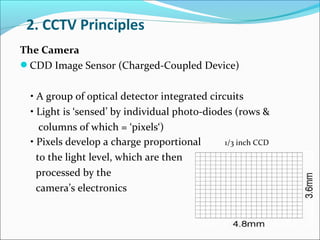
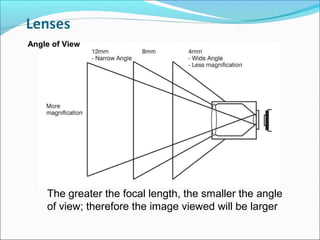
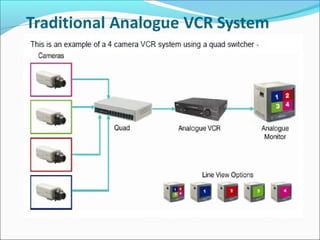
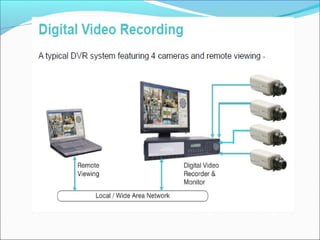
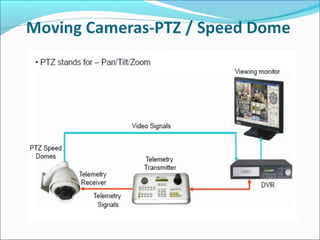
The document discusses closed-circuit television (CCTV) systems, including their purpose for monitoring and deterring crime, as well as explaining the basic components and technology of both analogue and digital systems. Key characteristics include types of cameras, the significance of image sensors, and the advantages of digital video recorders (DVRs) over older analogue systems. Additionally, it highlights considerations for recording duration, camera features, and the importance of data protection regulations.