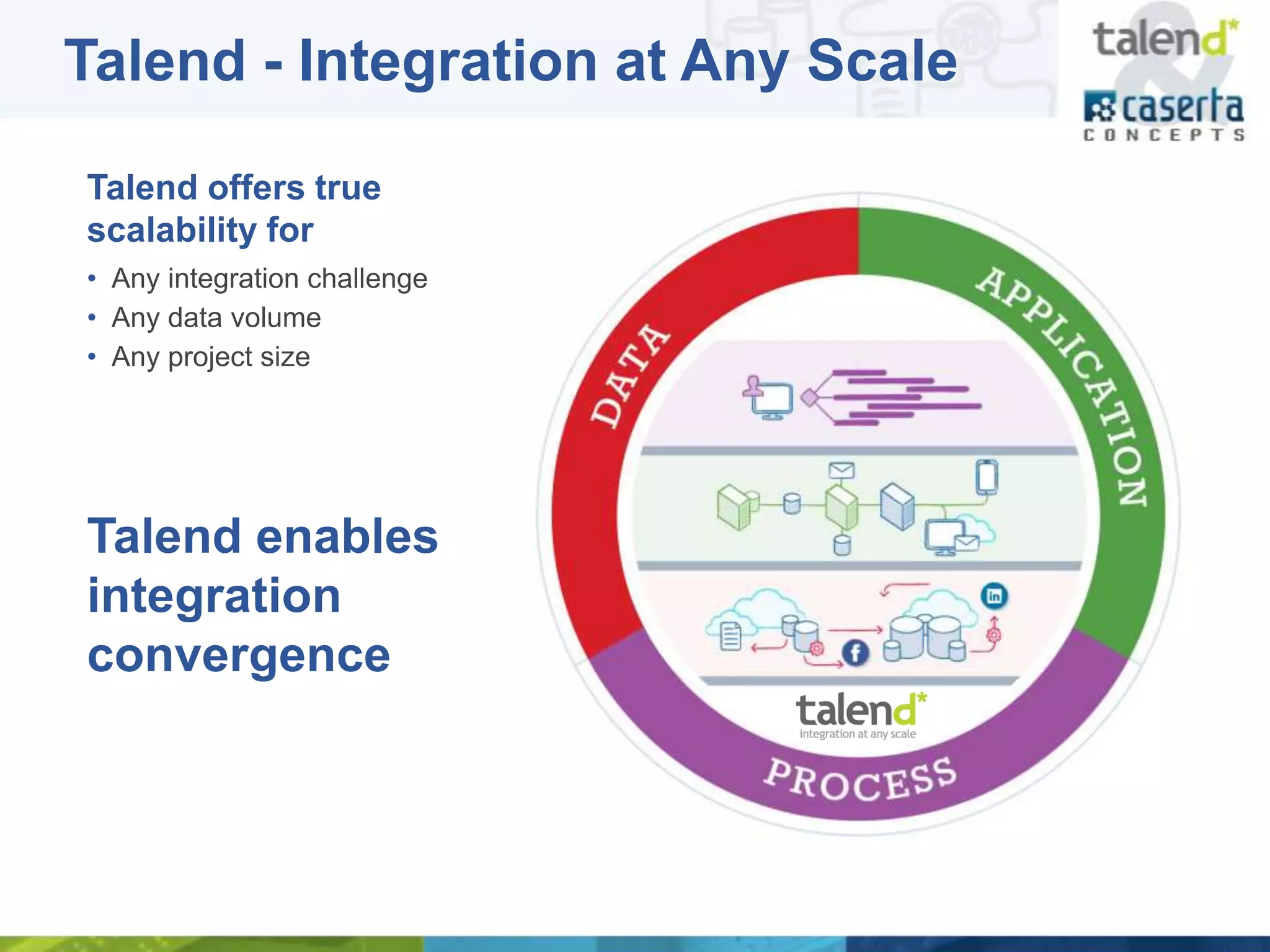
