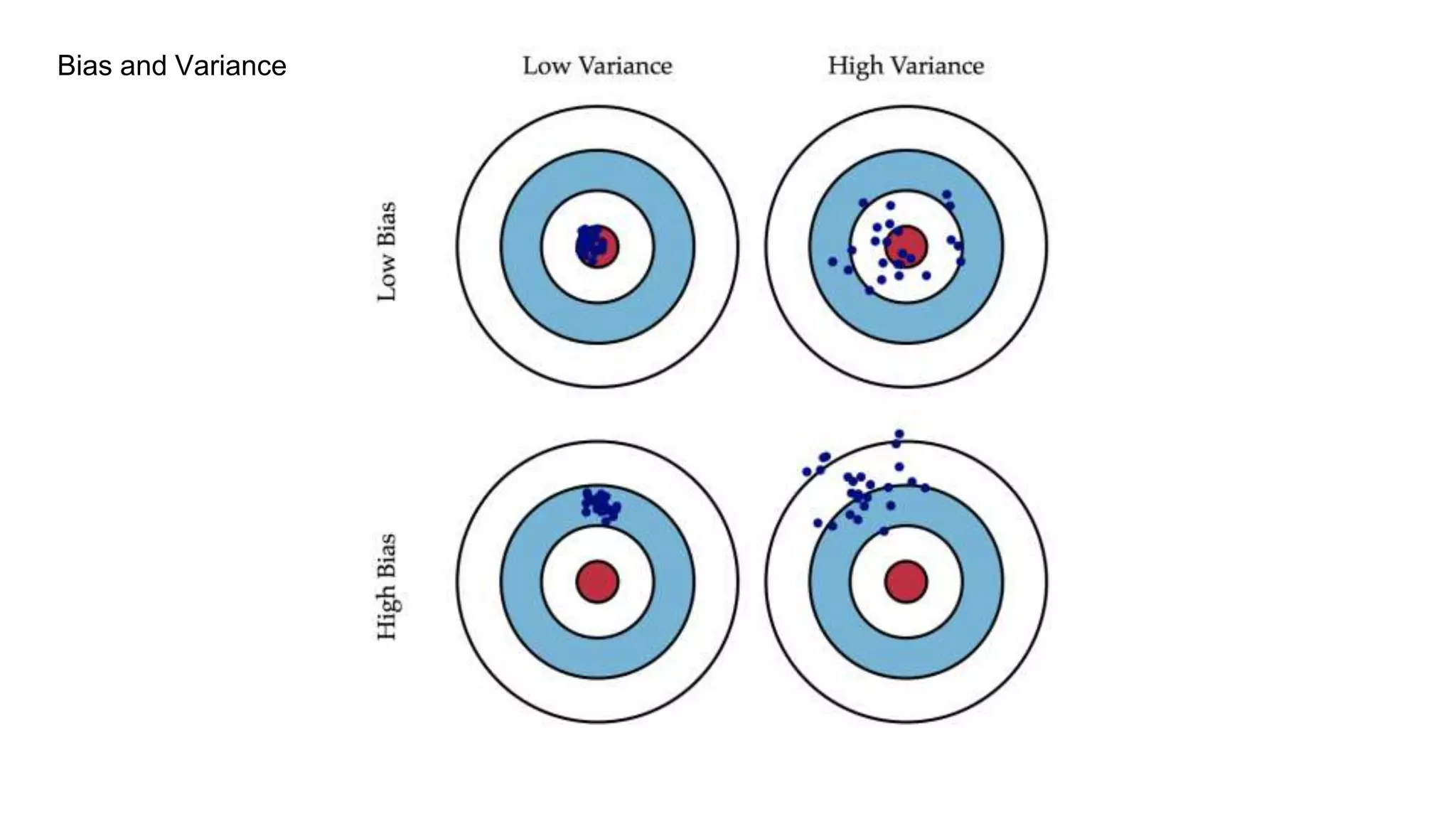
- Linear regression estimates the relationship between continuous dependent and independent variables using a best fit line. Multiple linear regression uses multiple independent variables while simple linear regression uses one.
- Logistic regression applies a sigmoid function to linear regression when the dependent variable is binary. It handles non-linear relationships between variables.
