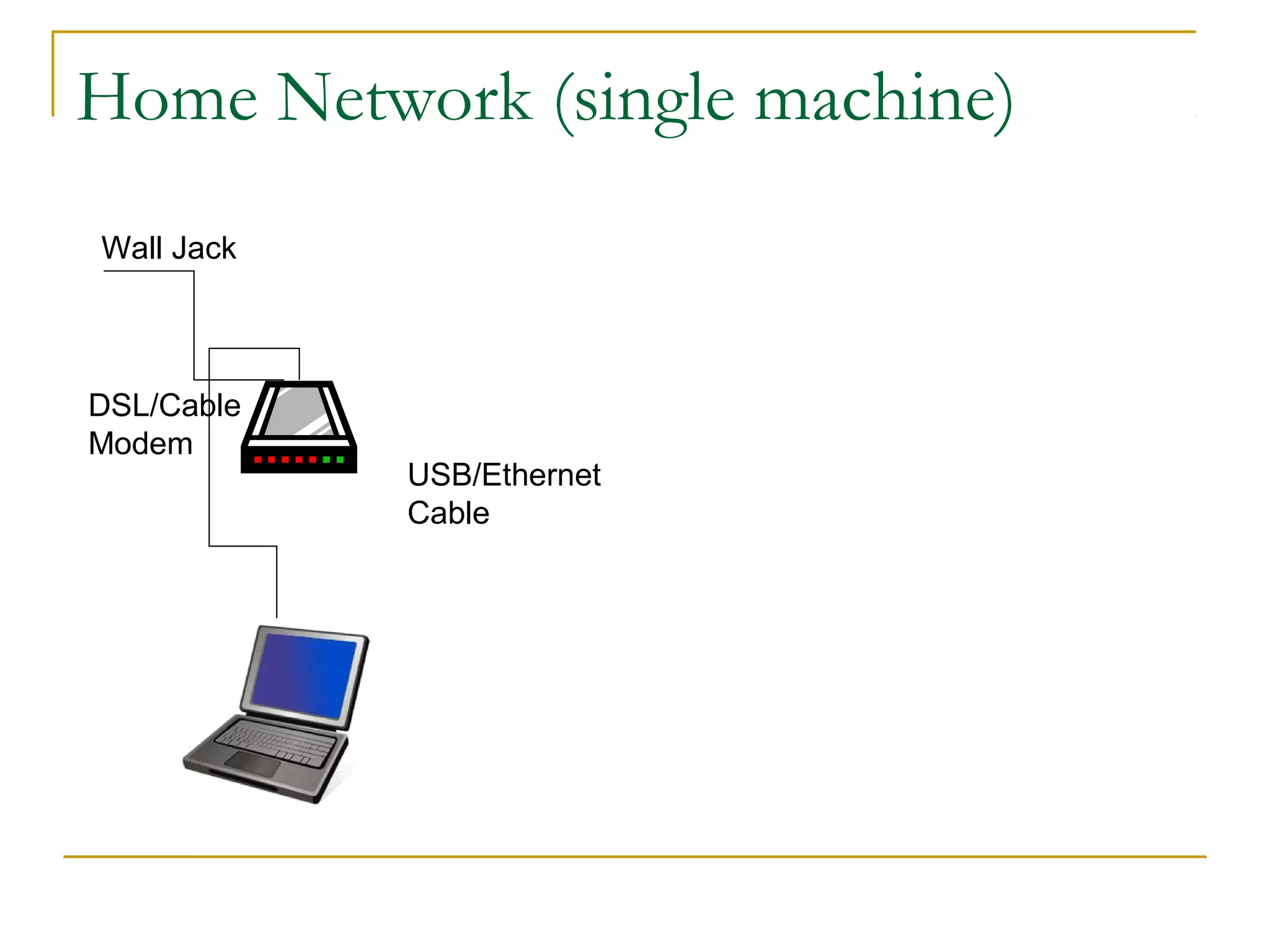
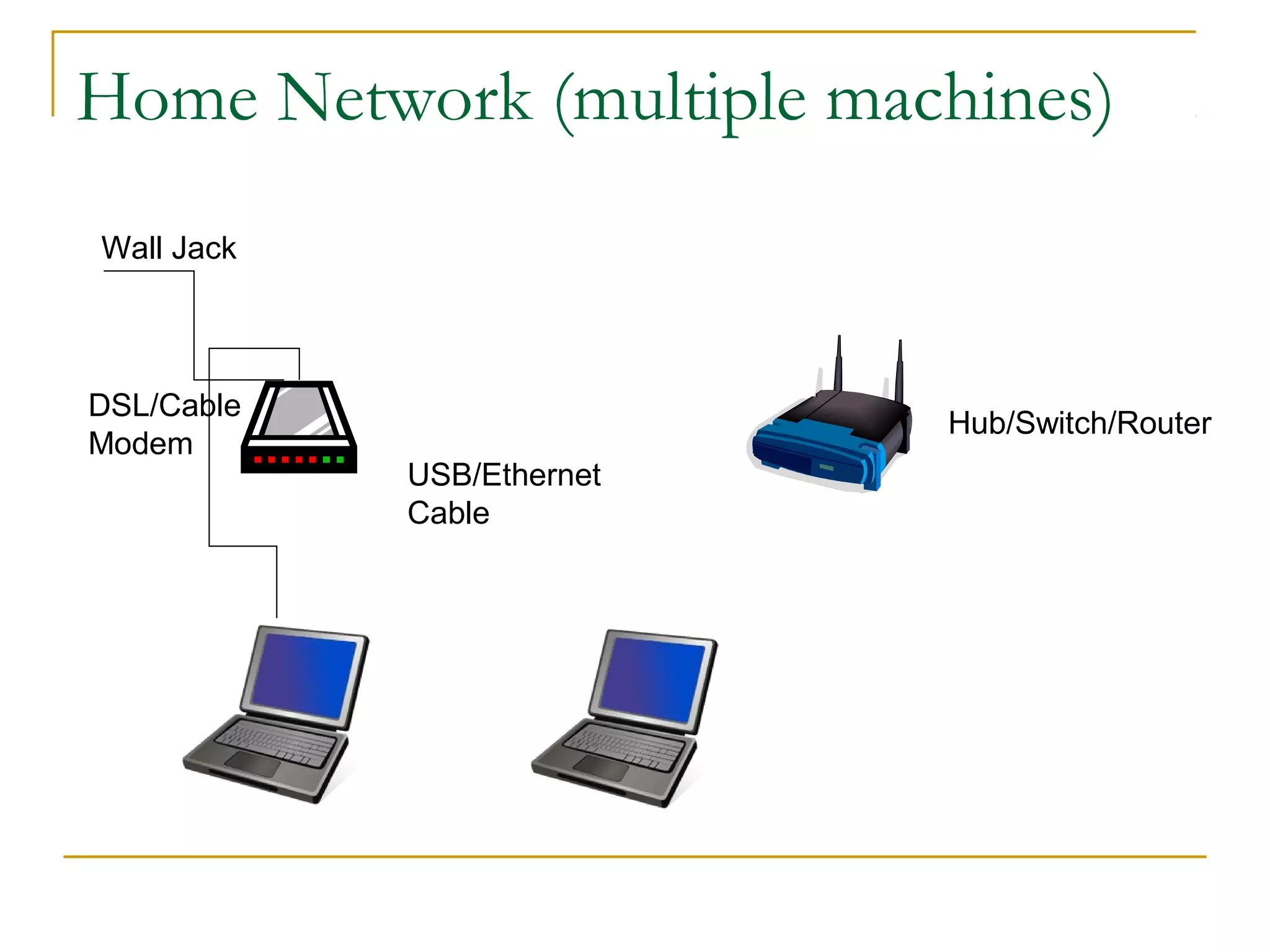
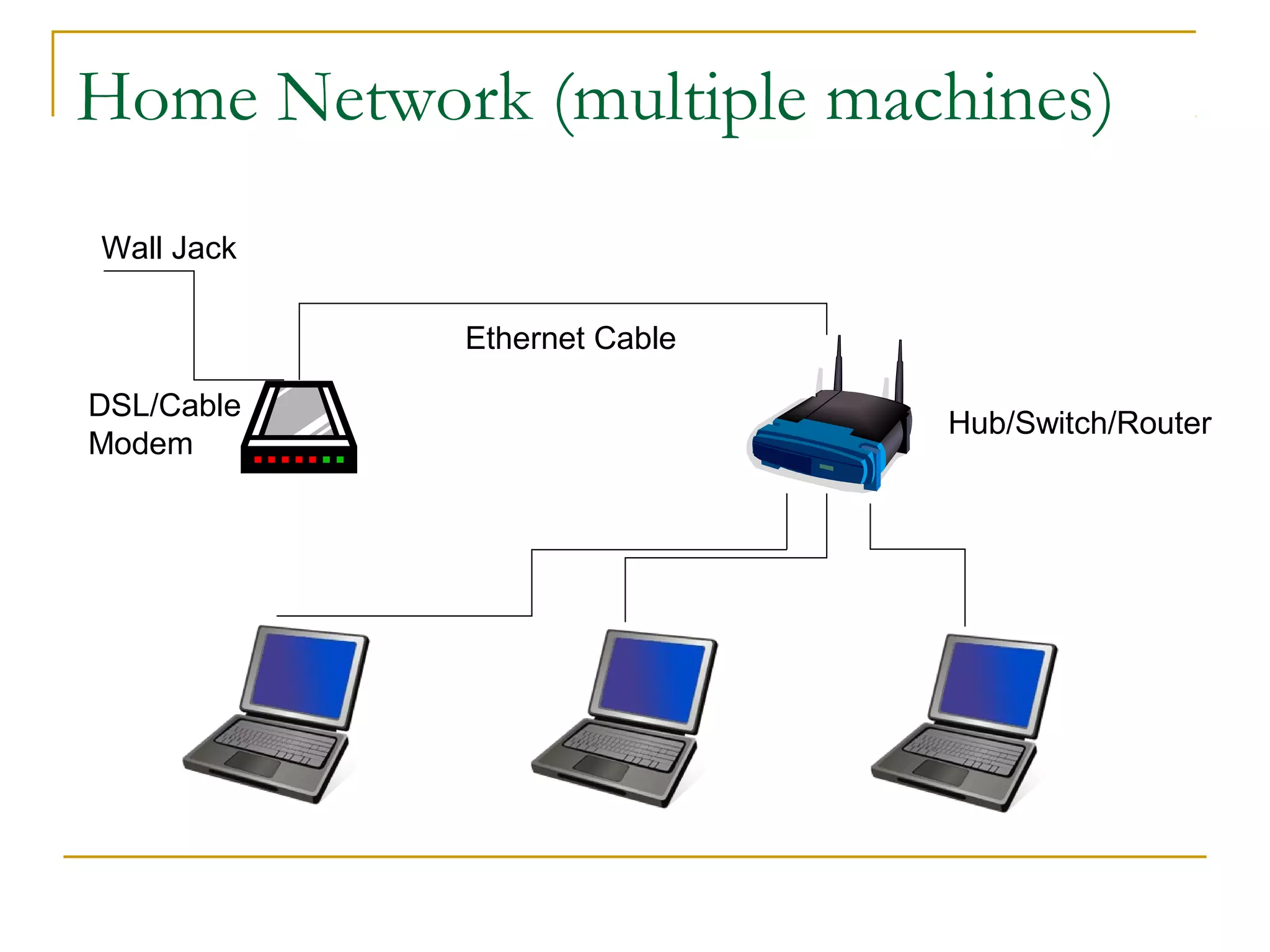
