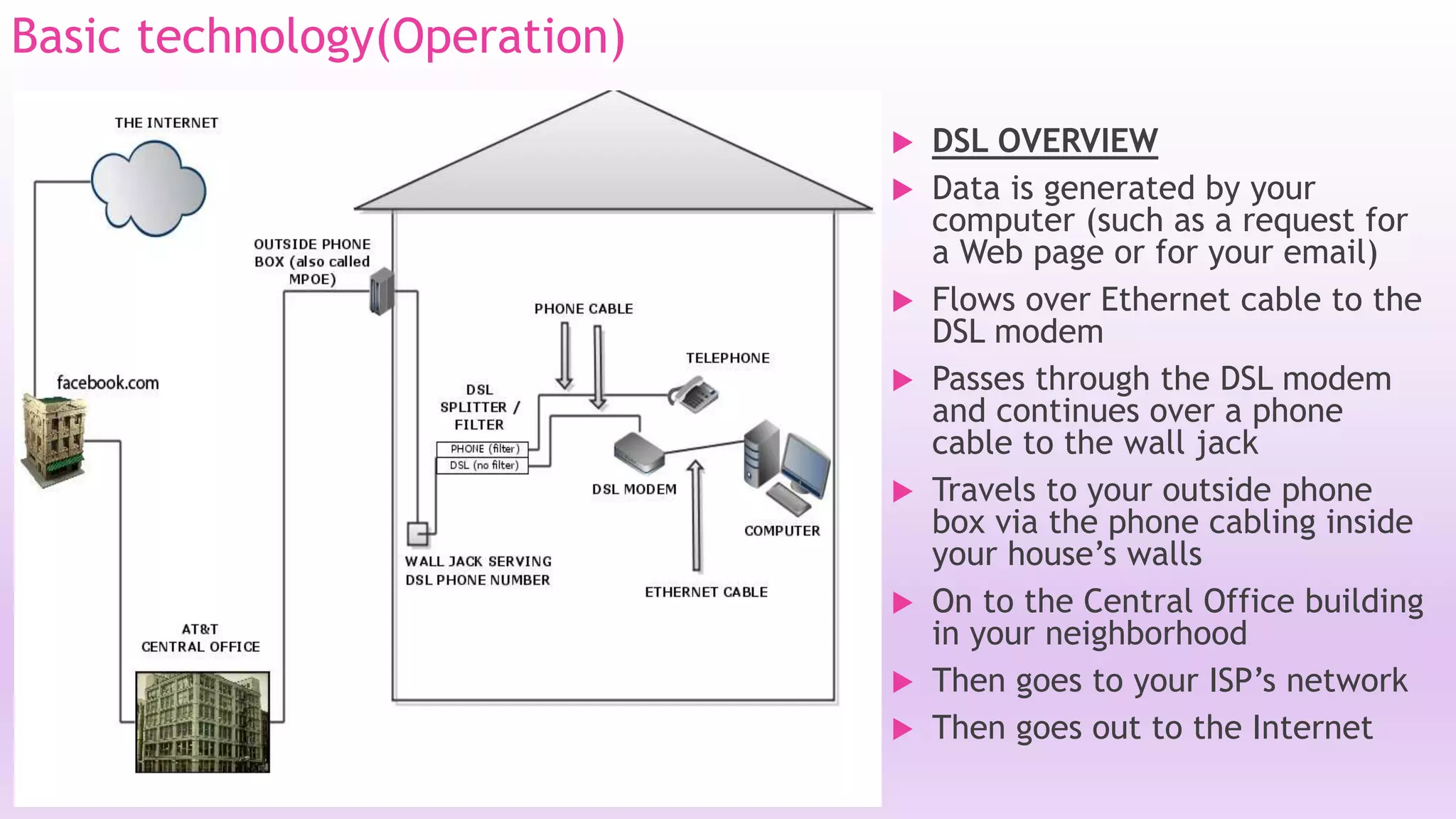
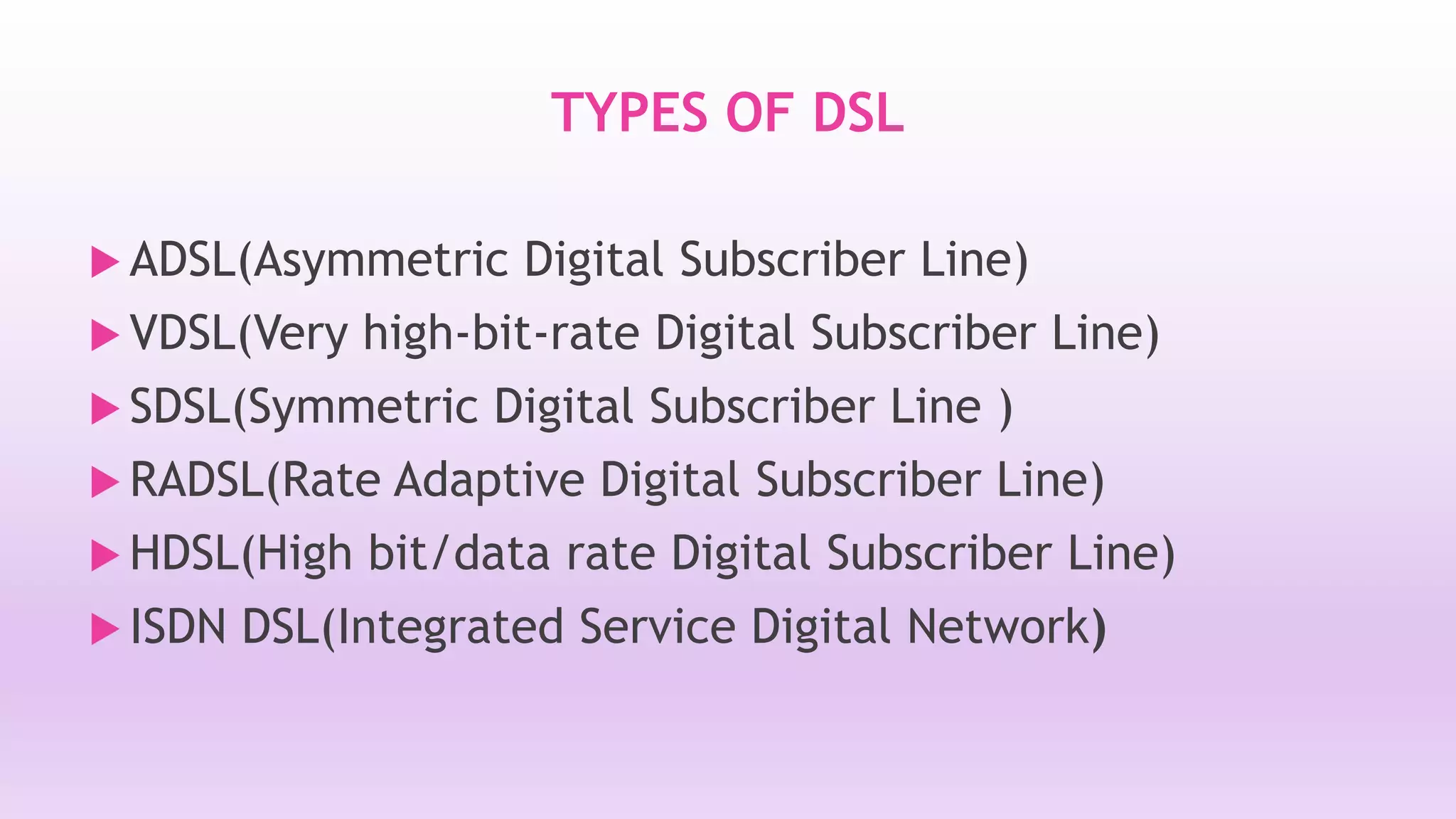
