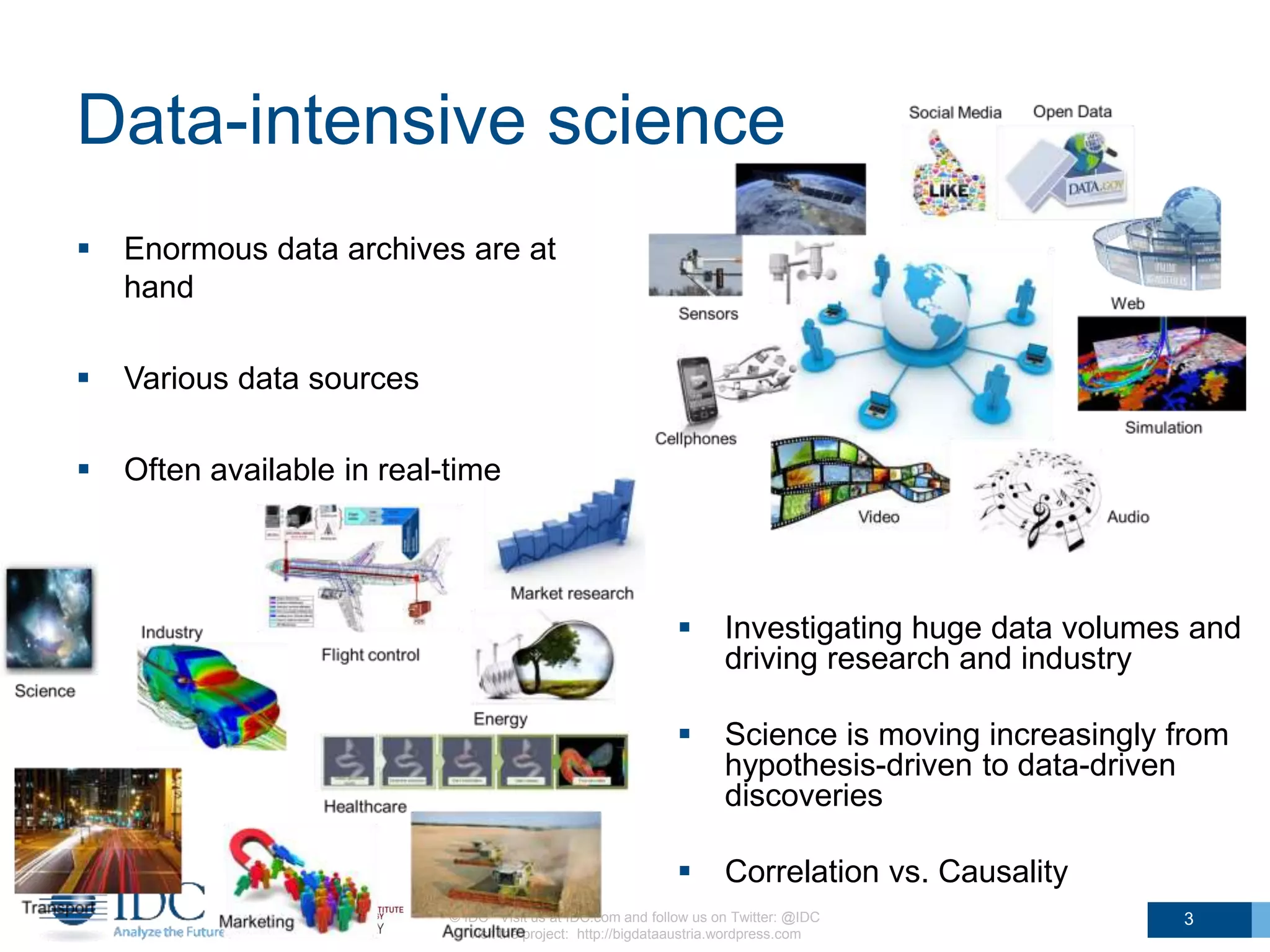
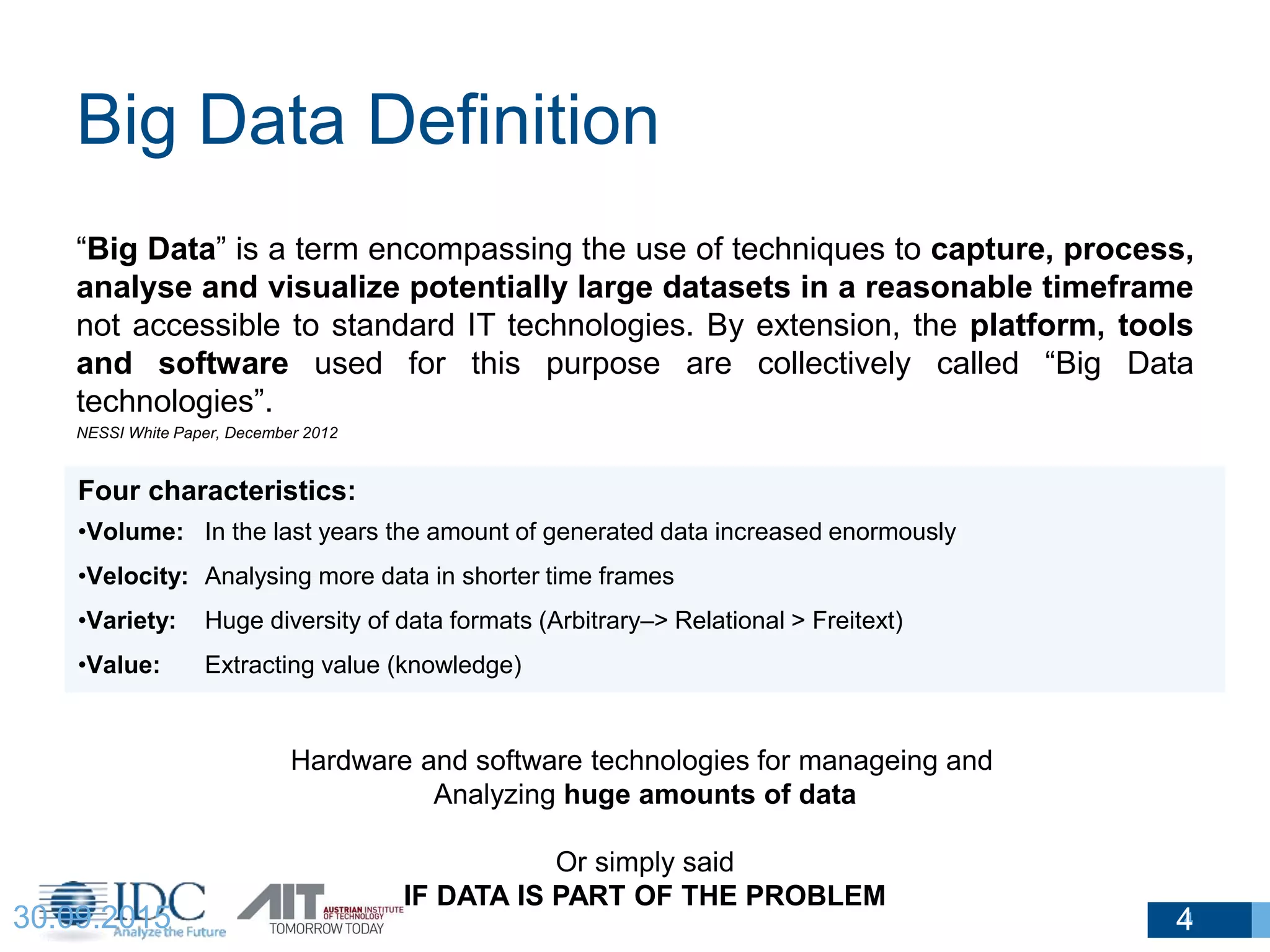
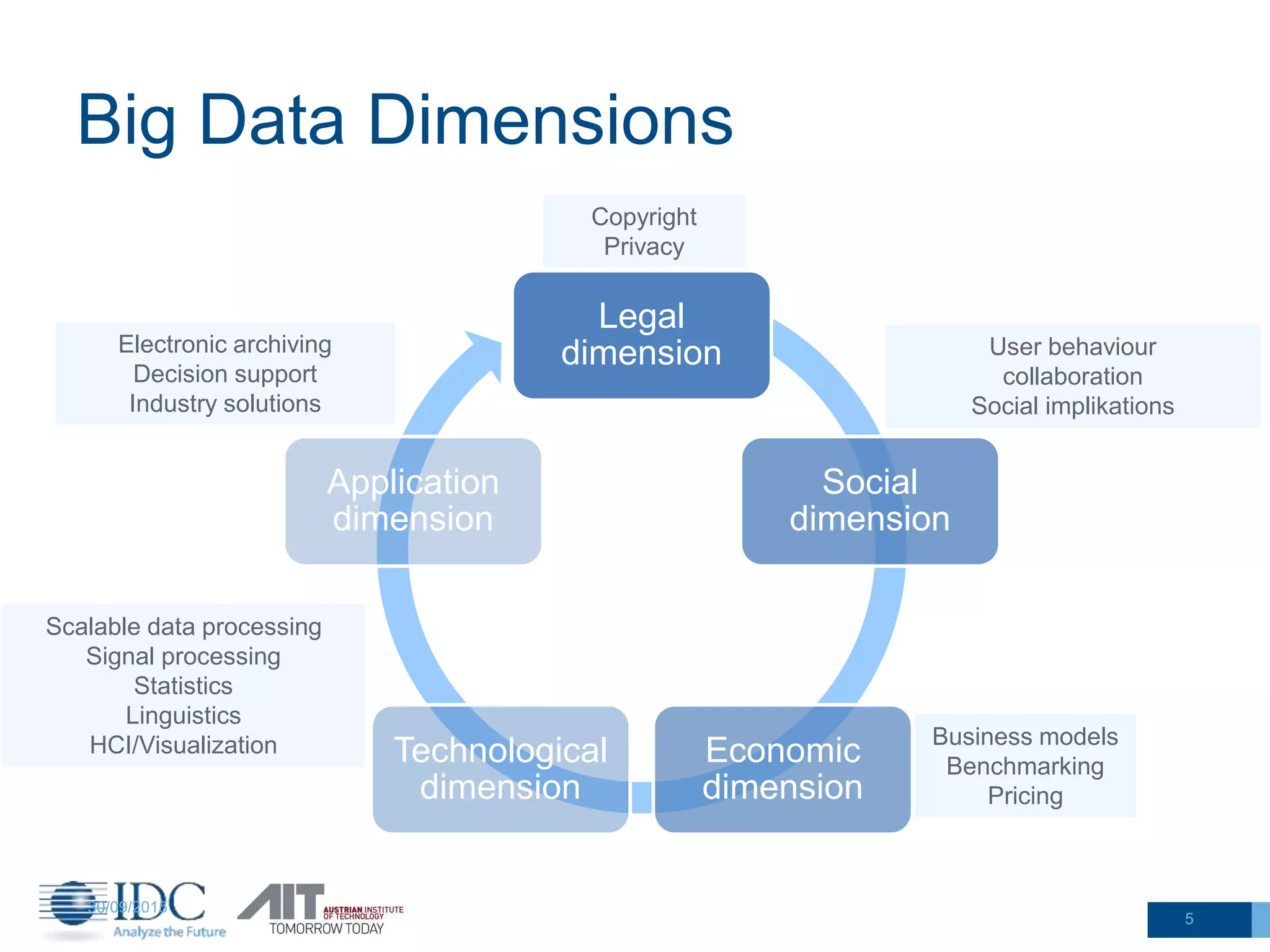
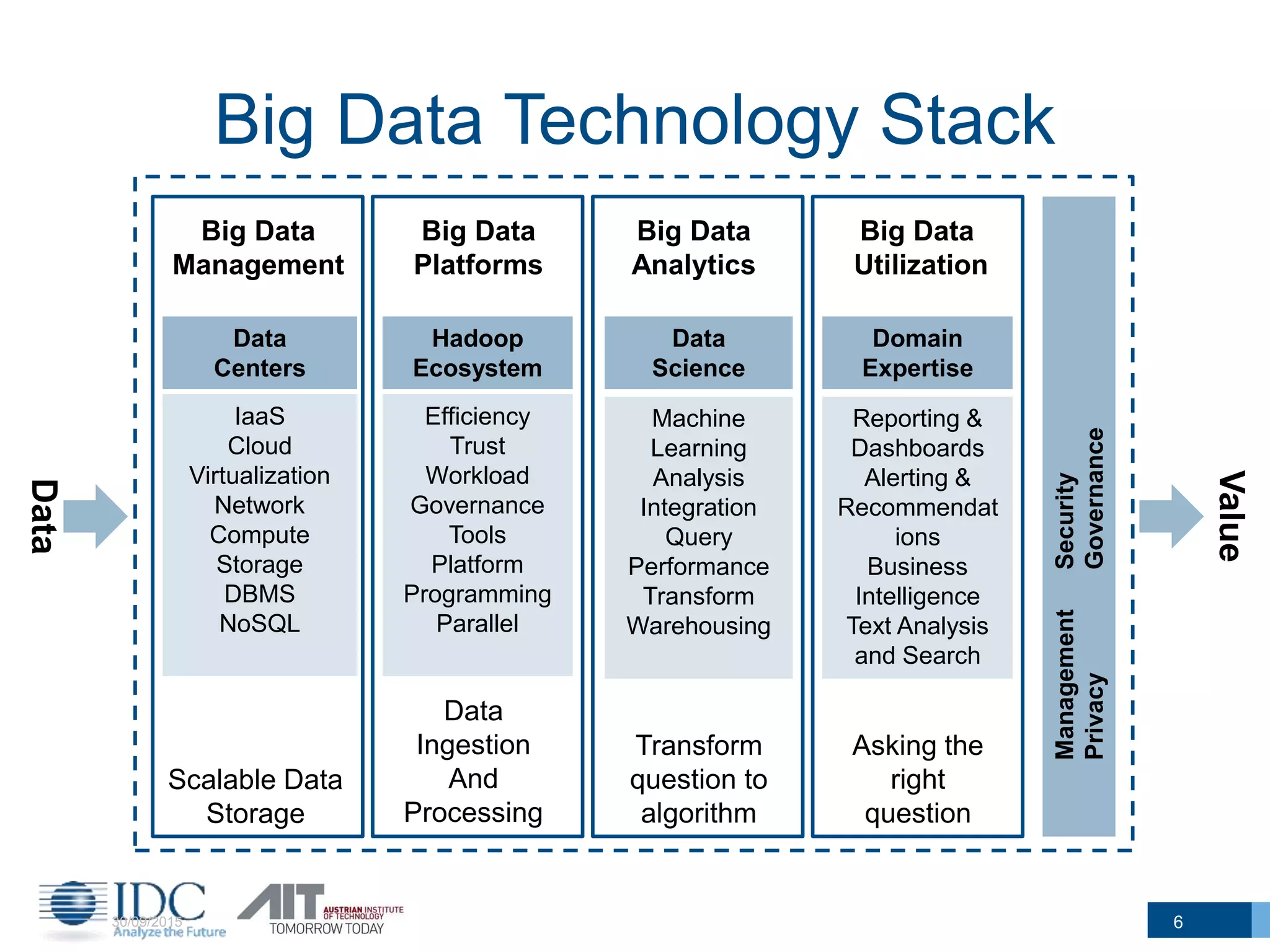
