Embed presentation
Downloaded 72 times

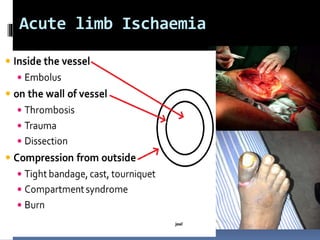





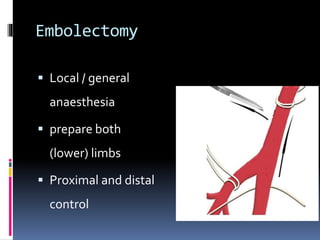



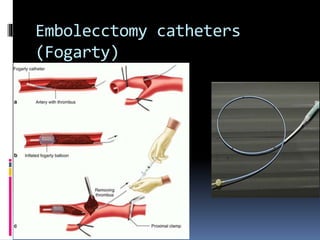
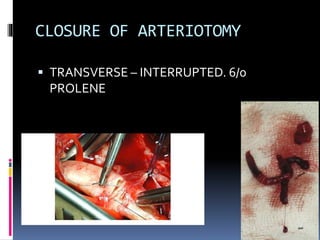




This document discusses the management of acute limb ischemia through thrombectomy or embolectomy. It provides details on: 1) Recognizing acute limb ischemia and starting heparin treatment while relieving pain and checking limb viability. 2) Performing an embolectomy by making a small arteriotomy above the bifurcation to insert a Fogarty catheter and remove the embolus. 3) Closing the arteriotomy with interrupted sutures and continuing heparin and warfarin treatment while monitoring for complications.















