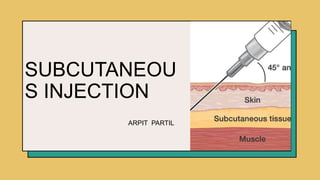
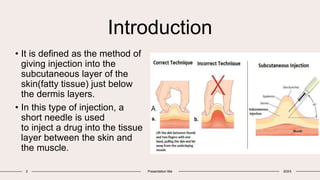
Subcutaneous injection involves injecting medication into the subcutaneous tissue just below the dermis. It uses a short needle to slowly diffuse drugs like insulin and vaccines over a sustained period. Subcutaneous injections are easier to perform than other types of injections and have less risk of pain or infection. They are commonly used to administer drugs that need to be continuously delivered at a low dose, for patients who cannot take oral medications, or for unconscious patients.