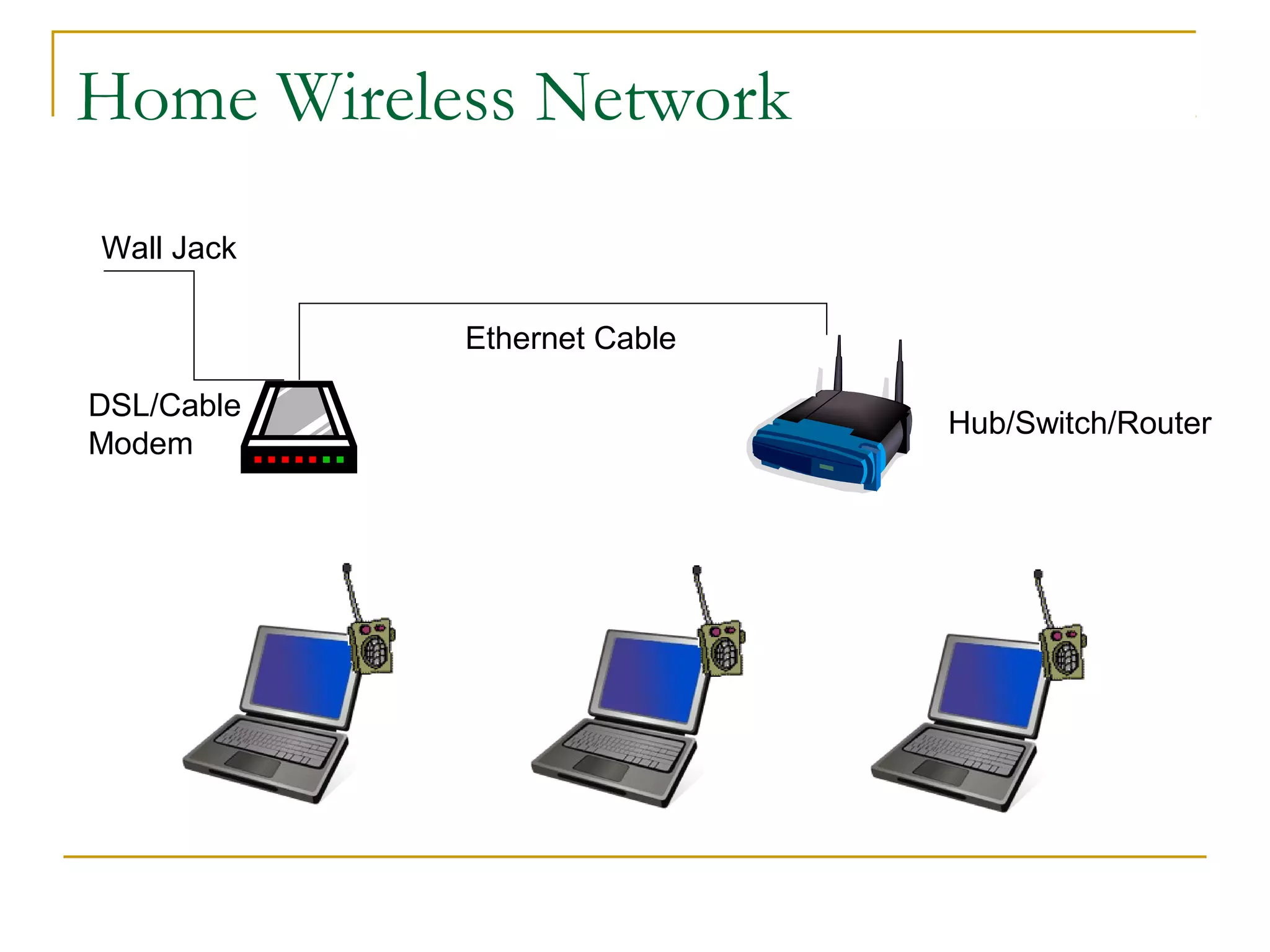
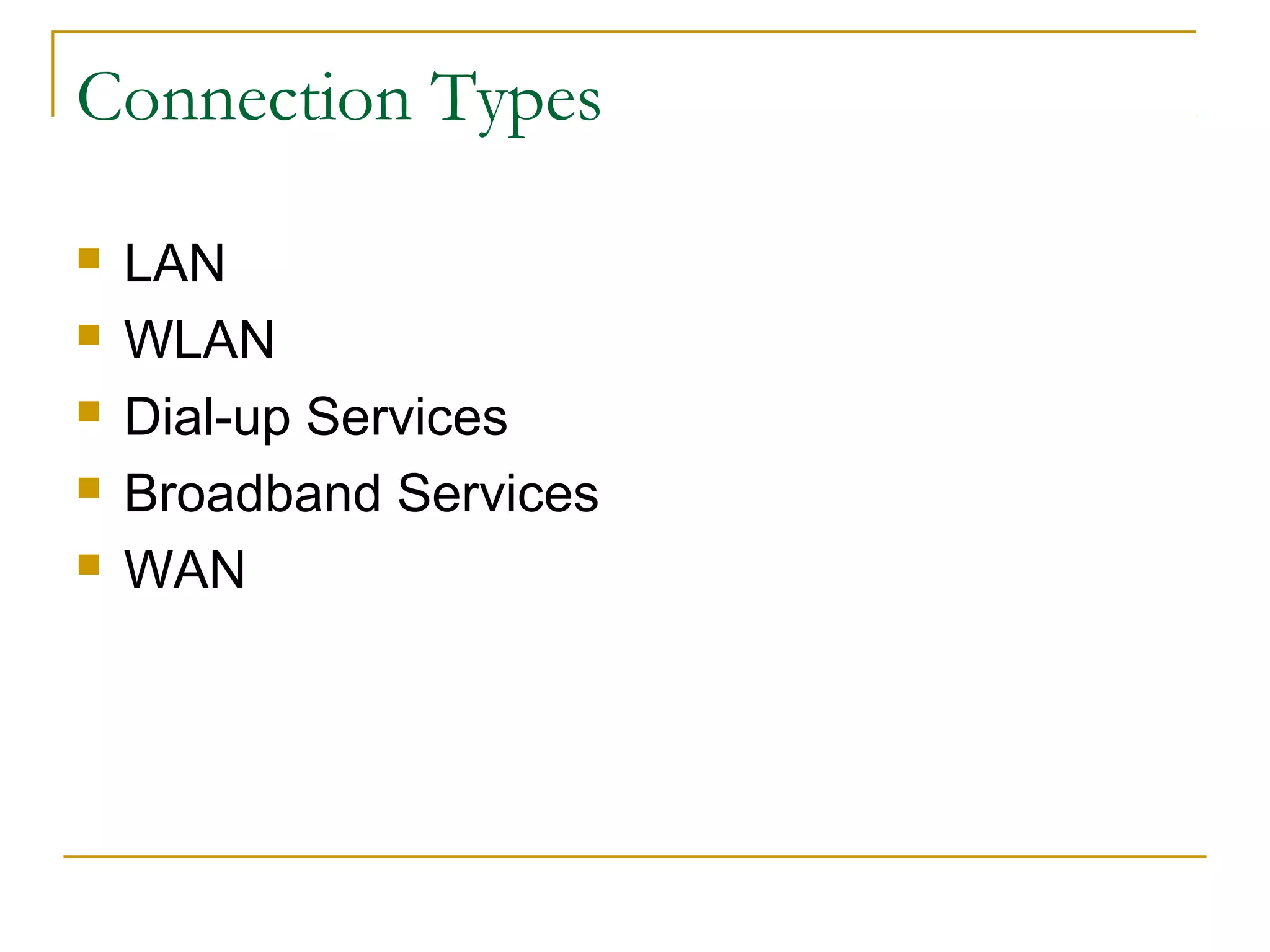
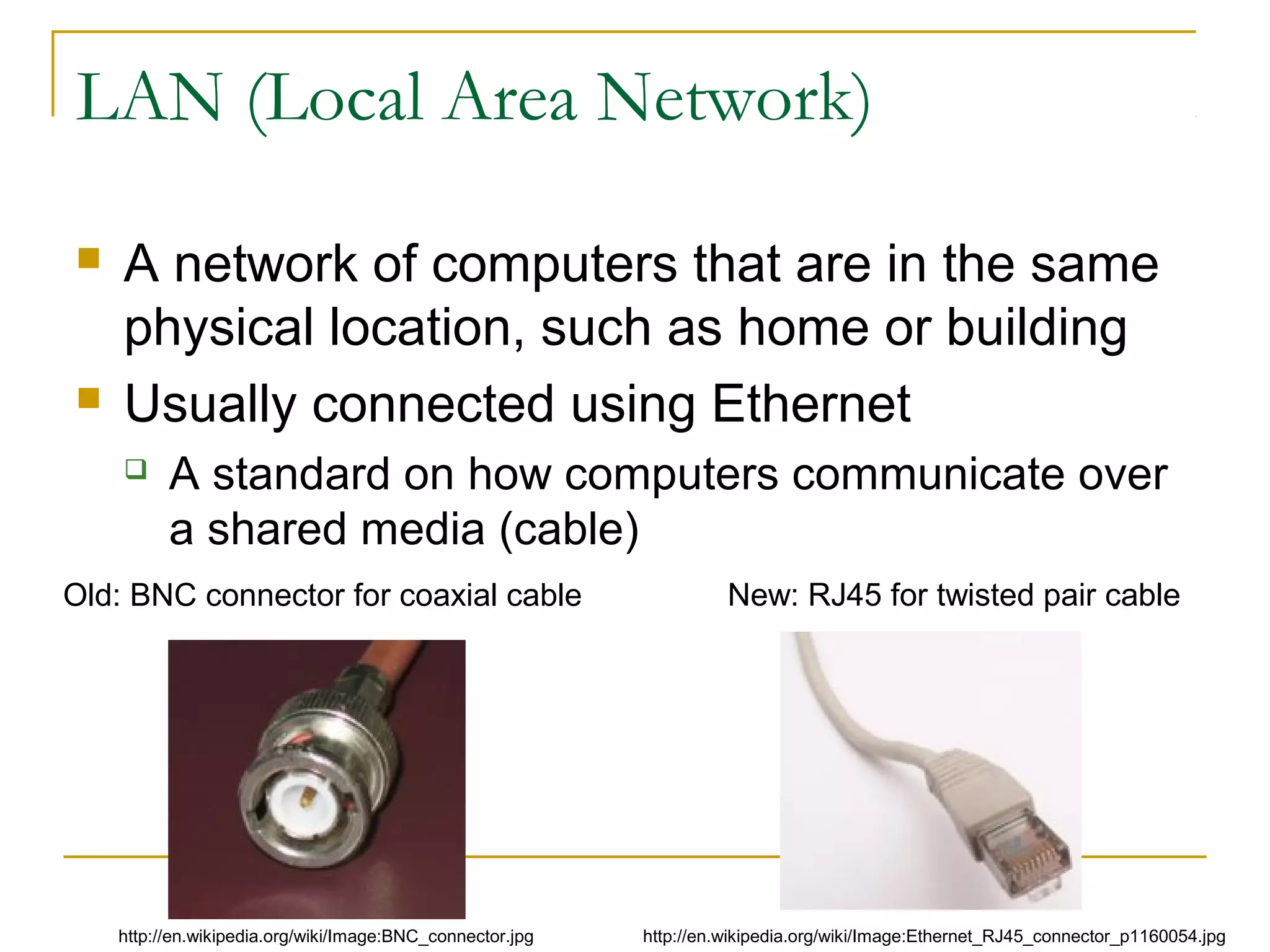
