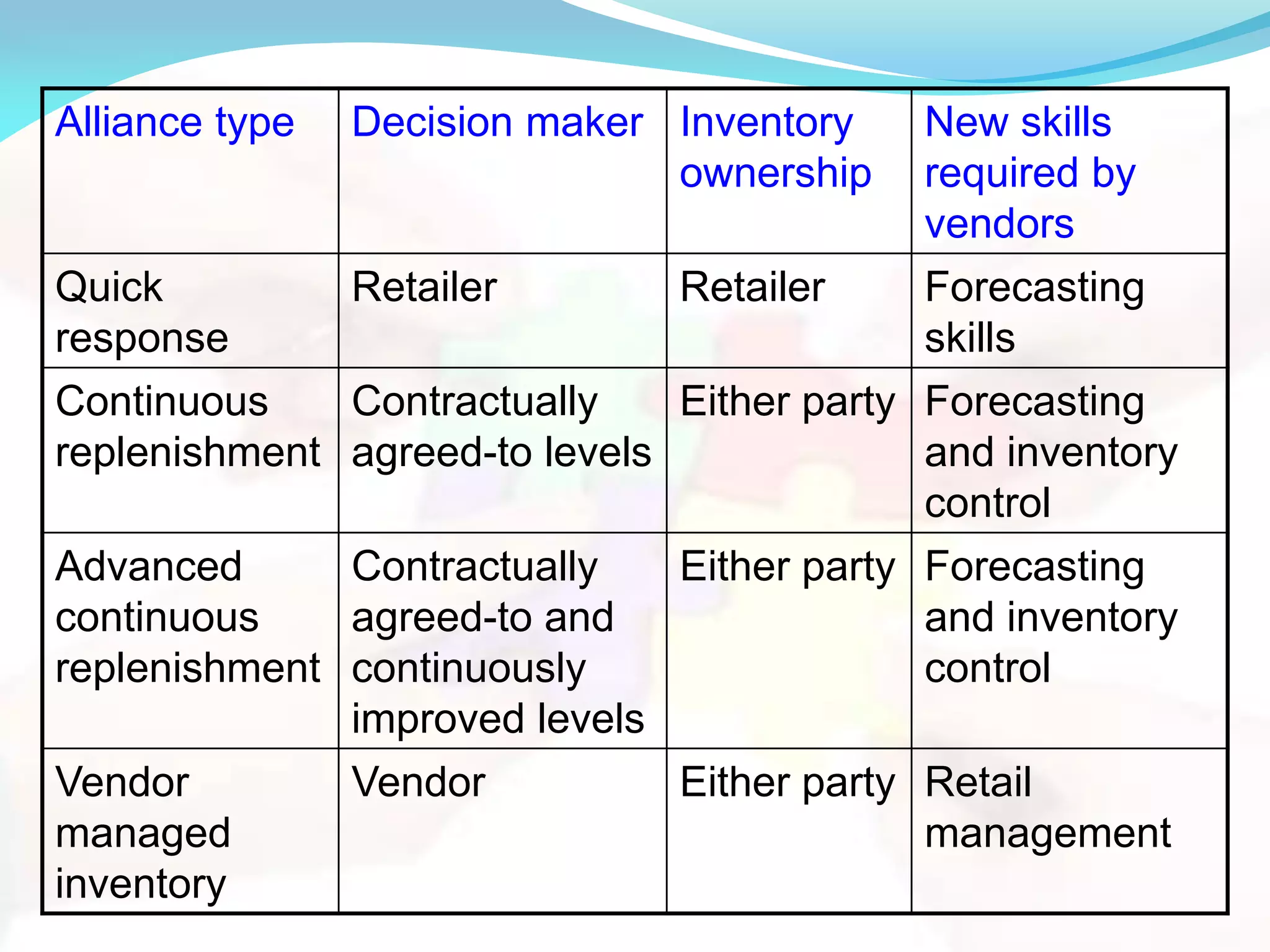
Supply chain management involves planning and managing all activities related to sourcing, procurement, conversion, and logistics management. Strategic alliances like third-party logistics and retailer-supplier partnerships aim to provide benefits greater than individual company efforts. Retailer-supplier partnerships range from quick response strategies to vendor-managed inventory systems, with different inventory ownership and skills required of vendors. Maruti worked to improve operational efficiency through strategic partnerships with top vendors that accounted for 34% of purchases.