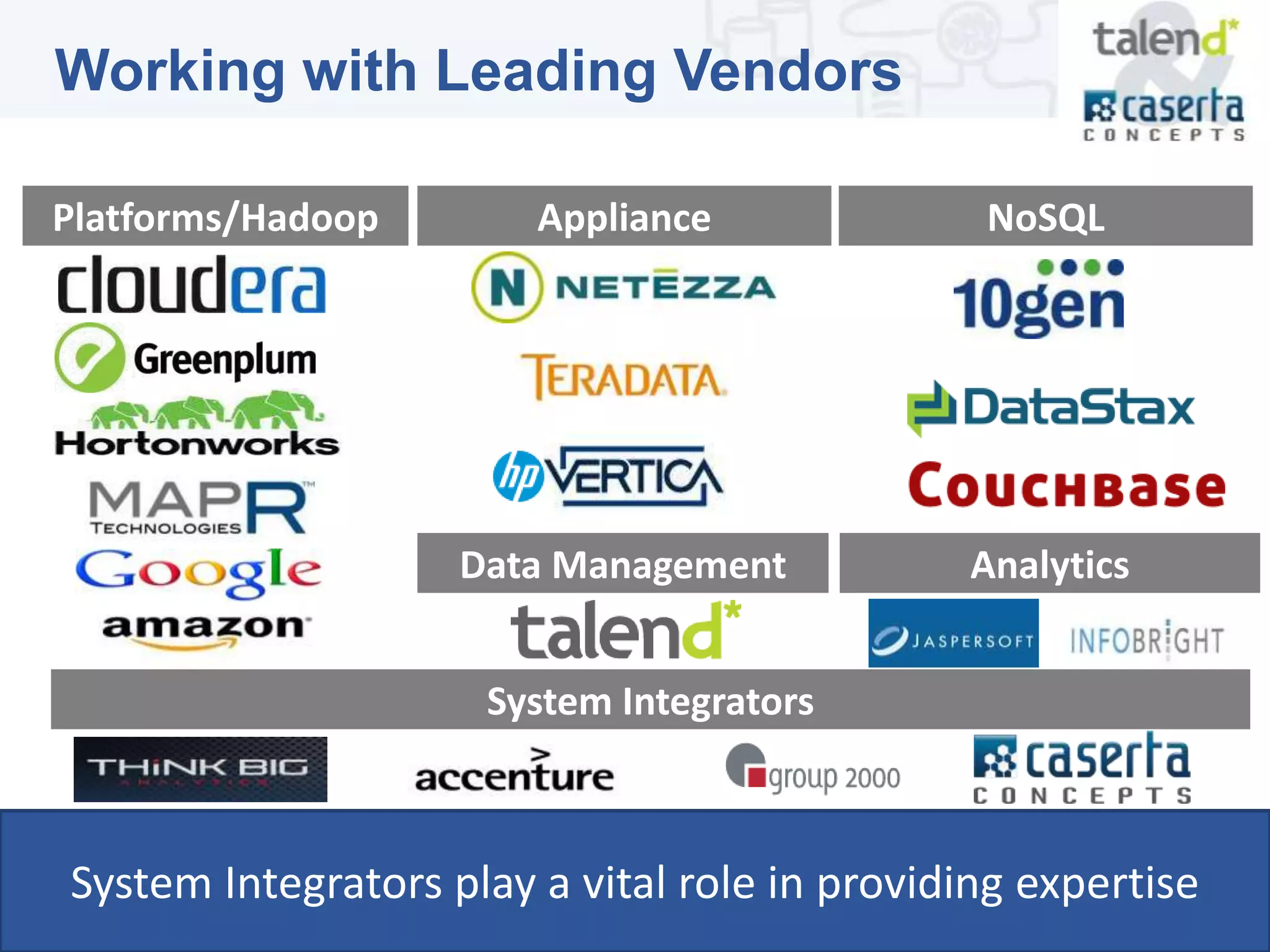