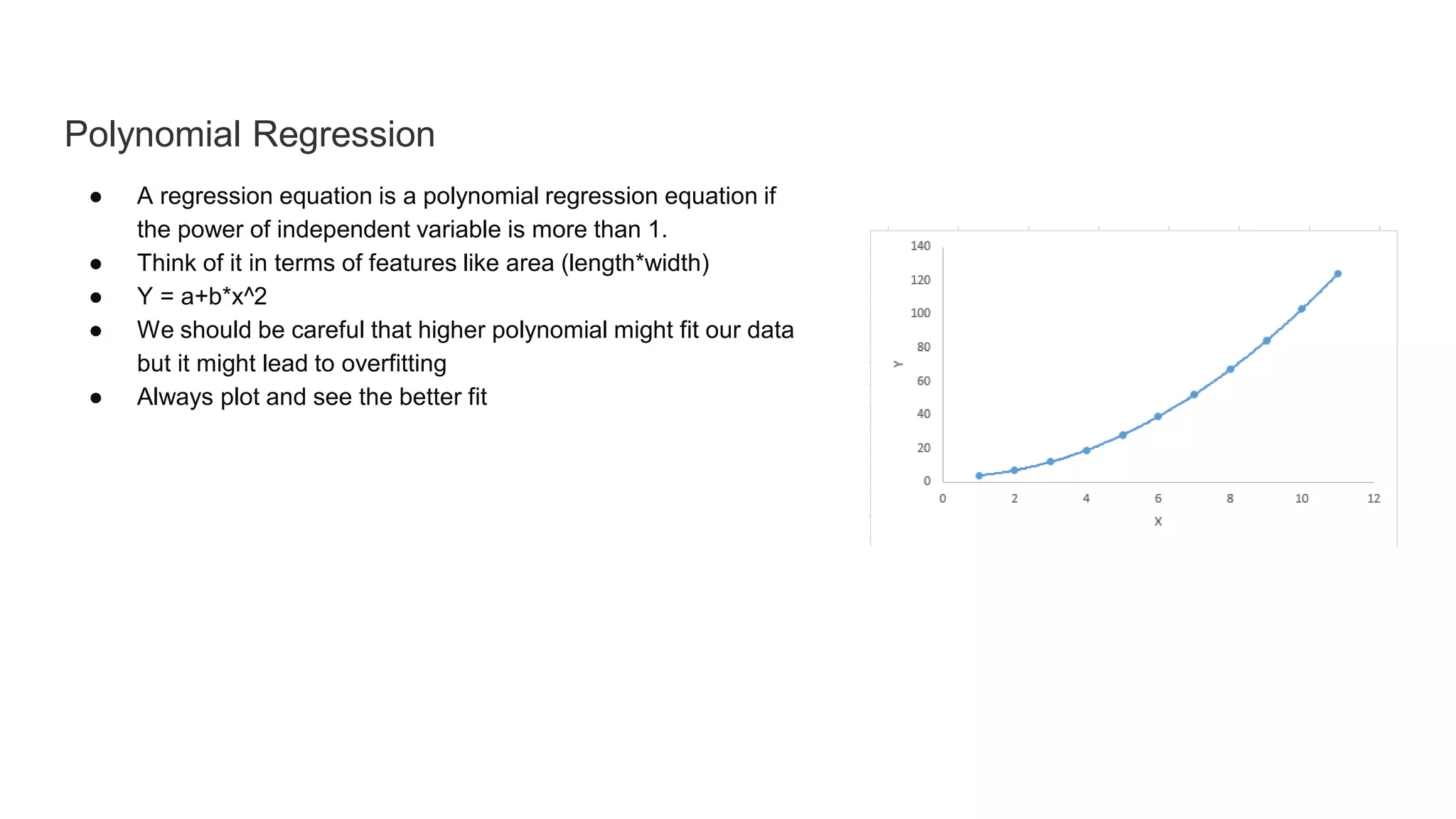
- Polynomial regression uses higher powers of independent variables which may lead to overfitting so model fit must be checked.
