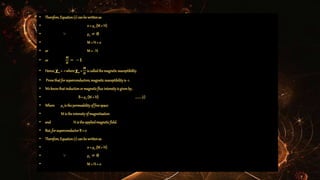
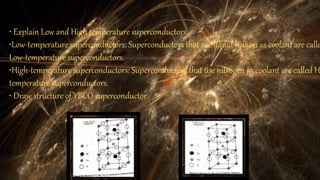
This document discusses superconductors and superconductivity. It begins by defining a superconductor as a material that loses all electrical resistance below a critical temperature. Two types of superconductors are described - Type I, which exhibit the Meissner effect, and Type II, which do not. Low and high temperature superconductors are distinguished based on the coolant used. Key properties of superconductors include zero resistance, effects of impurities and isotopes on critical temperature, critical magnetic and current fields, and the Meissner effect. Applications of superconductors include power transmission, generators, ore separation, and computing.