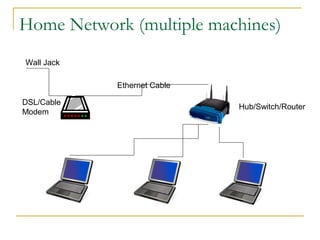
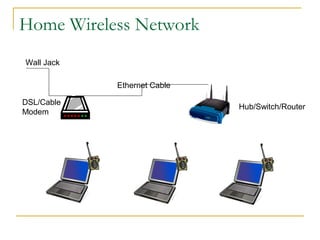
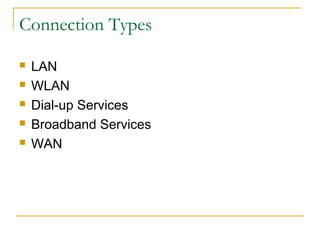
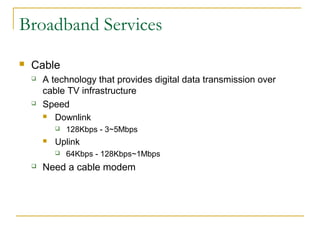
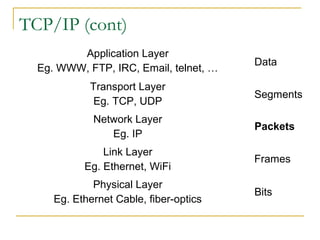
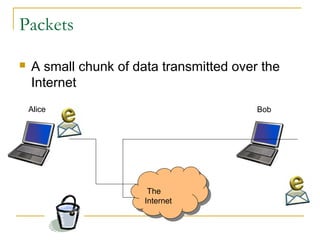
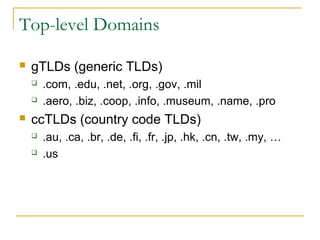
This document provides an overview of basic computer networks and connectivity. It defines key terms like bandwidth, bits per second, and connection types. It explains how to connect devices to a home network using Ethernet cables, WiFi, or broadband services. It also covers topics like IP addressing, domain name registration, and policies governing internet use. The document serves as a high-level introduction to computer networking concepts.