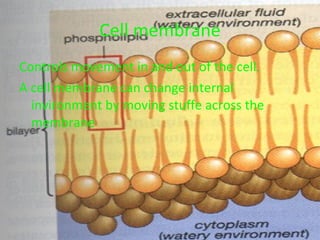
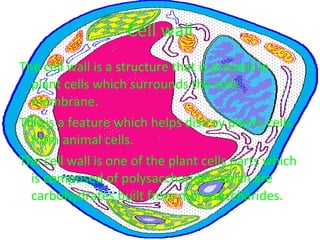
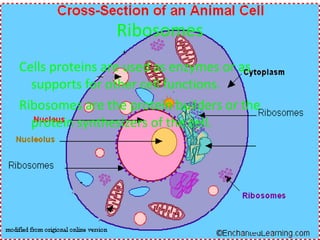
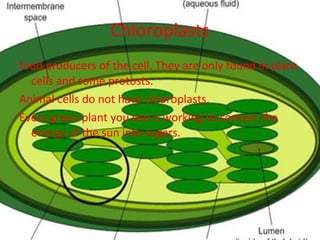
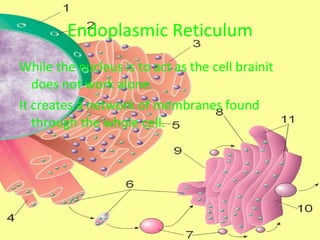
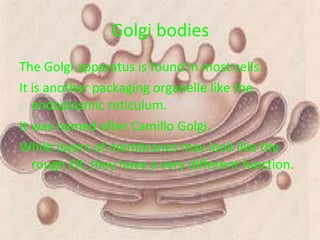
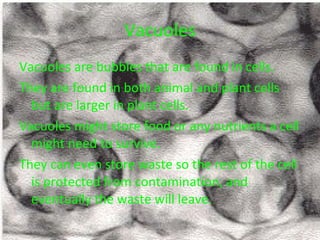
The document describes the key organelles and structures found within plant and animal cells, including the cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplasts, mitochondria, nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles, and cytoplasm. Each structure has a specific function, such as the cell membrane controlling movement in and out of the cell, chloroplasts producing food for plant cells, and the nucleus controlling cell processes.