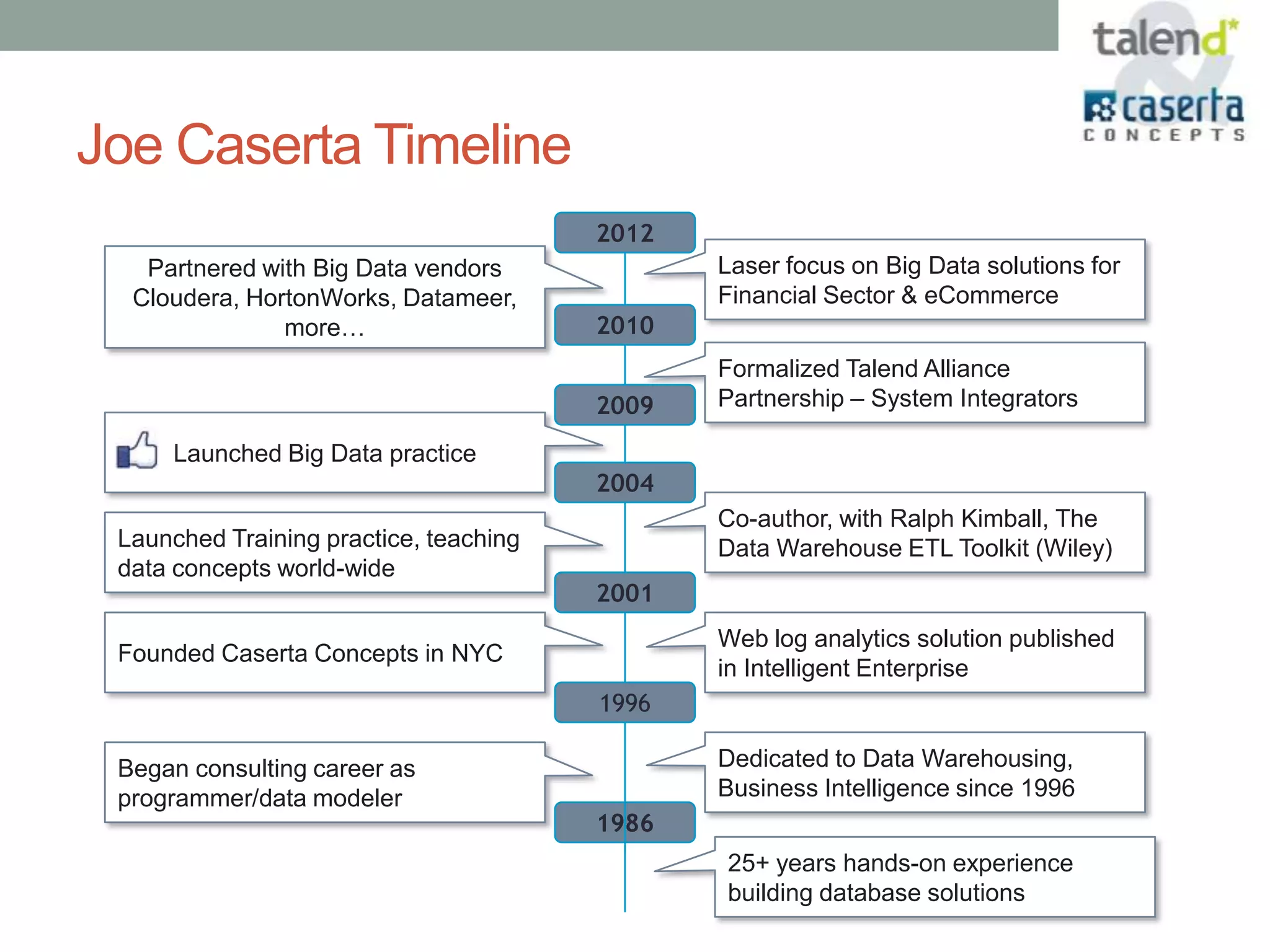
