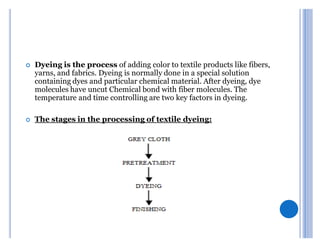
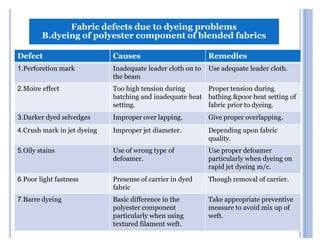
This document presents a presentation on dyeing problems and remedies given by five students. It begins by introducing the basic process of dyeing textiles and some key factors. It then shows that the most common dyeing problems occur during pretreatment (21%), dyeing and printing (23%), finishing (11%), biological and machine issues (24%), and other diverse problems (22%). The document provides details on common pretreatment, dyeing, and yarn defects and their potential causes. It lists remedies for many of the problems discussed. Finally, it provides five tips for remedying dyeing problems, emphasizing getting processes right the first time through process control and understanding causes before finding solutions.