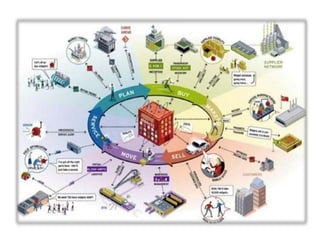
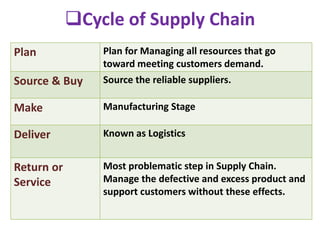
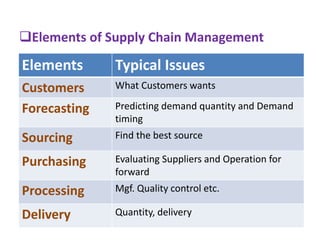
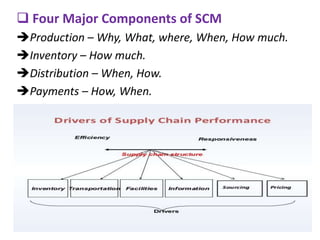
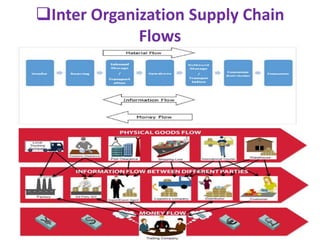
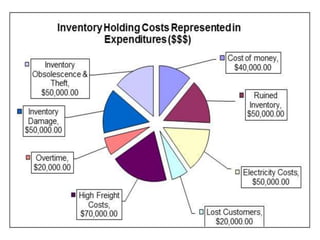
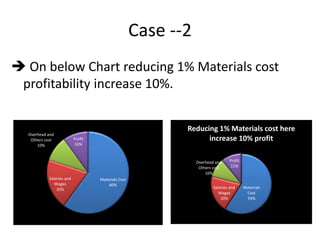
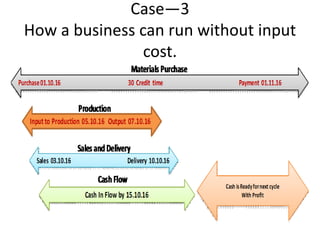
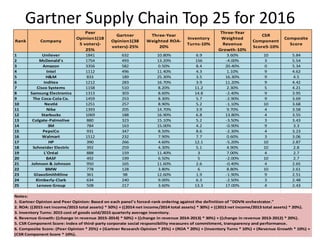
This document provides an overview of supply chain management. It defines SCM and its key concepts, including planning, sourcing, manufacturing, delivery, and returns. The goals of SCM are to create an efficient low-cost network to get products from concept to market while satisfying customers. SCM encompasses various activities like forecasting, purchasing, processing, delivery and more. The document also discusses SCM in different organization sizes and how it can increase profitability through cost reductions. It profiles the 2016 Gartner Supply Chain Top 25 companies and discusses career opportunities and courses in SCM.