The document summarizes research on synthesizing macrocyclic chelating agents for removing and concentrating perchlorate. It discusses:
1) Background on perchlorate contamination issues and calixarenes as potential extraction reagents.
2) The objectives to synthesize and characterize calix[4]arene-based polymeric materials and apply them to remove perchlorate from water.
3) Experimental methods including synthesis, characterization techniques, and column studies to test perchlorate removal efficiency.






![7
It acts as a competitive inhibitor of iodide
uptake by the NIS [sodium (Na+) iodide (I-)
symporter (S)] in humans.
Perchlorate can disrupt the production of thyroid
hormones and thus disrupt metabolism.
EPA considers the inhibition of
iodide uptake as the critical effect.
Health Hazards](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-8-10presentation1-copy-230814184248-98fdd33b/85/6-8-10-Presentation1-Copy-ppt-7-320.jpg)






![14
Members
OH O
H
O
H
O
H
O
H
OH
OH
OH
t-but
t-but
t-but
t-but
t-but
t-but
t-but
t-but
OH
OH
OH
t-but
t-but
t-but
O
H
O
H
OH
t-but
t-but
t-but
OH
OH
t-but
t-but O
H
OH
t-but
t-but
p-tert-Butylcalix[4]arene p-tert-Butylcalix[6]arene p-tert-Butylcalix[8]arene](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-8-10presentation1-copy-230814184248-98fdd33b/85/6-8-10-Presentation1-Copy-ppt-14-320.jpg)
![15
Synthesis and characterization of
calix[4]arene based polymeric materials.
Application of synthesized calix[4]arene
based polymeric materials for the removal
and preconcentration of perchlorate from
water, soil and complex matrices.
Objectives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-8-10presentation1-copy-230814184248-98fdd33b/85/6-8-10-Presentation1-Copy-ppt-15-320.jpg)
![16
1. Synthesis and characterization of
Calix[4]arene based polymeric
materials.
2. Application of synthesized Calix[4]arene
based polymeric materials for the
removal of perchlorate.
Experimental](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-8-10presentation1-copy-230814184248-98fdd33b/85/6-8-10-Presentation1-Copy-ppt-16-320.jpg)




![21
FT-IR Spectra
OH
OH
O
H
OH
CH2
N
CH2
N
CH2
N
CH2
N
3
5,11,17,23-Tetrakis(N-piperidinomethyl)-25,26,27,28-tetrahydroxycalix[4]arene](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-8-10presentation1-copy-230814184248-98fdd33b/85/6-8-10-Presentation1-Copy-ppt-21-320.jpg)

















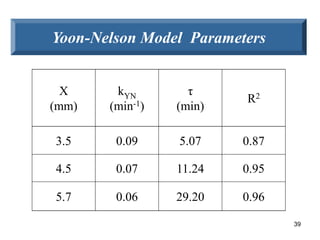
![40
Results achieved from present study reveals
that calix[4]arene based resin possess high
efficiency for the removal of perchlorate from
water.
The models used for mechanism of sorption best
fit the experimental data.
The study will find its applicability in the field of
material, analytical, and environmental sciences
Conclusion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-8-10presentation1-copy-230814184248-98fdd33b/85/6-8-10-Presentation1-Copy-ppt-40-320.jpg)
![41
Synthesis and characterization of calix[4]arene
based resins that are selective for perchlorate, in
this regard two schemes are under process of
synthesis in our synthetic labs.
The study will be extended to evaluate the
efficacy of the resins toward the real samples of
drinking water through preconcentration.
Future Plan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-8-10presentation1-copy-230814184248-98fdd33b/85/6-8-10-Presentation1-Copy-ppt-41-320.jpg)