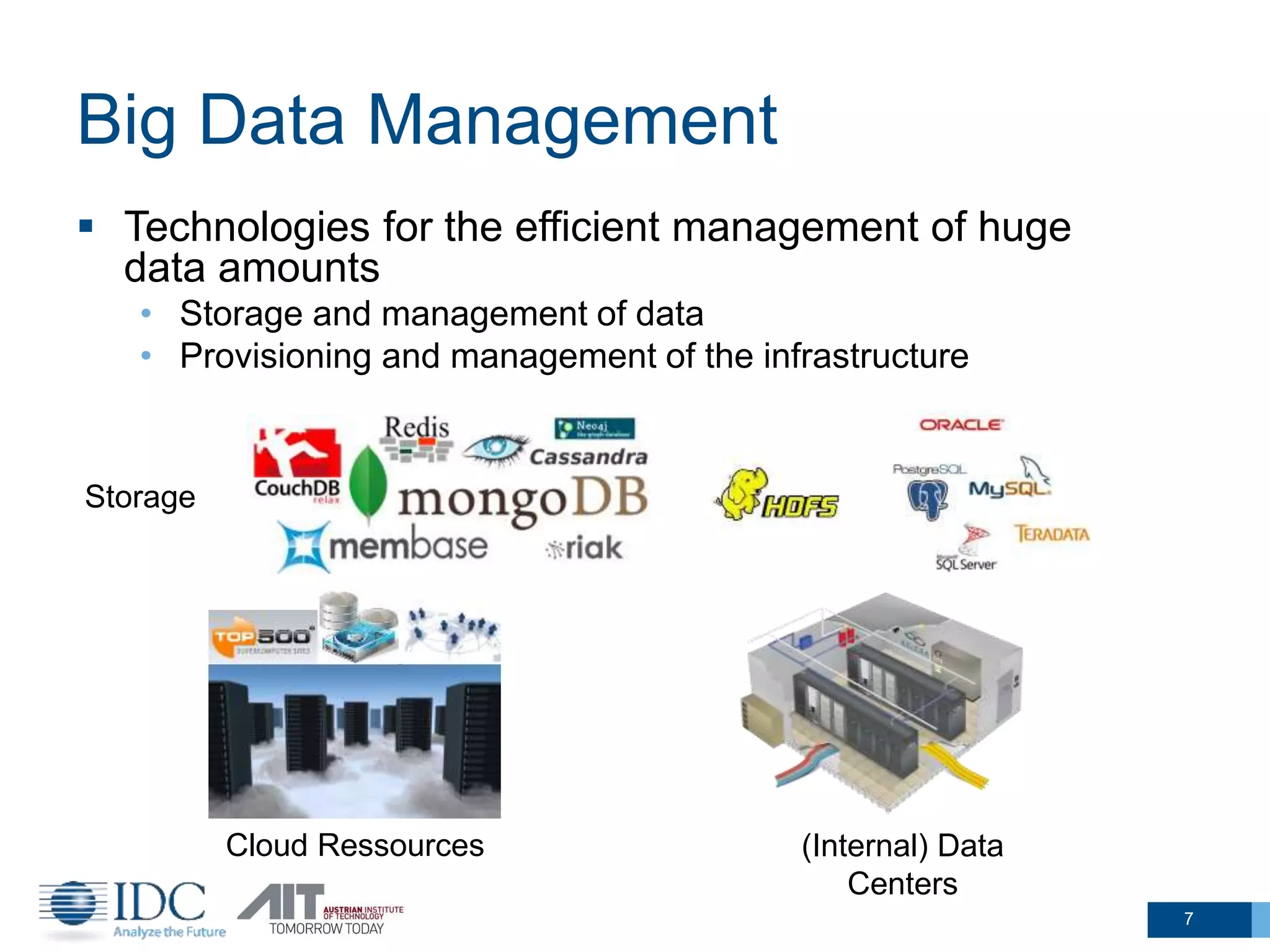
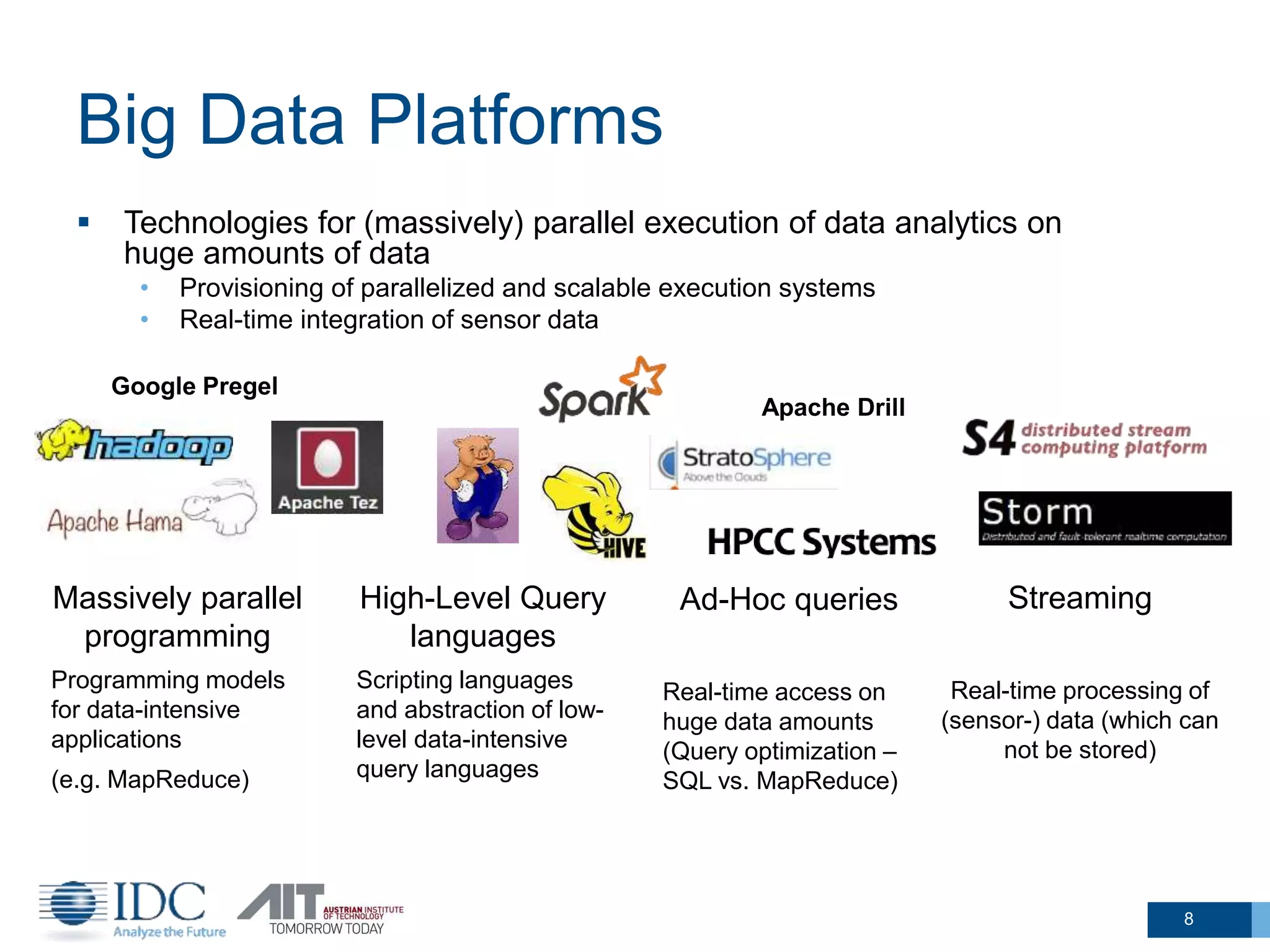
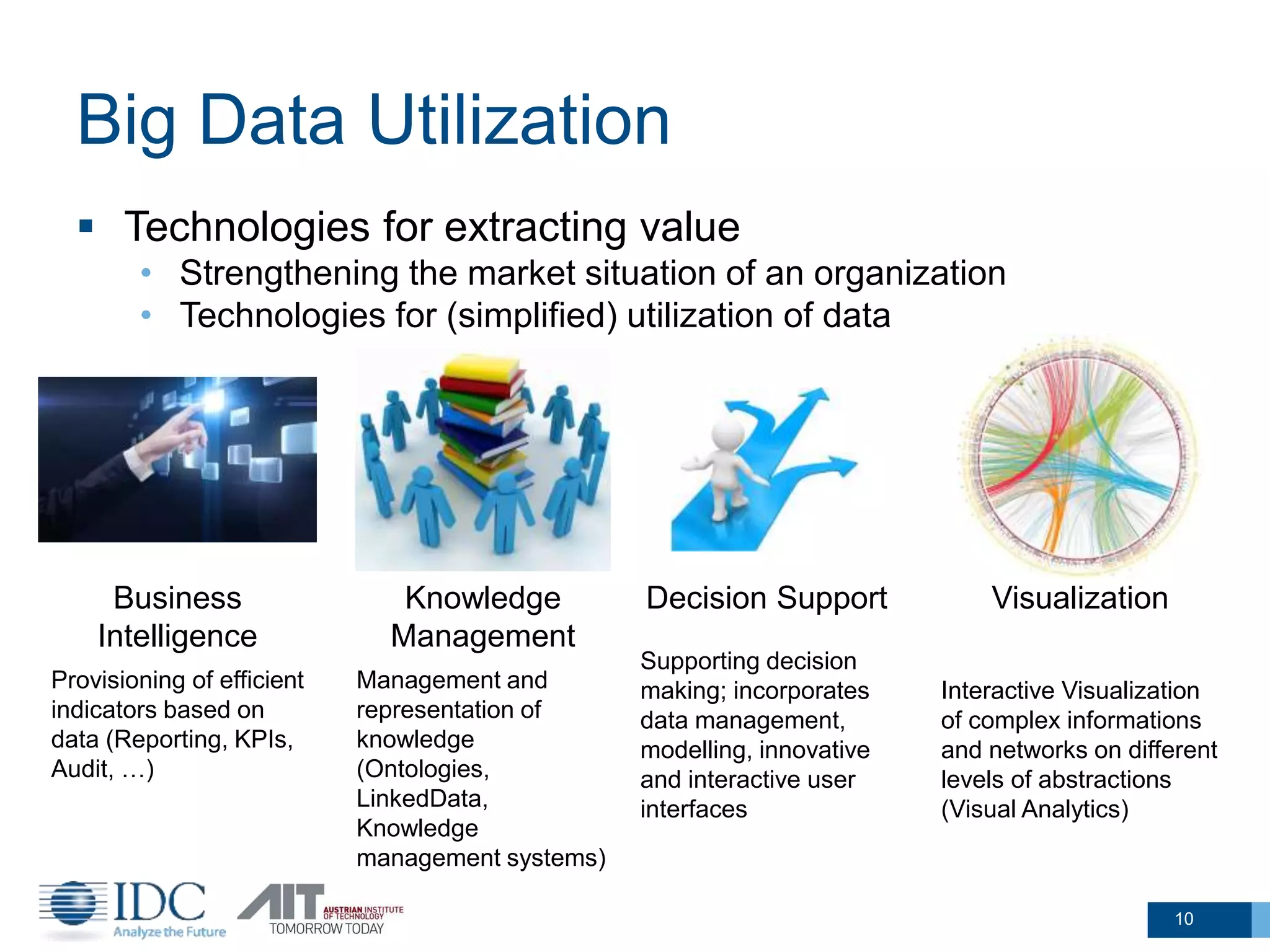