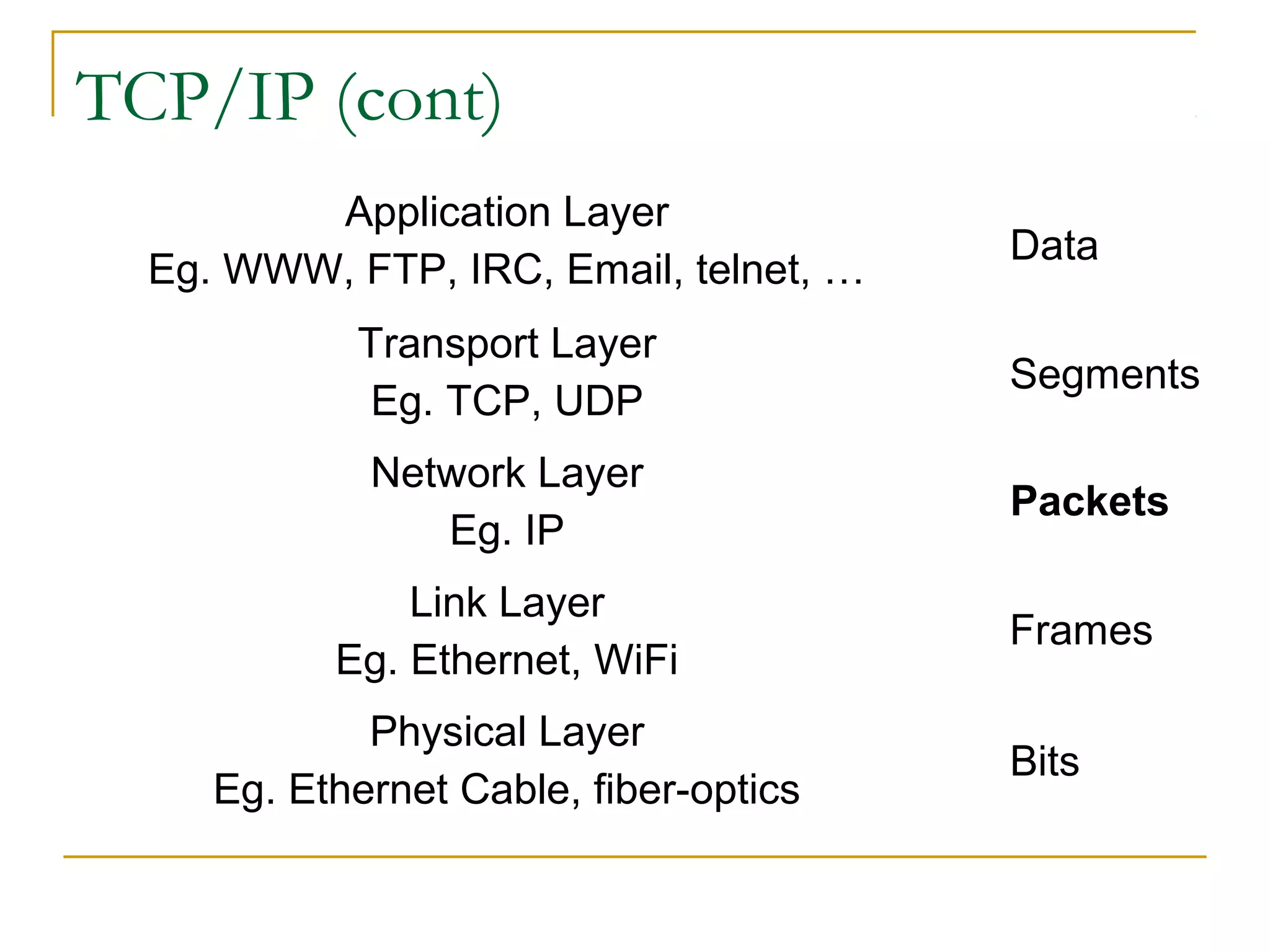
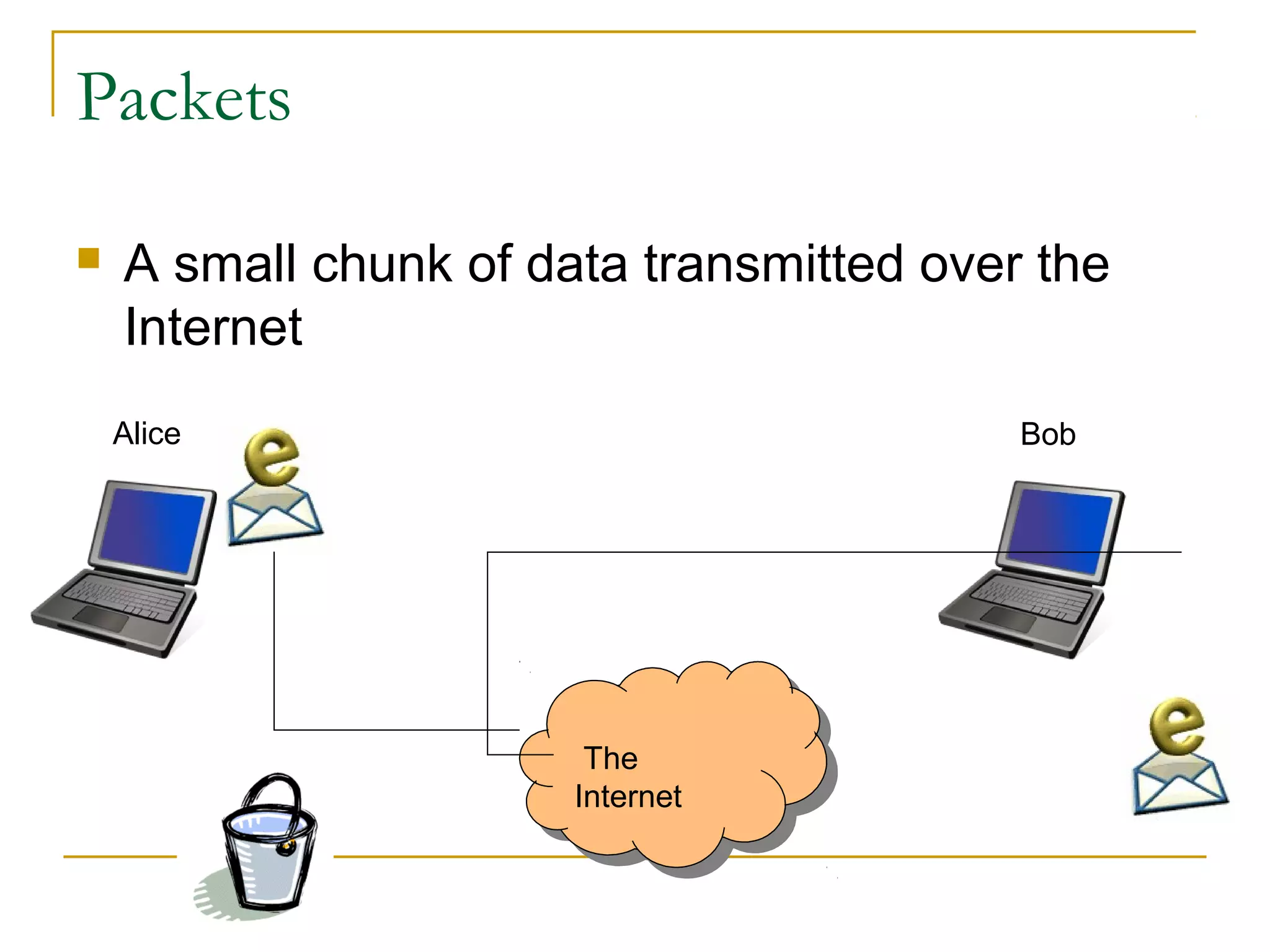
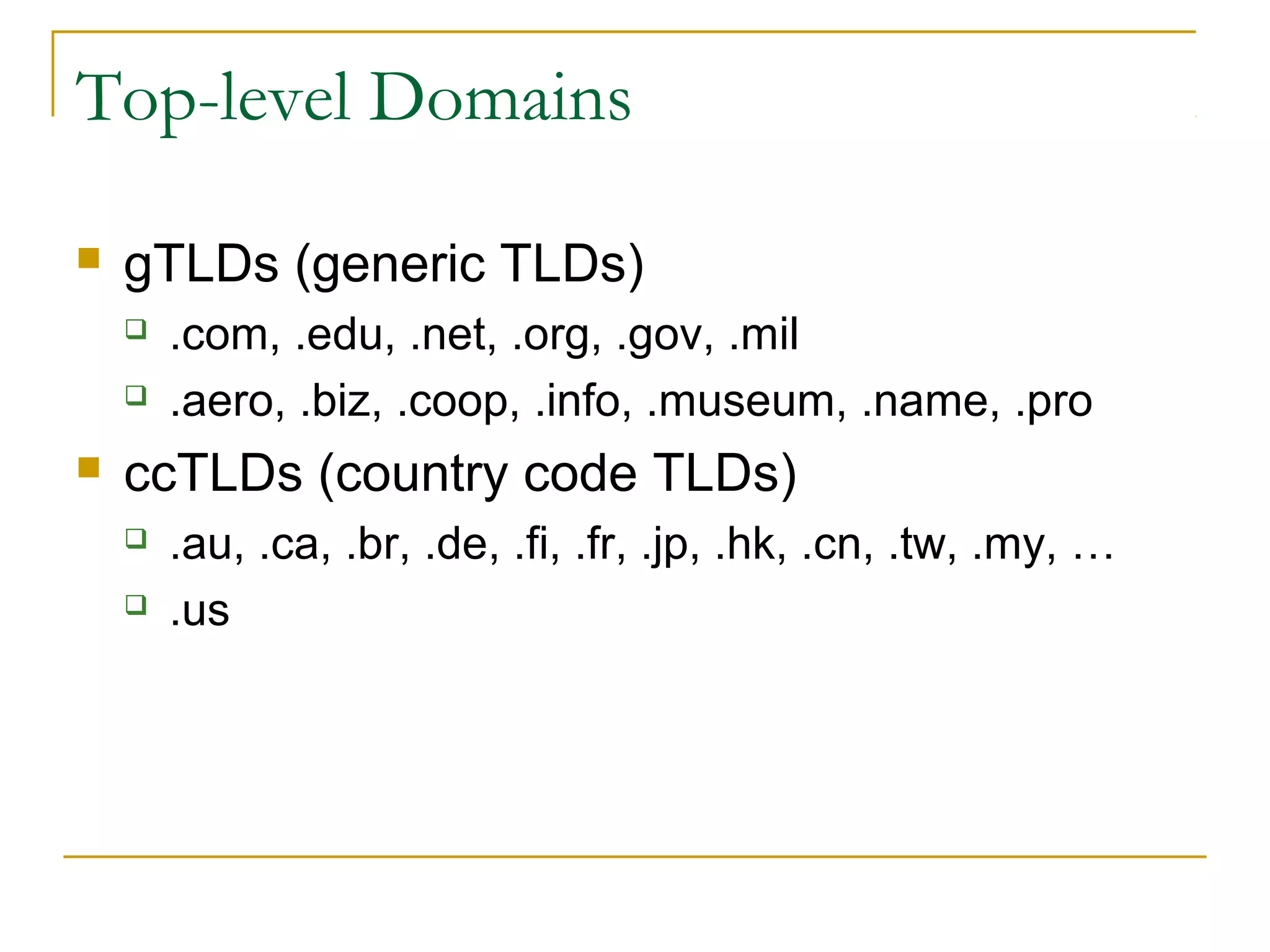
This document provides an overview of basic computer networks. It discusses bandwidth and connection types including LAN, WLAN, dial-up, broadband, and WAN. It describes hardware components like modems, routers, hubs, switches and how they connect individual devices into networks. Common network standards such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and protocols including TCP/IP are explained at a high level. Domain name system and its role in translating names to IP addresses is summarized. Finally, the document outlines policies and concludes with references for further reading.