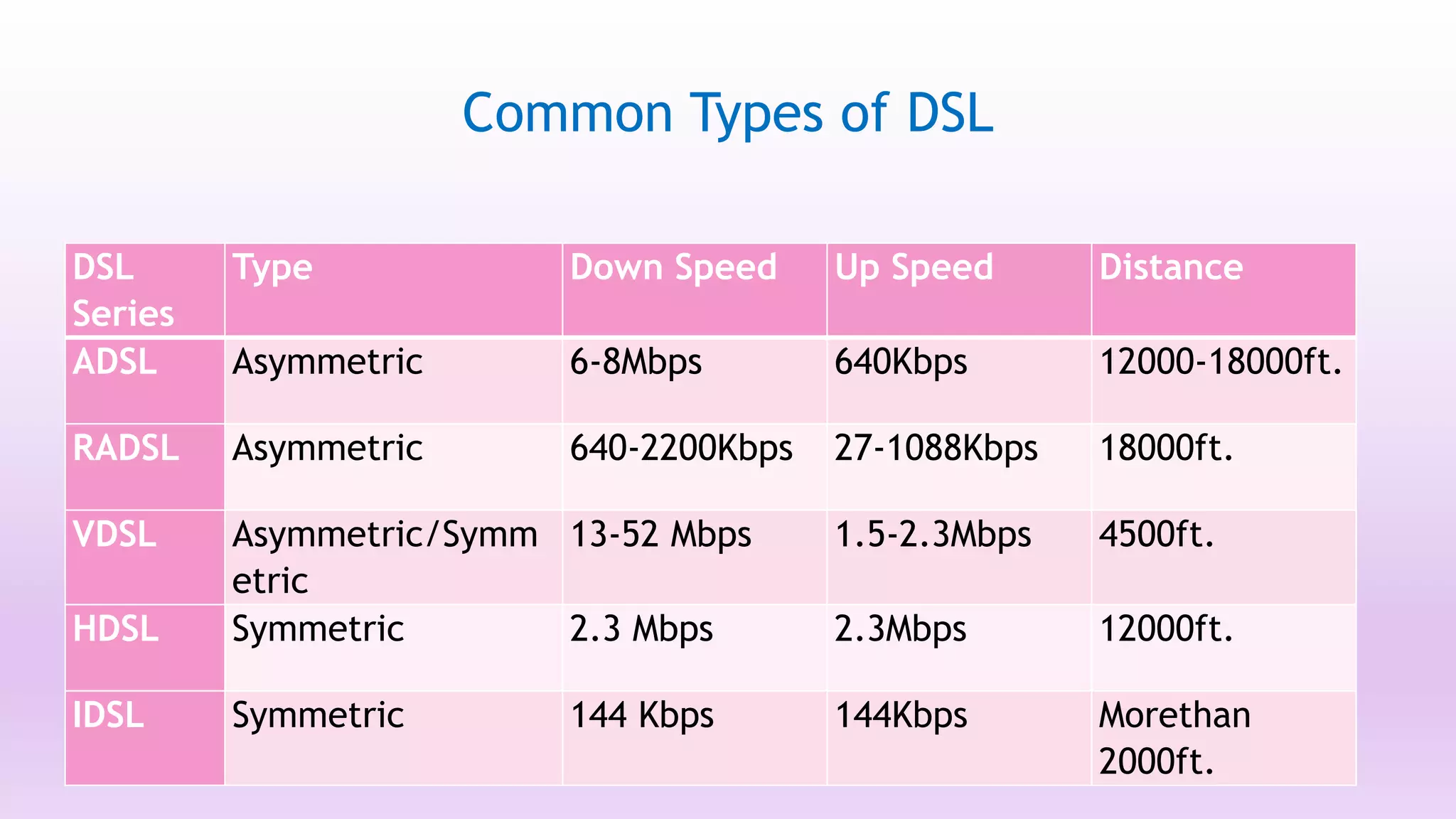
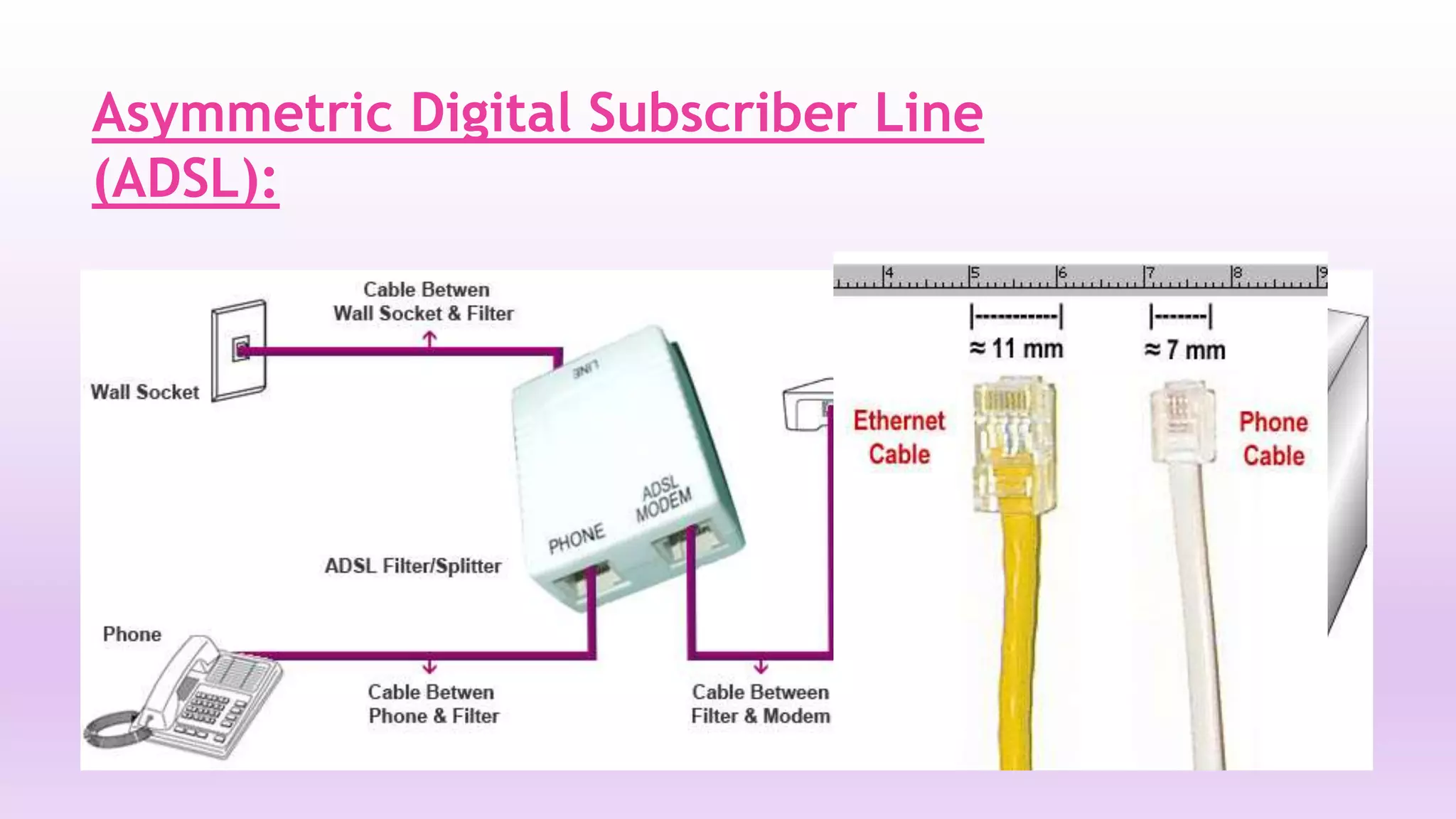
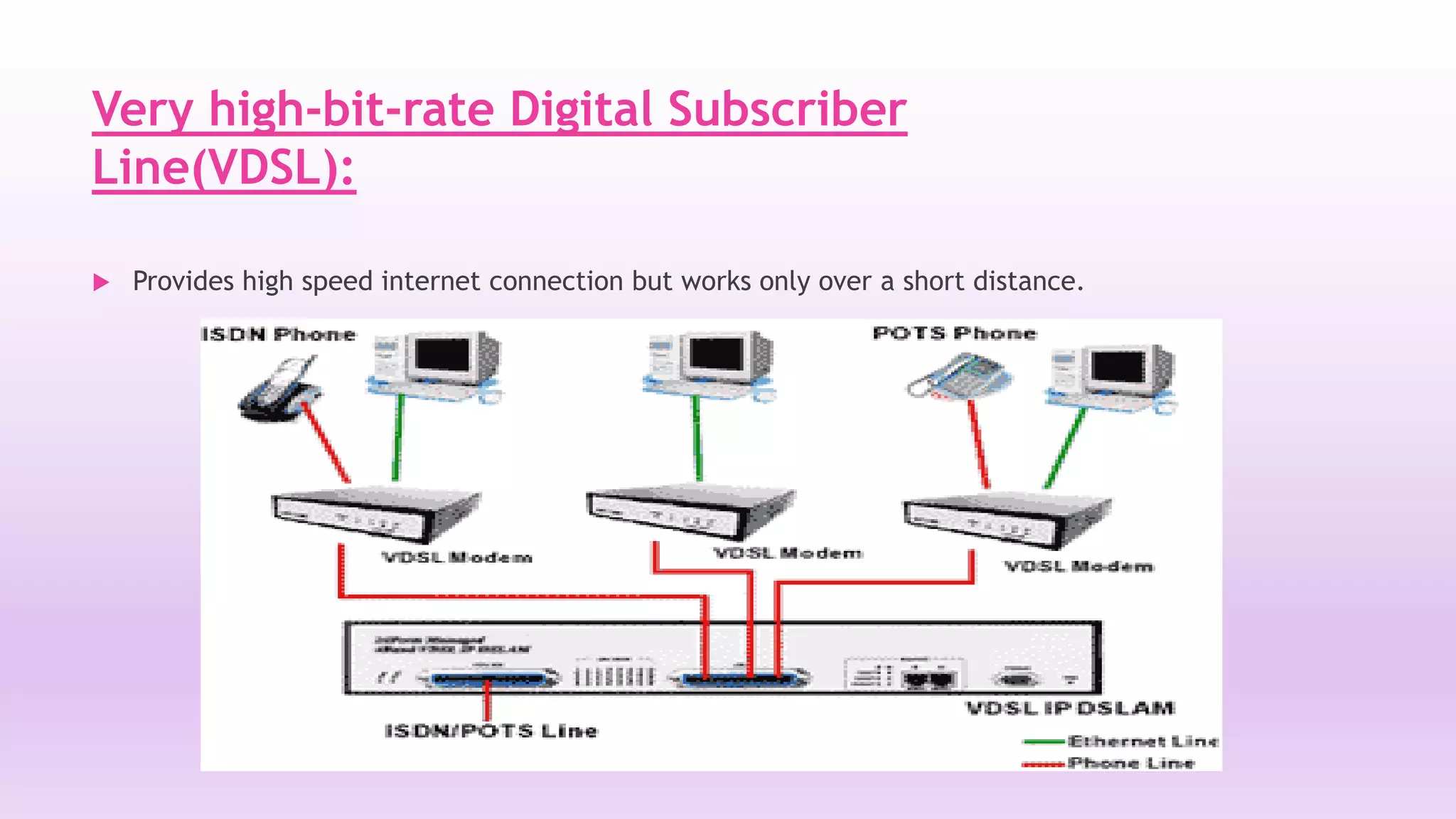