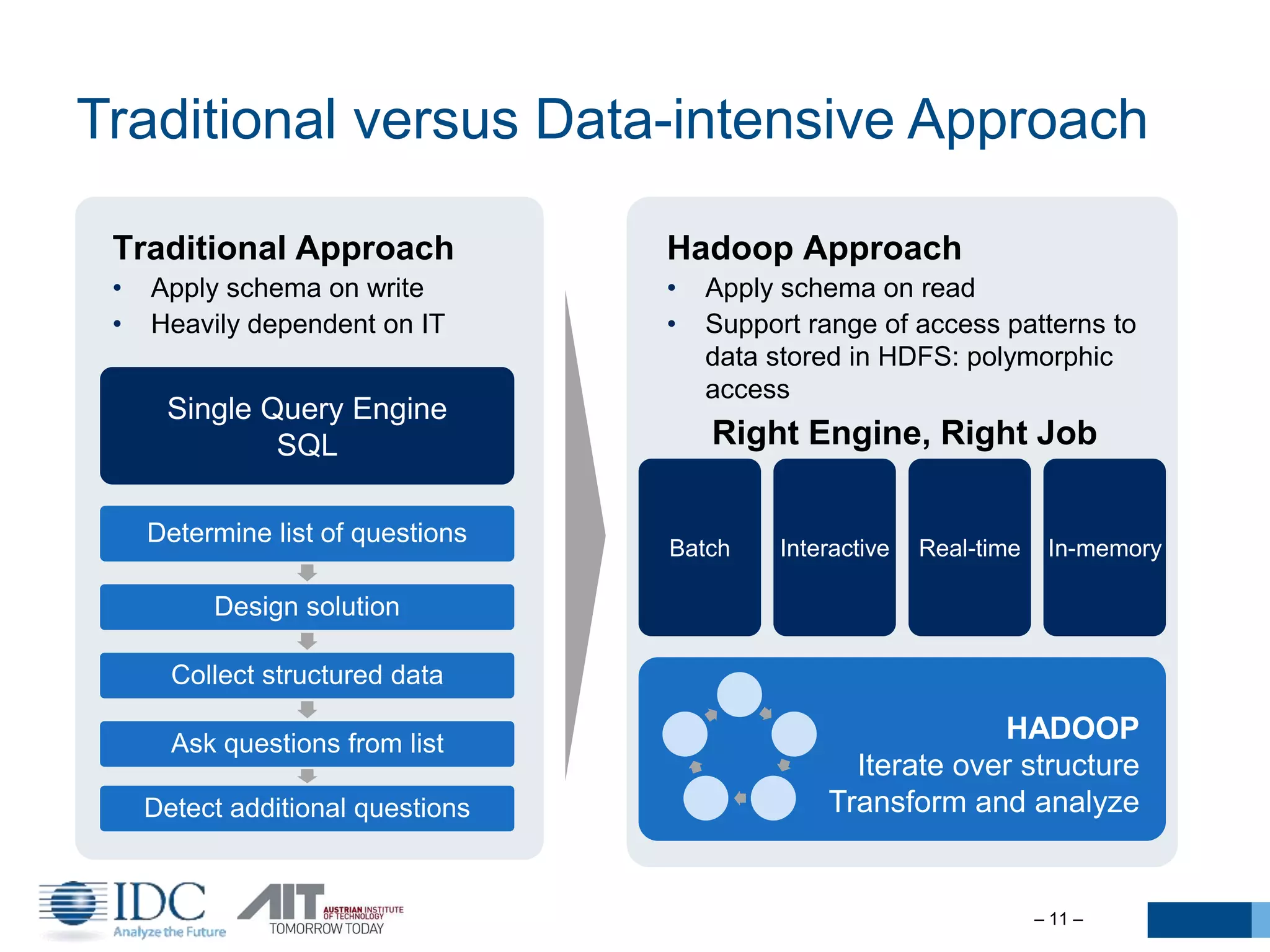
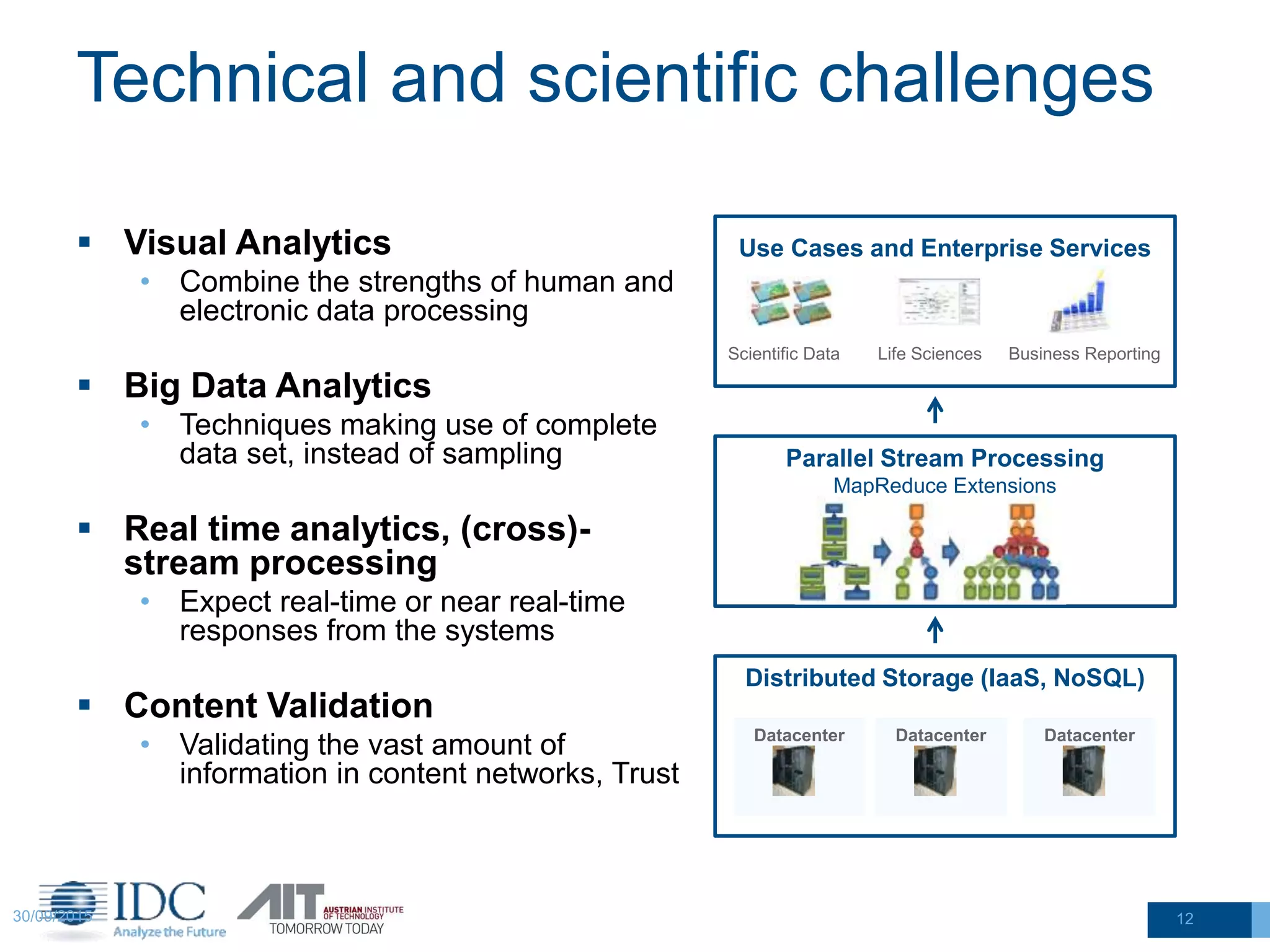
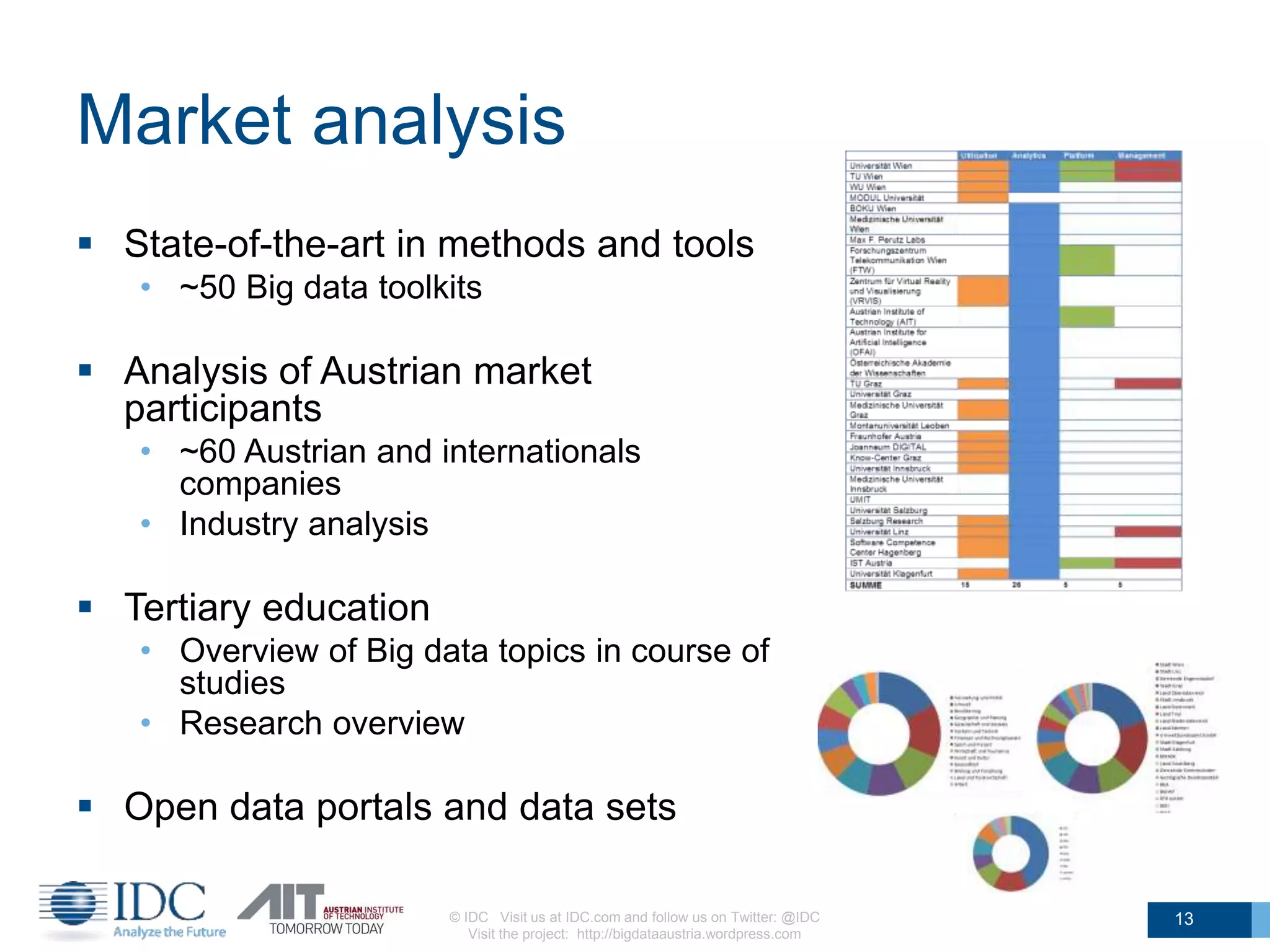
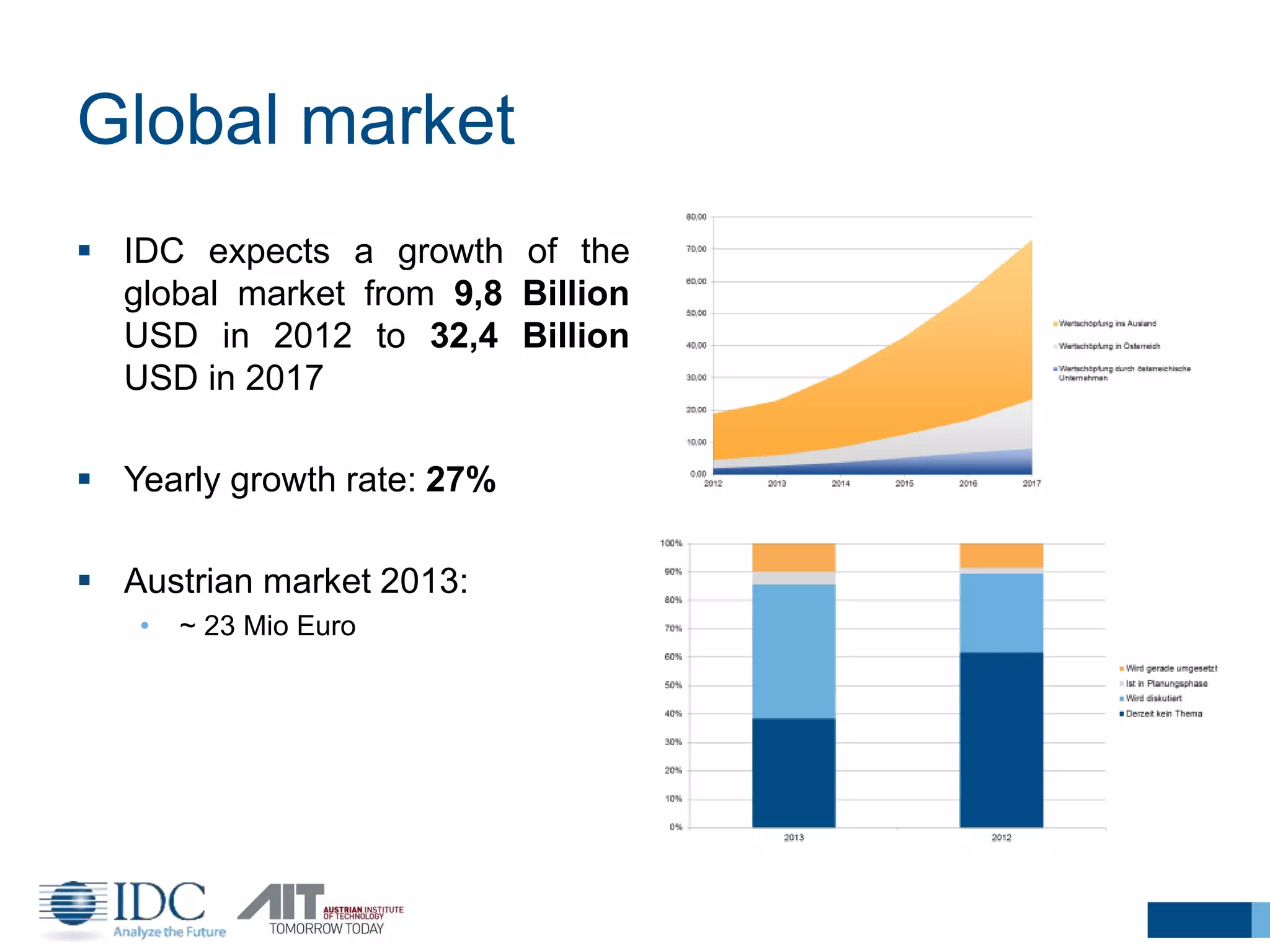