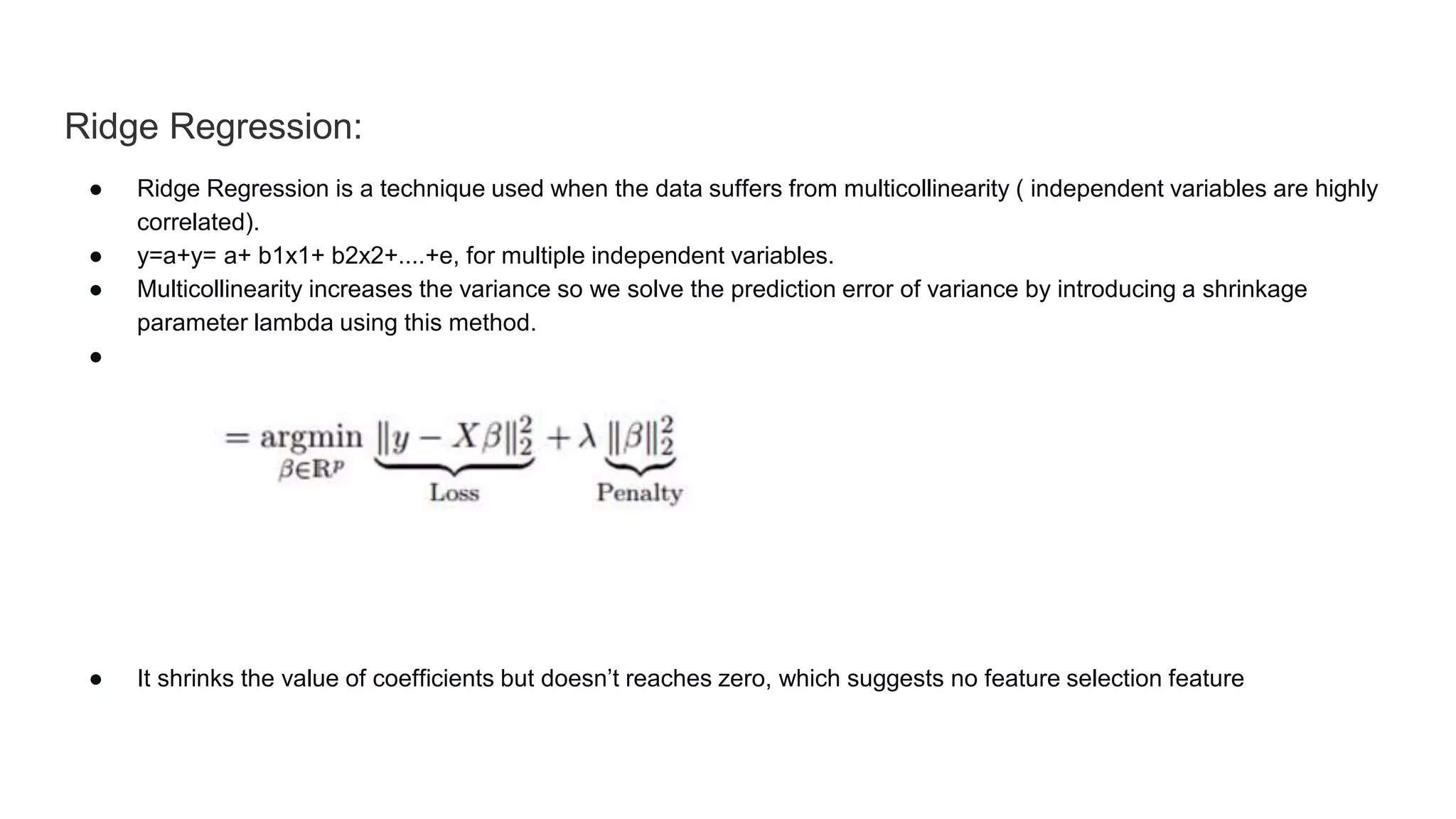
- Stepwise regression automatically selects independent variables using forward selection or backward elimination. Ridge and lasso regression address multicollinearity through regularization. Elastic net is a hybrid of ridge and lasso.
- Classification algorithms include k-nearest neighbors, decision trees, support vector machines, and naive Bayes which use probability



![Linear Regression:
● In this technique, the dependent variable is continuous, independent
variables can be continuous or discrete, and nature of regression line is
linear.
● Linear Regression establishes a relationship between dependent variable
(Y) and one or more independent variables (X) using a best fit straight
line (also known as regression line).
● Equation ( Y = W*X+b) [Y=dependent X=independent, b = bias]
● The difference between simple linear regression and multiple linear
regression is that, multiple linear regression has (>1) independent variables,
whereas simple linear regression has only 1 independent variable.
● We obtain the best fit by least squares method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aisaturdayspresentation-180227090231/75/Ai-saturdays-presentation-5-2048.jpg)