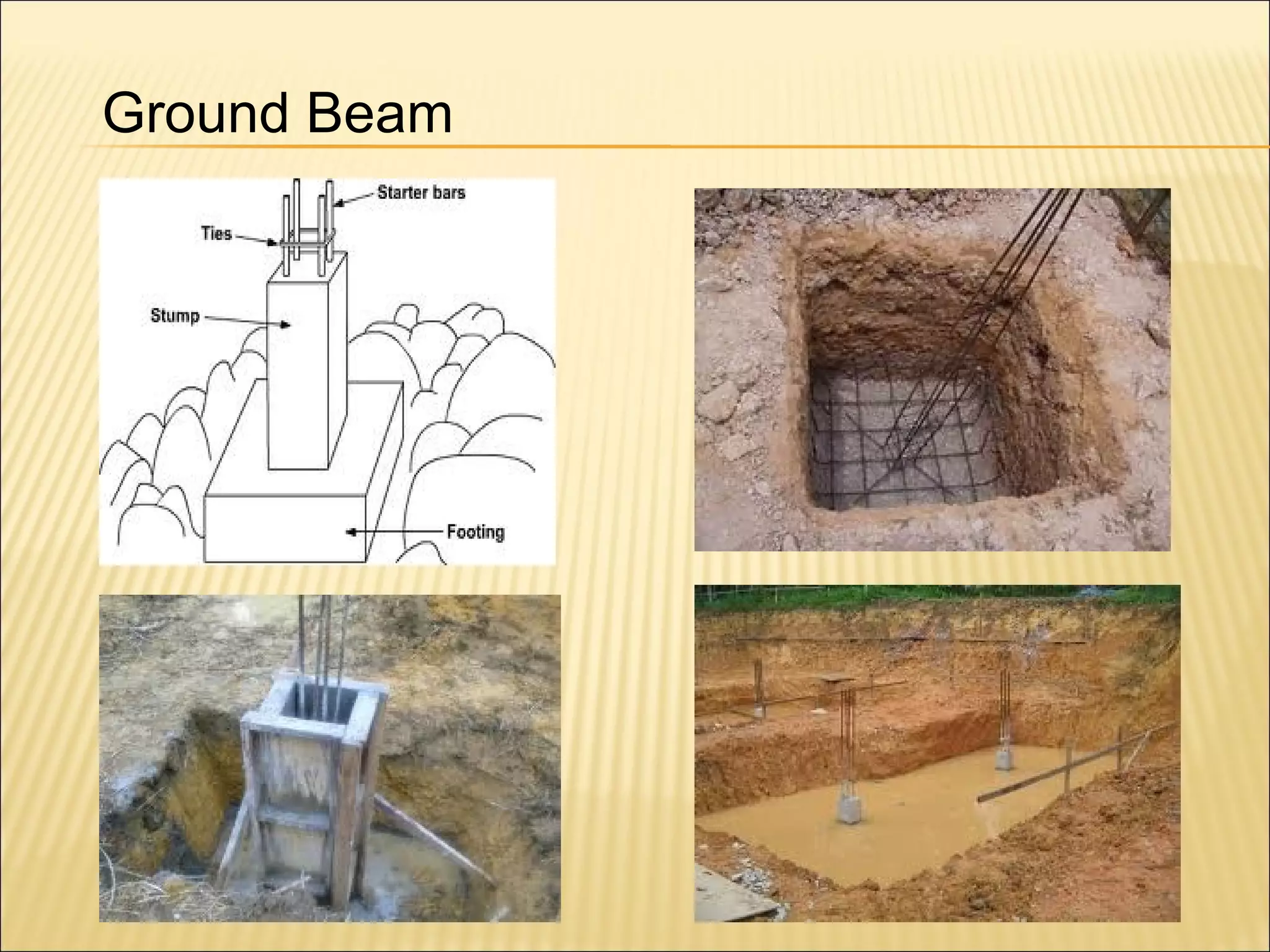
This document discusses quantity measurement in construction projects. It describes the importance of bills of quantities in costing, tendering, and valuing payment and variations. It explains the common units used to measure length, area, volume, weight, amounts, and items. It also defines structural drawings and their purpose in showing architectural and structural details. Finally, it outlines the key elements to take off quantities for substructures, such as piling, foundations, column stumps, ground beams, and ground slabs.