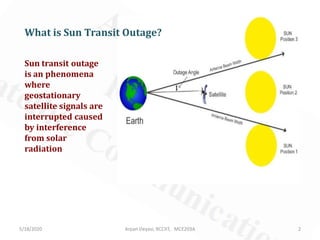
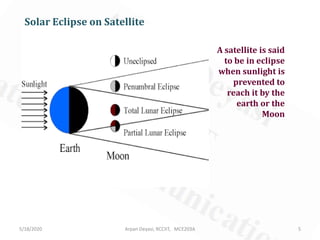
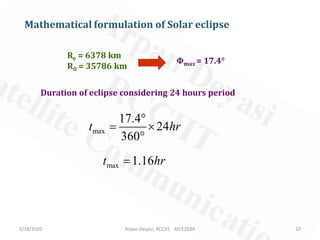
Sun transit outage occurs for geostationary satellites around the equinoxes for up to 10 minutes, interrupting signals due to interference from solar radiation. A satellite experiences a solar eclipse when the Earth or Moon prevents sunlight from reaching it. For geostationary satellites, eclipses due to Earth occur in the 23 days before and after equinoxes. To avoid eclipses impacting operations, satellites should be positioned west of Earth stations.