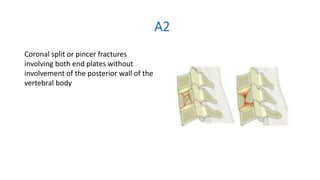
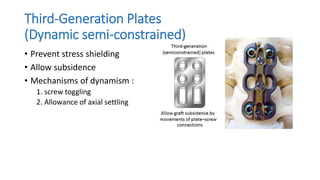
The document discusses the anatomy, biomechanics, classification systems, and management of injuries to the subaxial cervical spine (C3-C7). Key points include: the subaxial spine consists of 7 vertebrae joined by ligaments and disks; common injury mechanisms are flexion, extension, compression, and rotation; the Allen-Ferguson and AO classification systems describe injury patterns; clinical instability is defined as loss of ability to avoid neurologic injury or deformity; the SLIC score guides treatment; and initial management priorities are airway control, immobilization, and prevention of hypoxia.