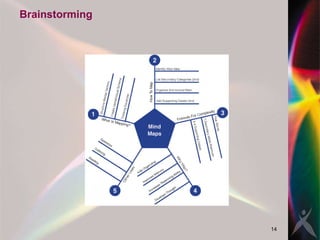
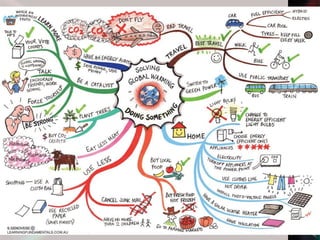
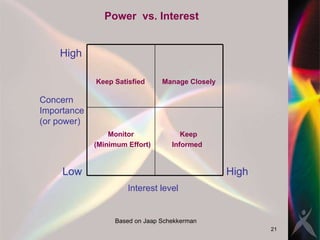
The document discusses key concepts in project management including scope management, risk management, change management, stakeholder management, and project review. It outlines the project life cycle and importance of project management. Effective project managers are visionaries who anticipate problems, manage stakeholders, communicate well, and resolve conflicts.