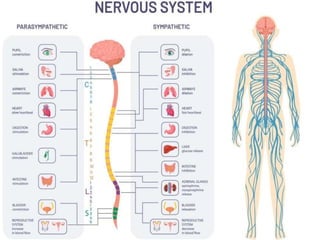
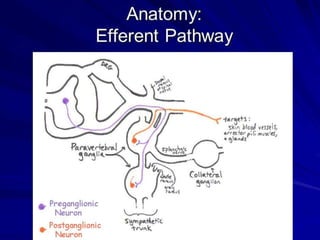
The sympathetic nervous system is formed from preganglionic fibers exiting the spinal cord from T1-L2 levels. These fibers synapse with postganglionic fibers in sympathetic ganglia near the spinal cord or travel to other ganglia nearer the organ. Sympathectomy increases blood flow by vasodilating arterioles, and is used to treat primary hyperhydrosis, Raynaud's syndrome, and other conditions. It can be performed chemically via percutaneous injection of alcohol/phenol or surgically via open, thoracoscopic, or laparoscopic approaches. Complications may include compensatory hyperhydrosis, gustatory sweating, or Horner's syndrome.

















![Contraindications
• Intermittent claudication's
• ABPI >0.3
• Diabetics [ autonomic neuropathy]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sympathectomyagp-wpsoffice-231102115210-89c1ed2b/85/SYMPATHECTOMY-pptx-20-320.jpg)








