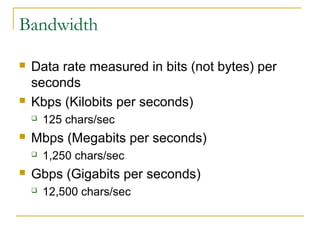
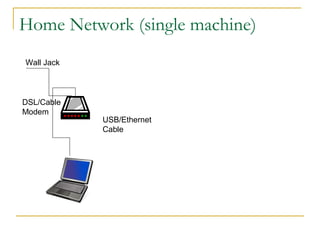
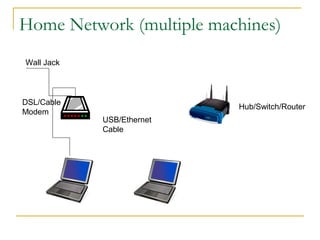
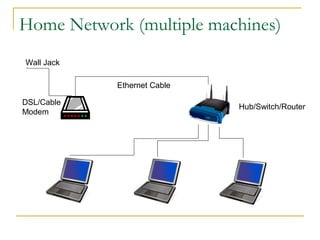
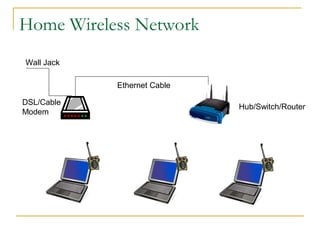
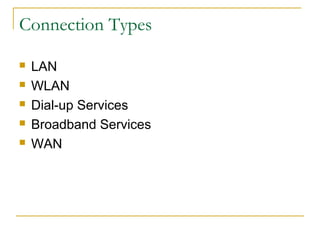
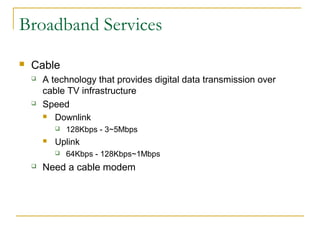
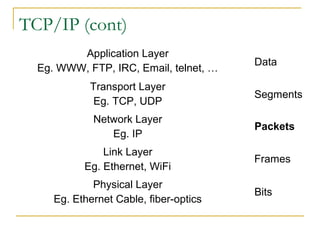
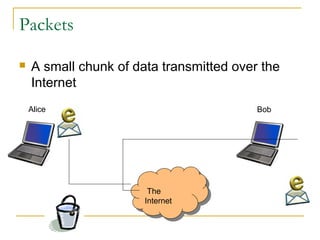
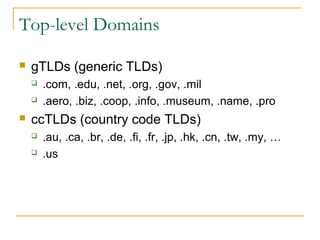
This document provides an overview of basic computer networks. It defines key network terminology like bandwidth, discusses how to connect devices to the internet using modems or network interface cards, and describes different types of home and wireless networks. It also explains various connection types like LANs, WANs, dial-up, broadband, and VPN. The document outlines network devices like hubs, switches and routers. It defines domains, IP addresses, and DNS. Finally, it discusses network policies and provides references for further reading.