This document discusses subaxial cervical spine injuries, including:
- Assessment and emergency treatment of cervical spine injuries following trauma.
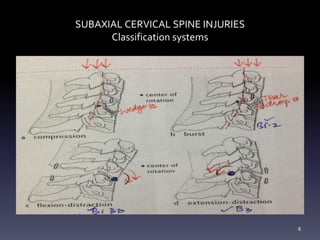
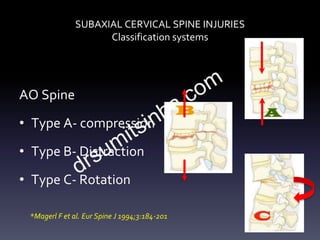
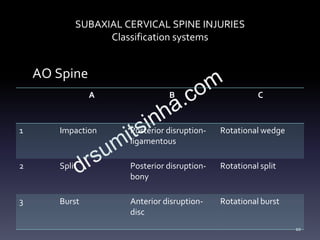
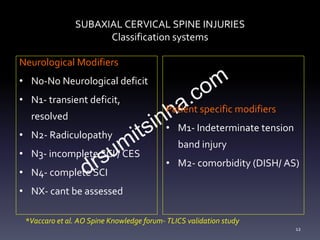
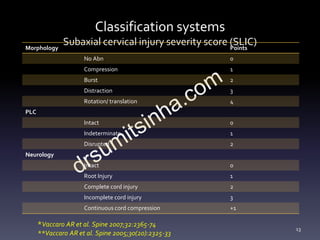
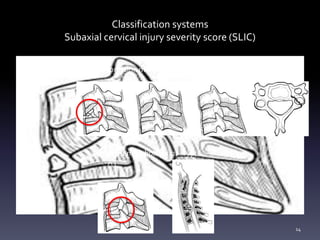
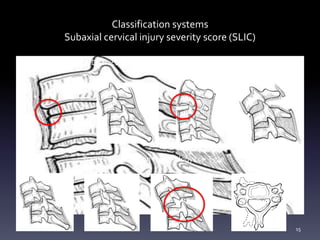
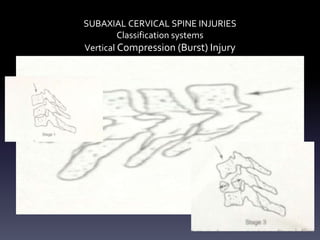
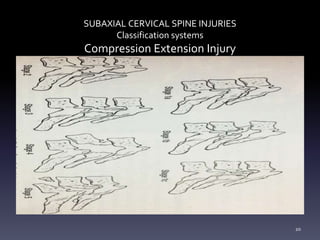
- Classification systems for cervical spine injuries including AO Spine, SLIC, and others which classify injuries based on morphology, neurological status, and stability.
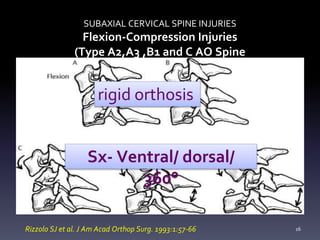
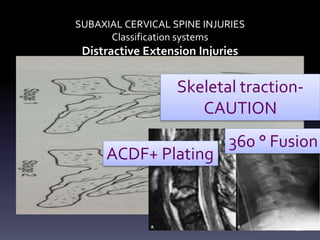
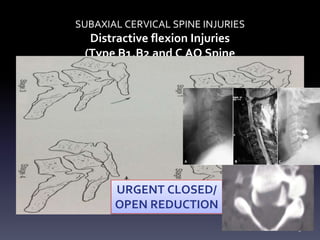
- Types of cervical injuries such as flexion-compression, burst fractures, distraction injuries, and recommendations for treatment and surgery based on classification.
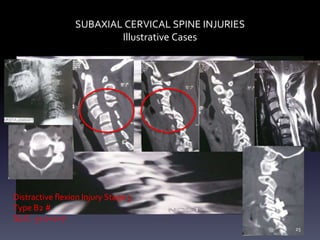
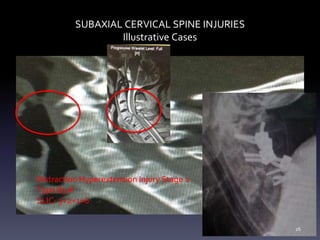
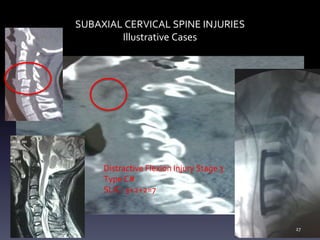
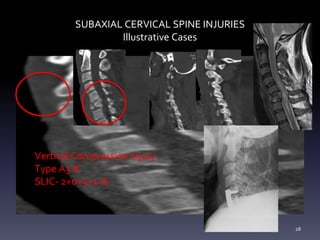
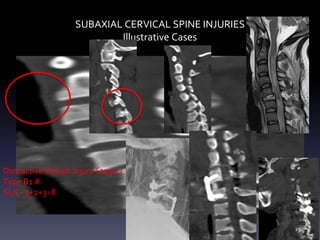
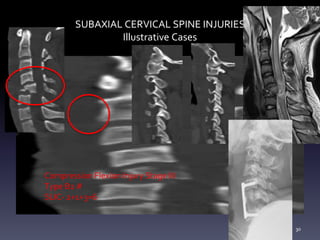
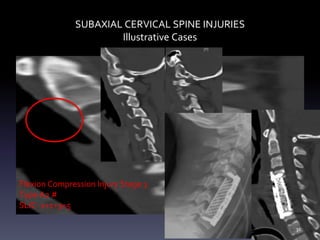
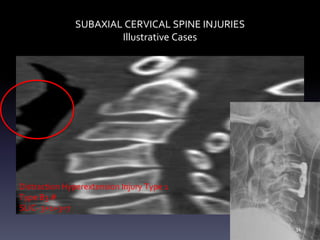
- Illustrative case examples of different cervical injury types classified using AO Spine and SLIC systems along with their treatments.
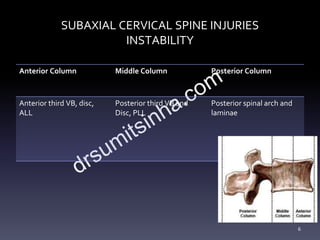
- Key points about immobilizing the cervical spine, rational use of imaging, importance of stability especially the posterior column, and indications for early surgery.