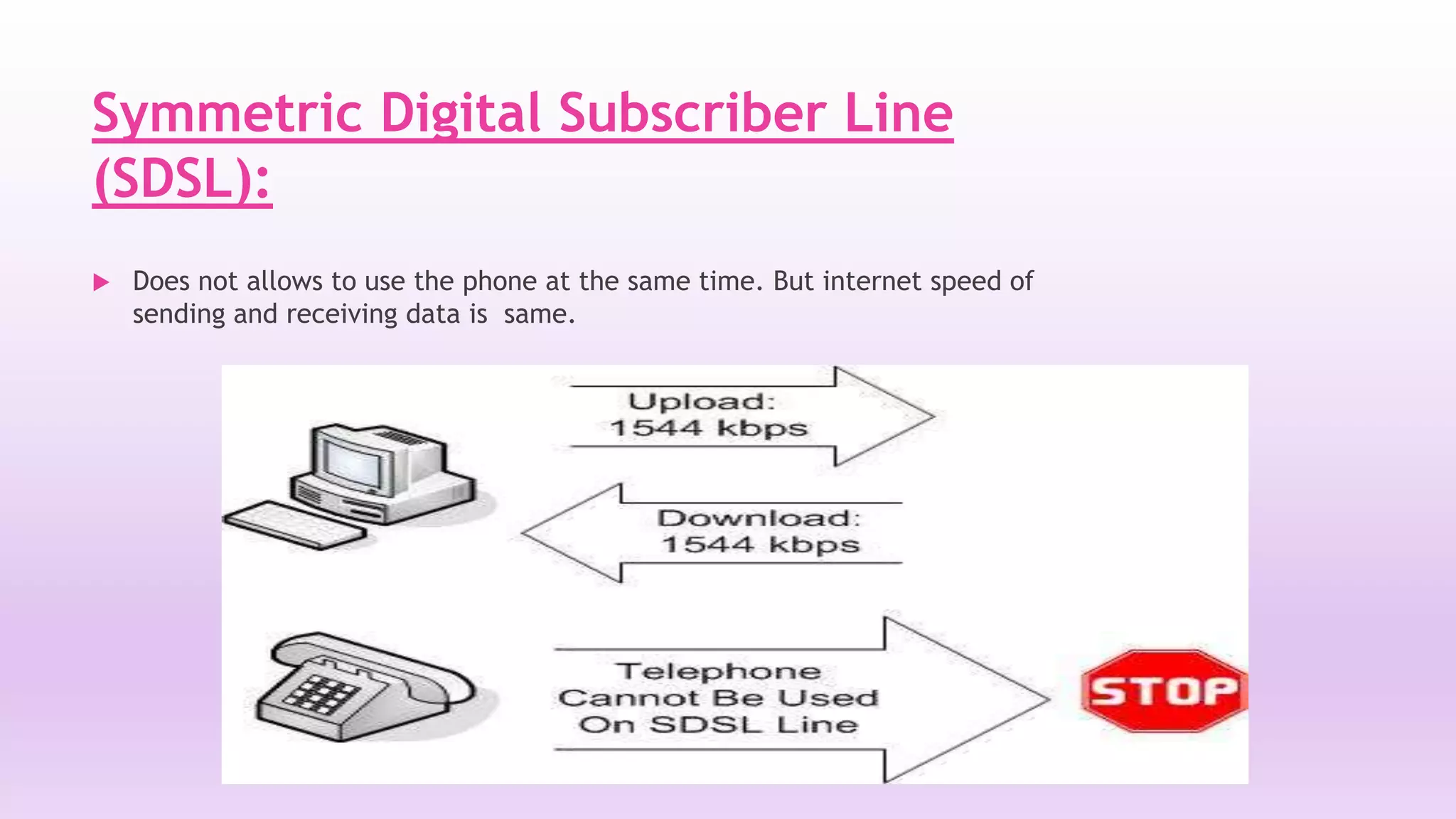
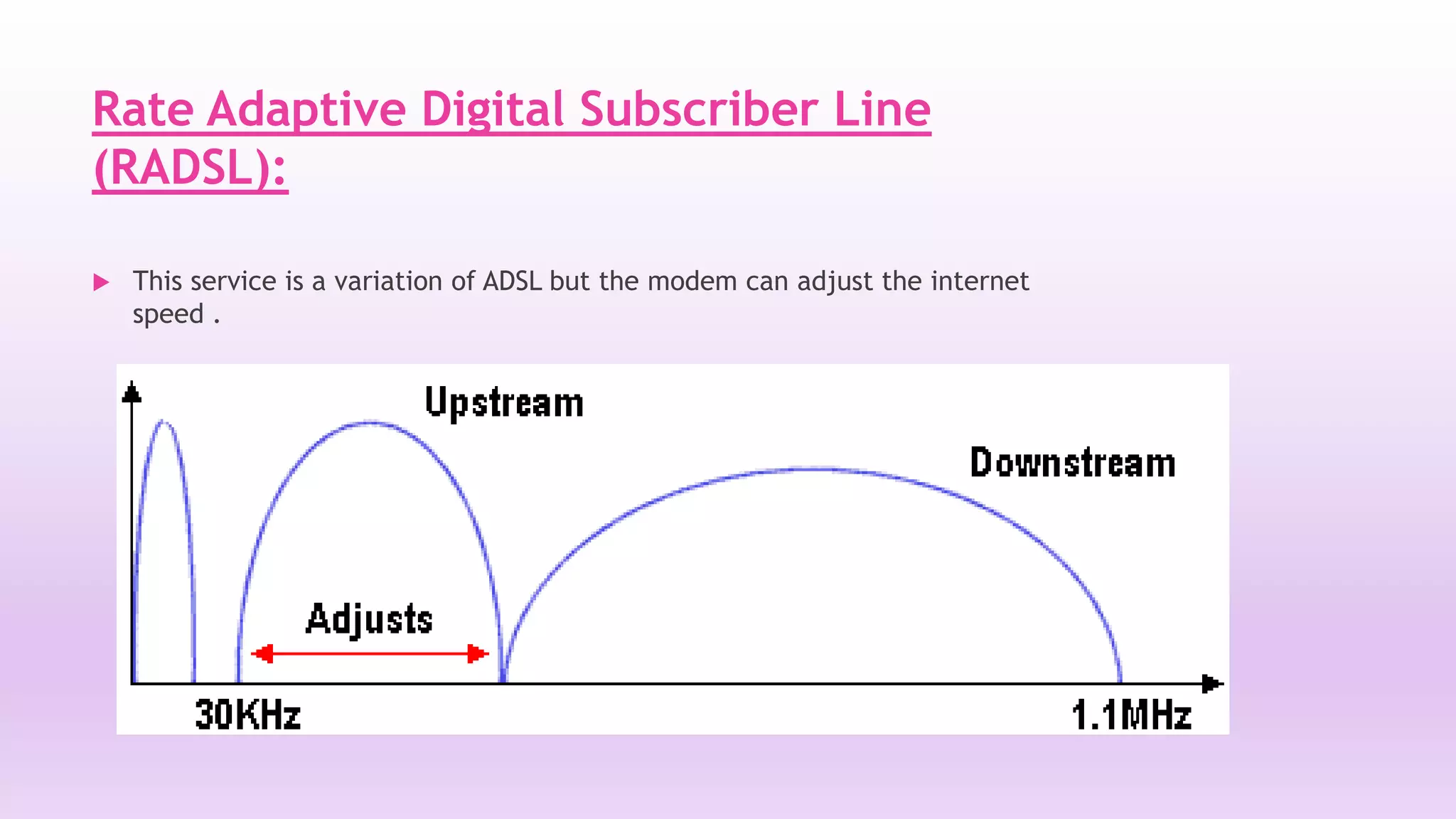
