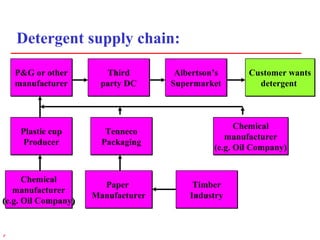
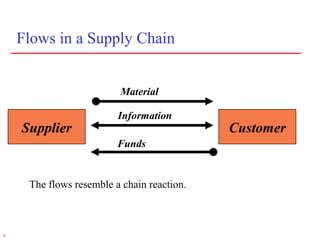
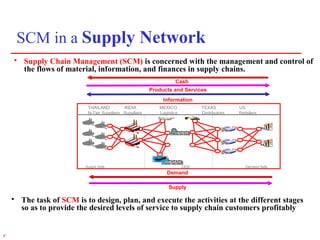
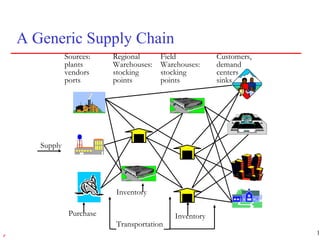
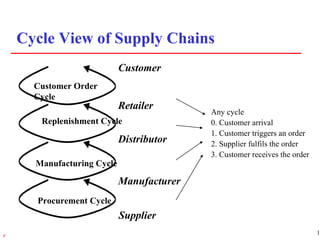
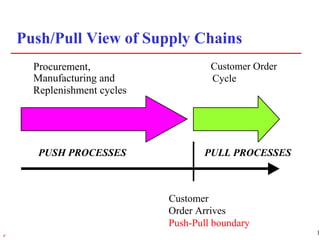
1) Supply chain management involves managing the flow of materials, information, and finances between suppliers and customers. It aims to meet demand profitably through coordination across companies.
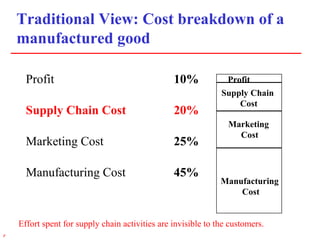
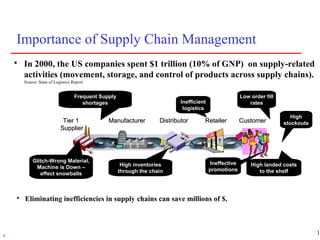
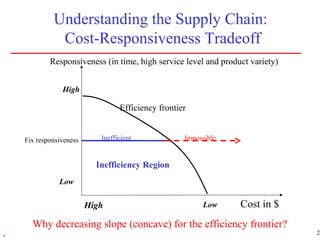
2) Traditional views of supply chains focused on transportation, inventory, and administrative costs, which combined accounted for over 10% of GDP in the 1990s. Effective supply chain strategies can save billions by reducing these costs.
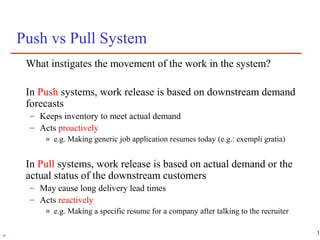
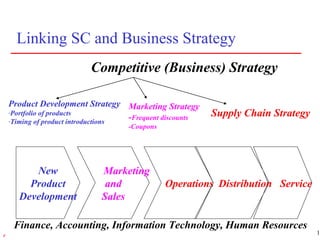
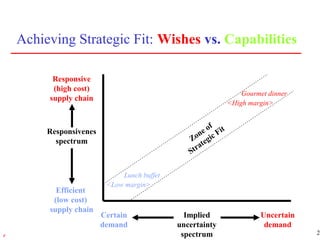
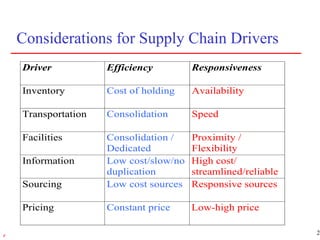
3) Supply chain management strategies must fit a company's overall business strategy regarding product development, marketing, and operations to be effective. Strategic fit is achieved by understanding customer needs and matching supply chain capabilities accordingly.