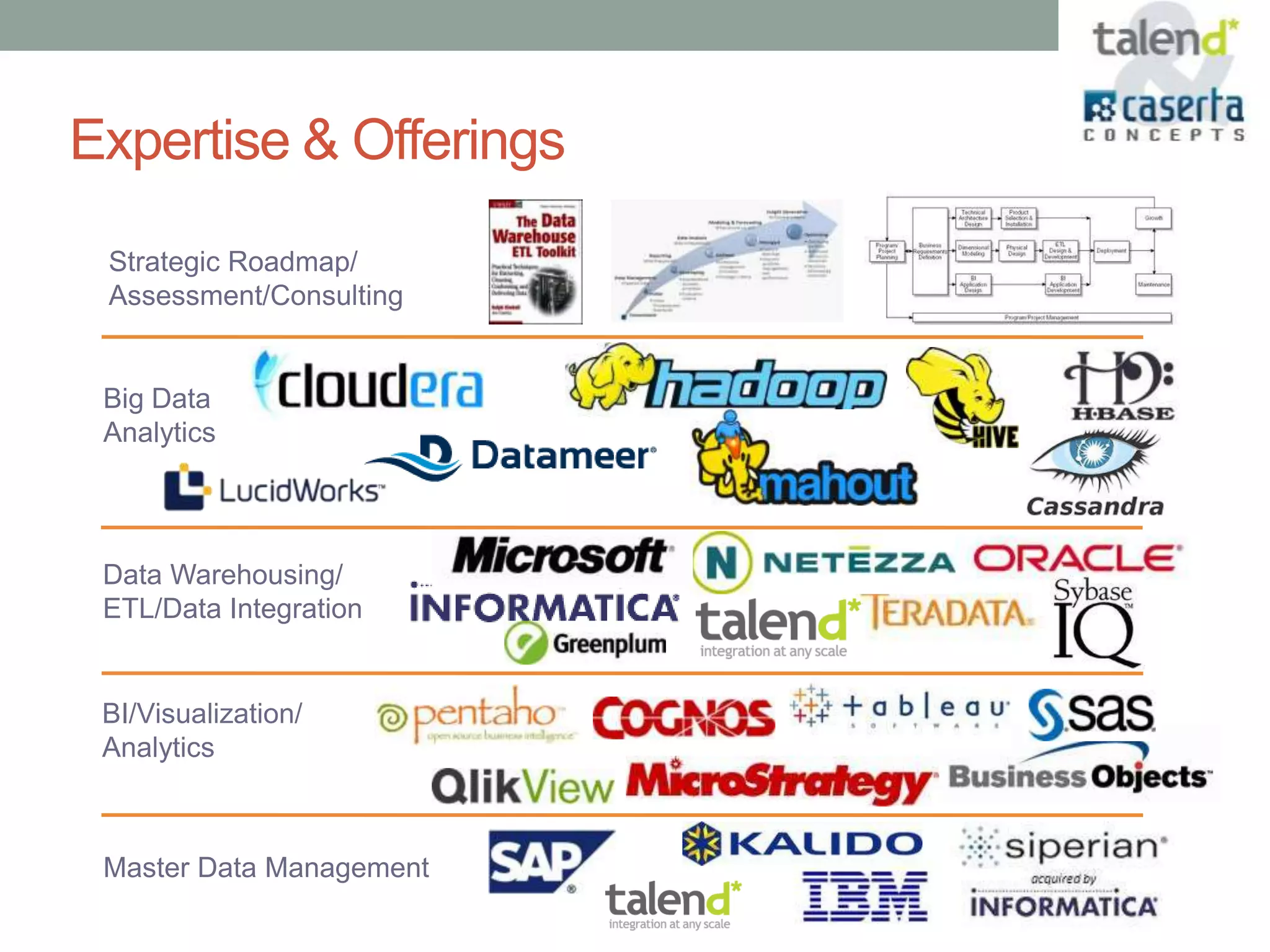