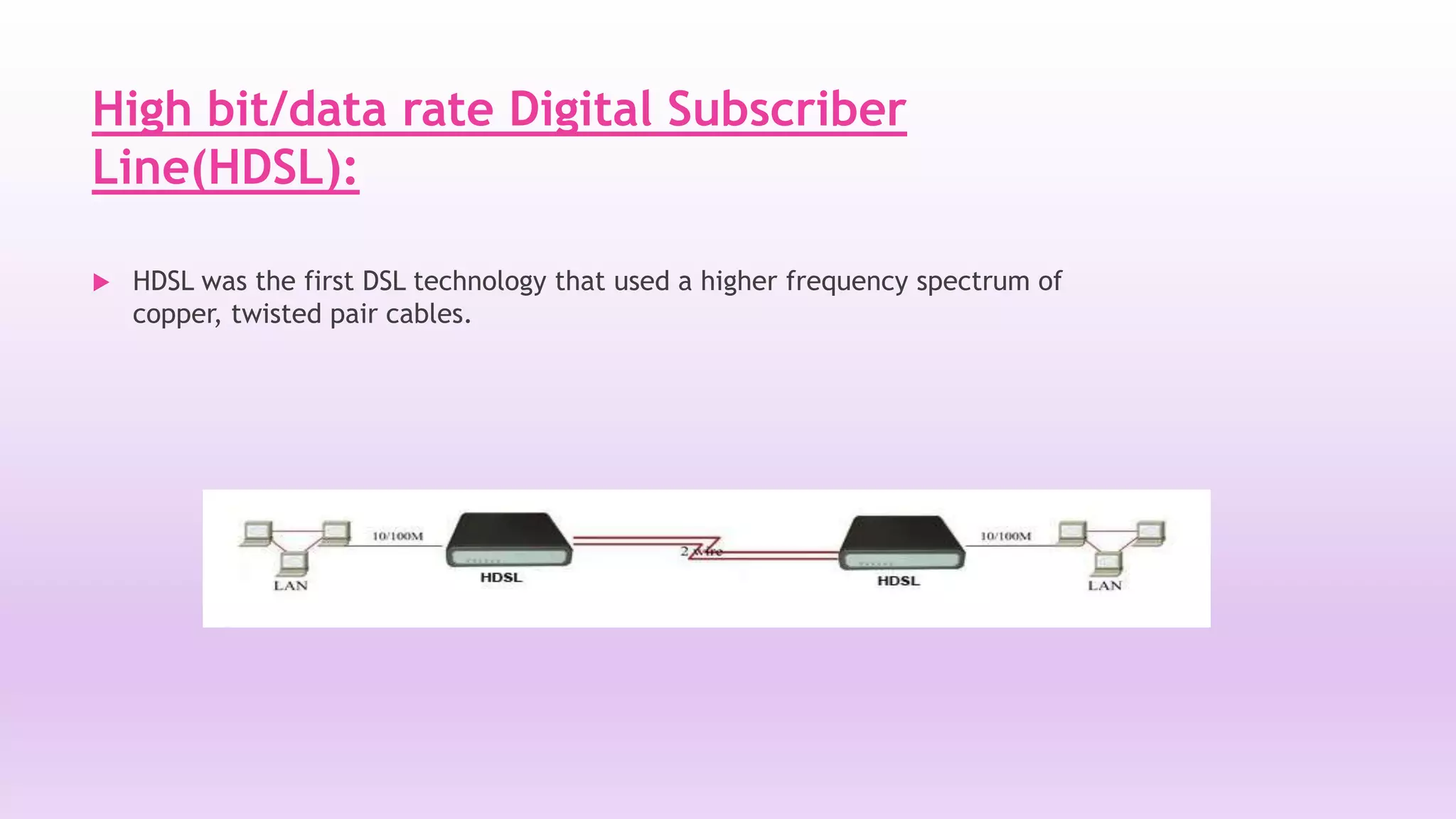
DSL is a technology that provides high-speed internet access over ordinary copper telephone lines. It works by using higher frequencies on the line that do not interfere with normal telephone calls. There are different types of DSL including ADSL, VDSL, and SDSL that offer different speeds and distance capabilities. DSL uses a modem at the user's location and a DSLAM at the telephone provider's central office to connect users to the internet at speeds much faster than dial-up.