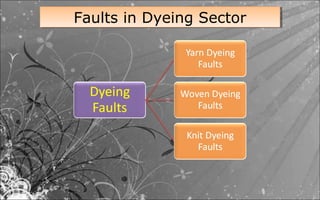
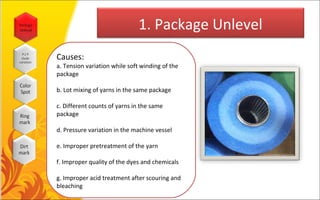
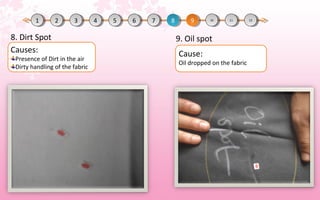
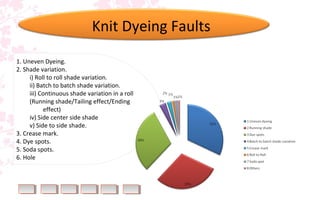
This document discusses common faults that occur in yarn dyeing and woven fabric dyeing processes. For yarn dyeing, the main faults discussed are package unlevelness, package to package shade variation, color spots, ring marks, and dirt marks. The causes of each fault are explained. For woven fabric dyeing, faults like white spots, color spots, crease marks, long stripes, uneven shade, running shade, and listing effects are discussed along with their typical causes. The document also mentions knit dyeing faults such as uneven dyeing, shade variation, crease marks, dye spots, soda spots, and holes. Finally, the document provides links to the author's Facebook pages on textile manufacturing technologies and