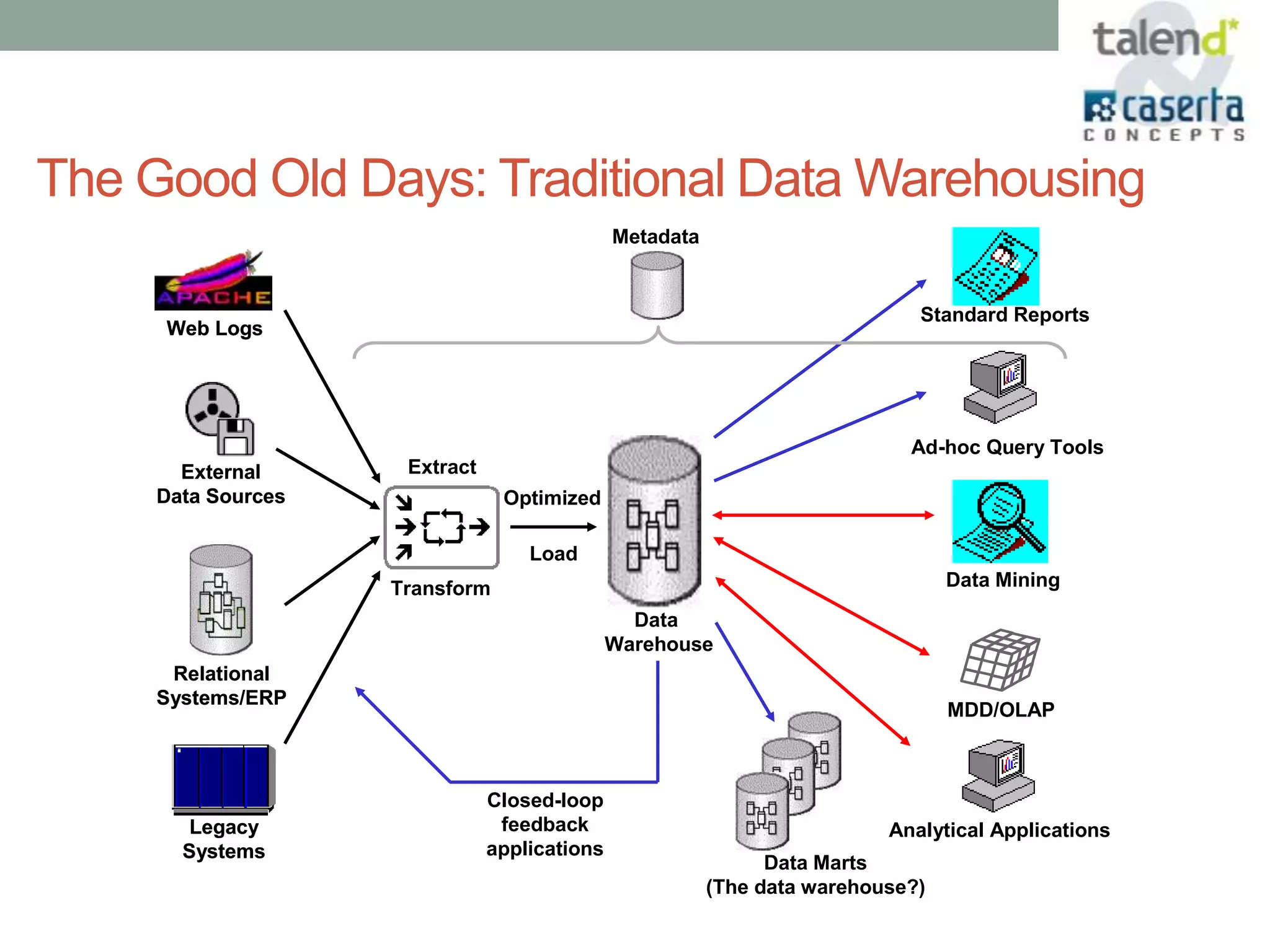
