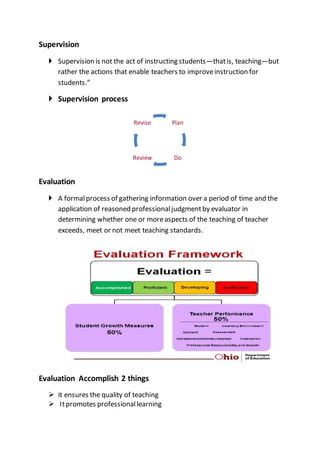
Supervision involves enabling teachers to improve instruction for students and is not the same as teaching. The supervision process includes evaluation, which is a formal process of gathering information over time to determine if a teacher meets teaching standards. Evaluation aims to ensure quality teaching and promote professional learning. Supervision includes goal setting, using evaluation tools and instruments, different supervisory styles like directive and collaborative, and providing focused assistance. A key part of supervision is the circle of supervision which involves pre-observation meetings, observations, and post-observation discussions between the teacher and evaluator.

![Circle of supervision
Pre-observation ; A meeting between the teacher and evaluator to
determine the context of observation the purposeof the data collection
observation; the evaluator will conduct the observation,typically in the
teacher classroom. A written summary is prepared and shared at the
post-observation.
Post-observation; a meeting between the teacher and the evaluator to
collaboratively discuss theobservation.Descriptivefeedback provided to
the teacher
Differentiatedapproach3 supervisory choice for teacher
IntensiveDevelopment; a systematic, sequential and cycle supervisory
process that involves the interaction between supervisor and teacher
Cooperative development; a process of fostering teacher growth
through a systematic collaboration with the peers.
Self-directive development; the individual teacher works independently
on a programof a professionalgrowth
Staff development is an activity or process intended to improve skill,
attitude ,understanding or performancein presentor future roles [
Fullen 1990]
The only way we are going to get from wherewe are wherewe want to
be is through staff development
Quality supervision requires
Clear and specific worker objectives.
Awareness of worker’s needs.
Willingness to facilitate the step-by-step progression of workers.
A willingness to accept the diversity of workers including differences in
viewing the role of working, differences in motivation, differences in
interest and differences in cultural perspectives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/supervision-180921115957/85/Supervision-3-320.jpg)