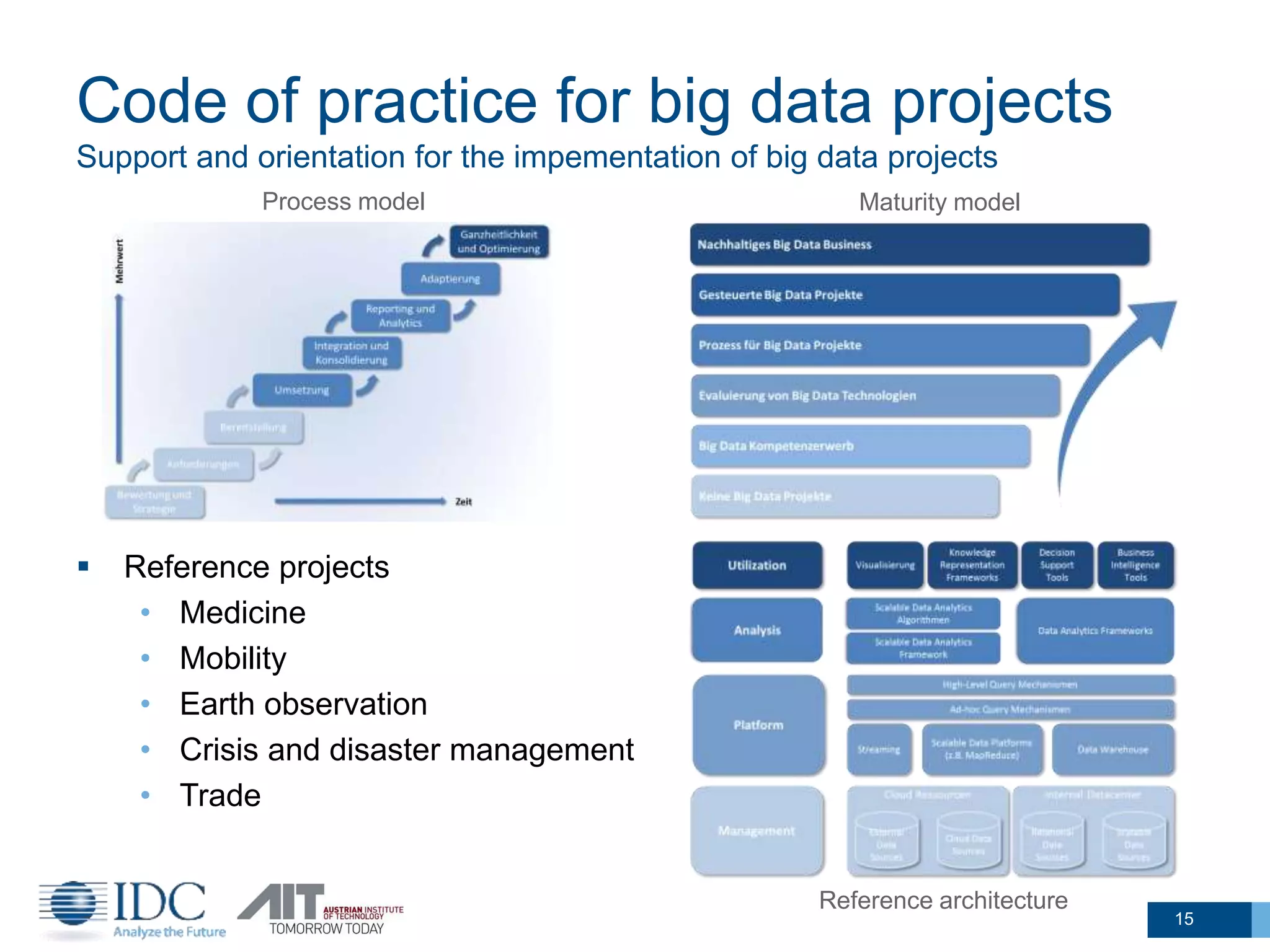
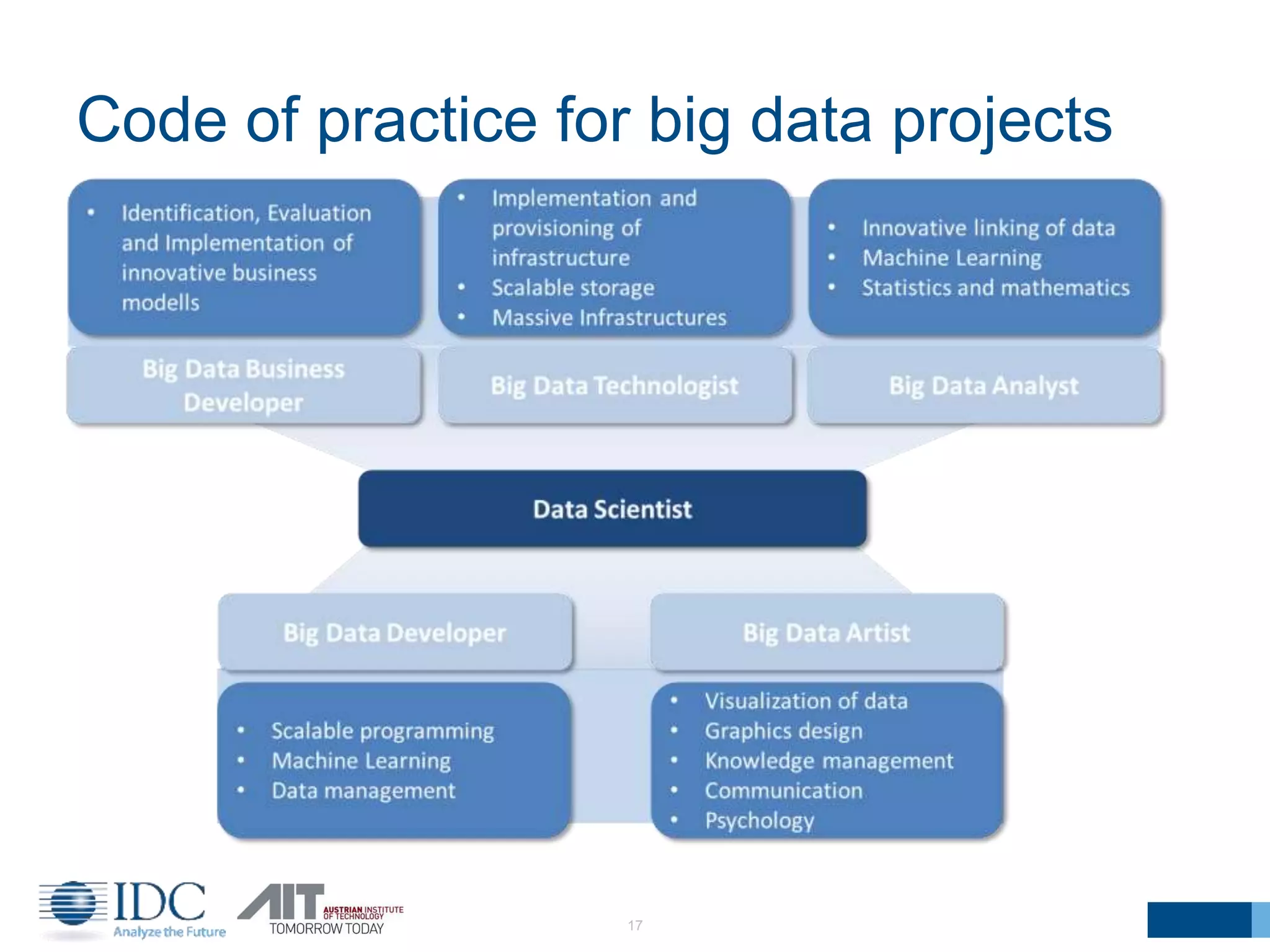
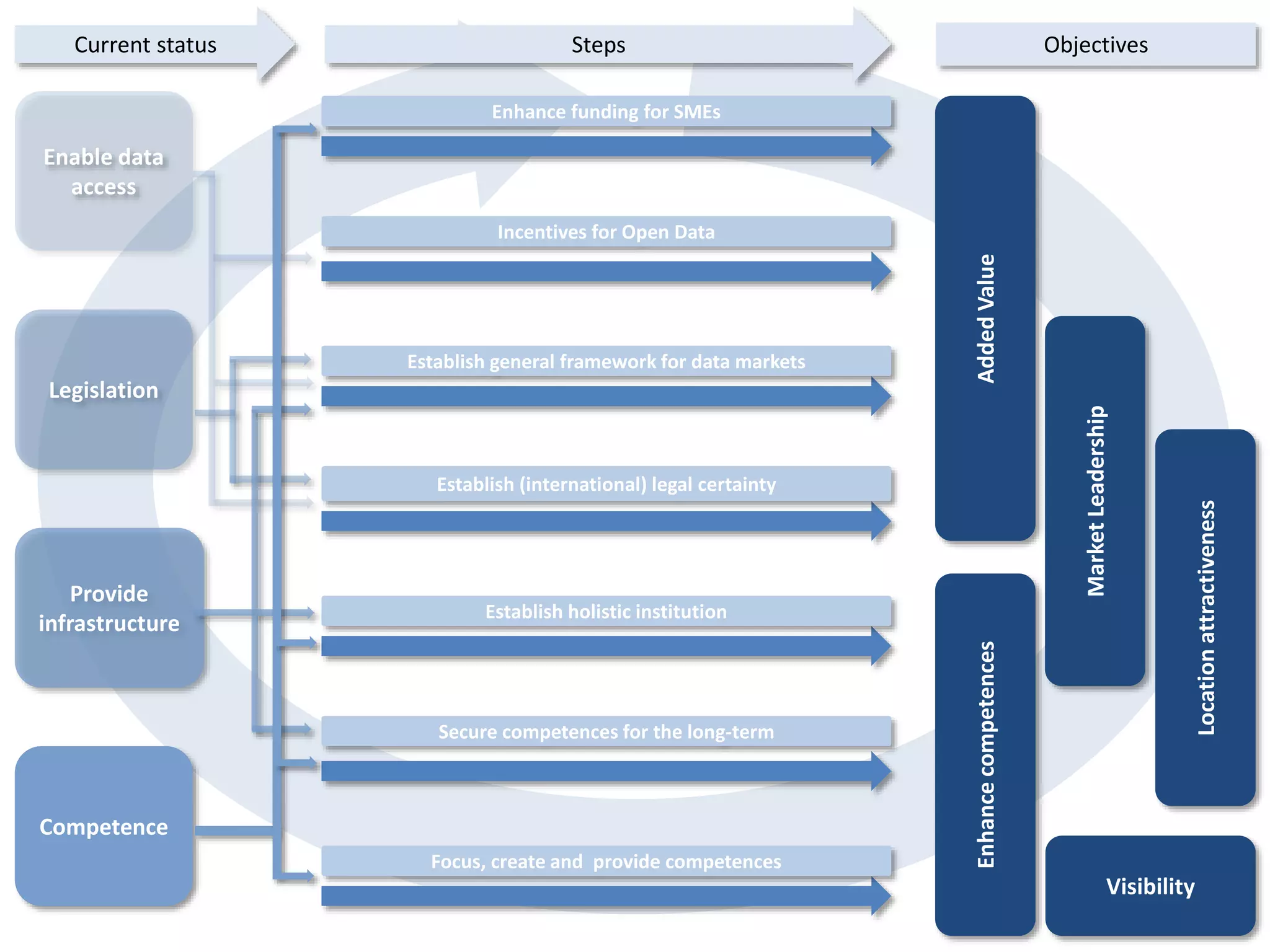
The document discusses the challenges and potentials of big data in Austria, highlighting a study conducted from 2013 to 2014 that examined the state-of-the-art, market analysis, and best practices for big data projects. It outlines the characteristics of big data, including its volume, velocity, variety, and value, and emphasizes the need for efficient technologies for data management and analytics. The report also forecasts growth in the global big data market, addresses skill shortages in data-related jobs, and offers recommendations for improving competencies and infrastructure in the field.