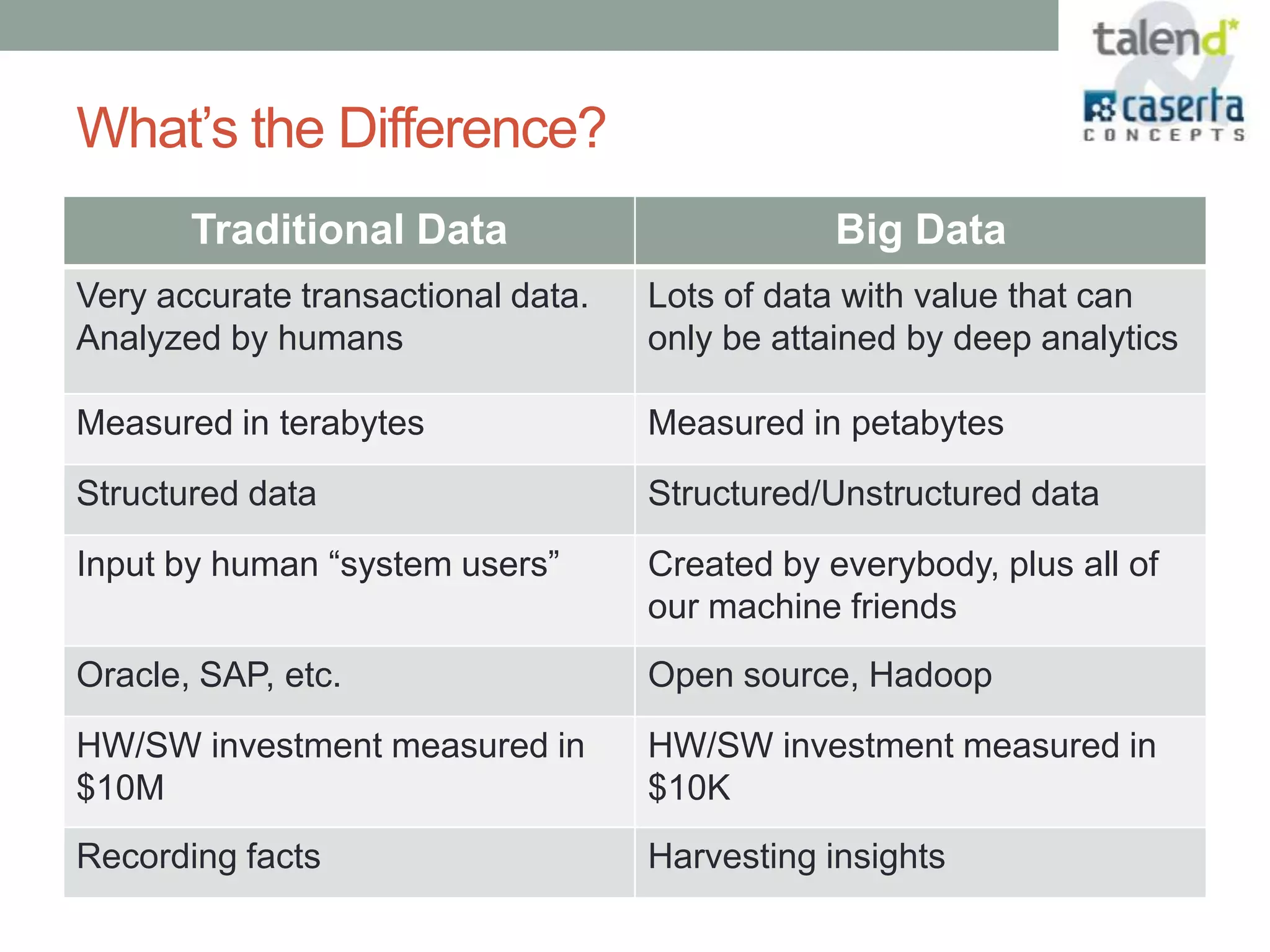
