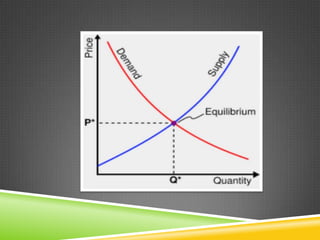
Supply and demand determine the price of goods and services in a market. Supply represents the quantity that producers are willing to sell at a given price, and is impacted by factors like production costs and the prices of related goods. Demand represents the quantity that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price, and can change due to consumer tastes, income levels, and population changes. The equilibrium price is reached when the supply and demand curves intersect, where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.