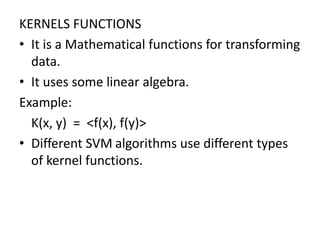
Support vector machines (SVMs) are a supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression analysis. SVMs find the optimal boundary, known as a hyperplane, that separates classes of data. This hyperplane maximizes the margin between the two classes. Extensions to the basic SVM model include soft margin classification to allow some misclassified points, methods for multi-class classification like one-vs-one and one-vs-all, and the use of kernel functions to handle non-linear decision boundaries. Real-world applications of SVMs include face detection, text categorization, image classification, and bioinformatics.