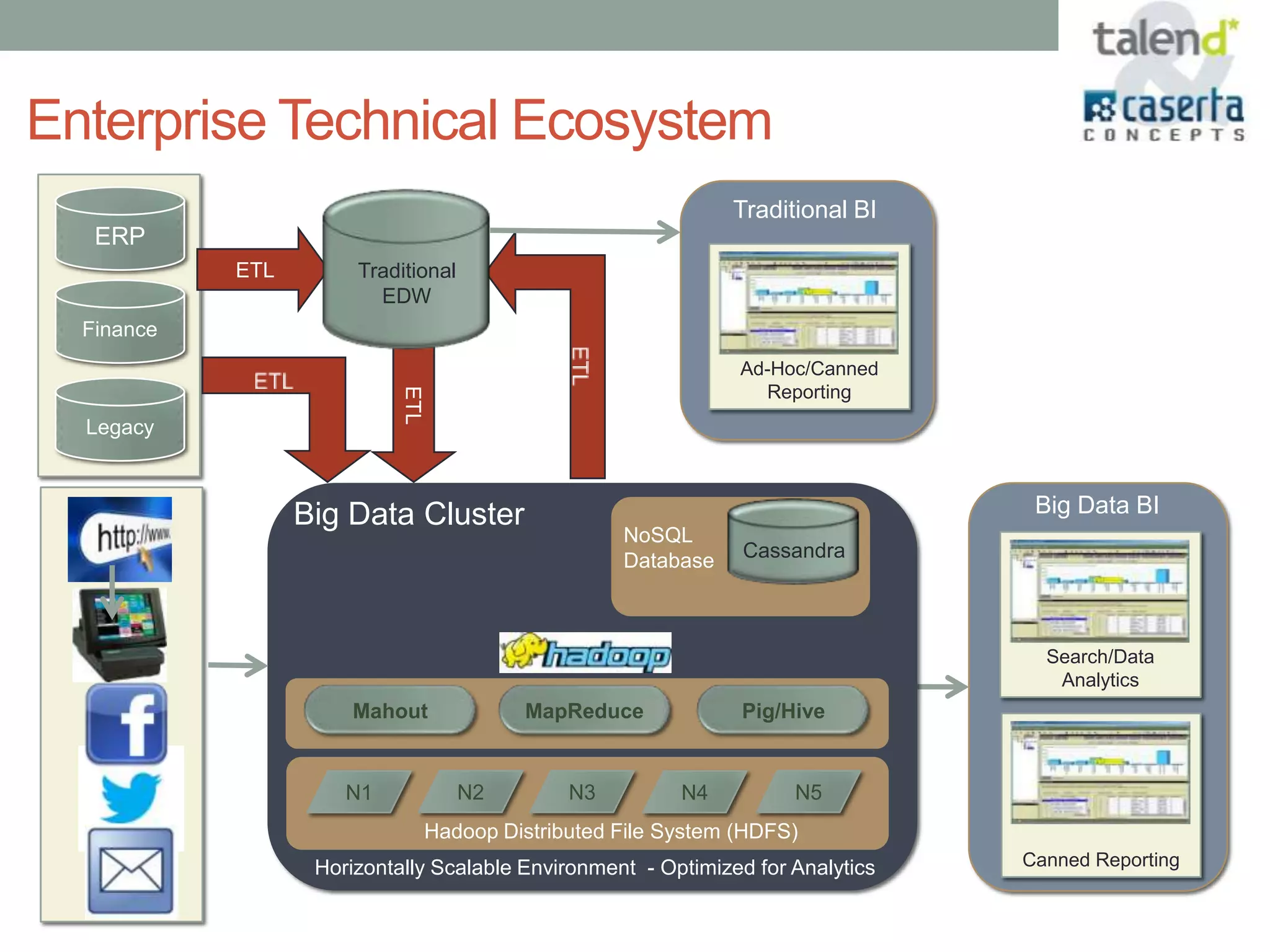
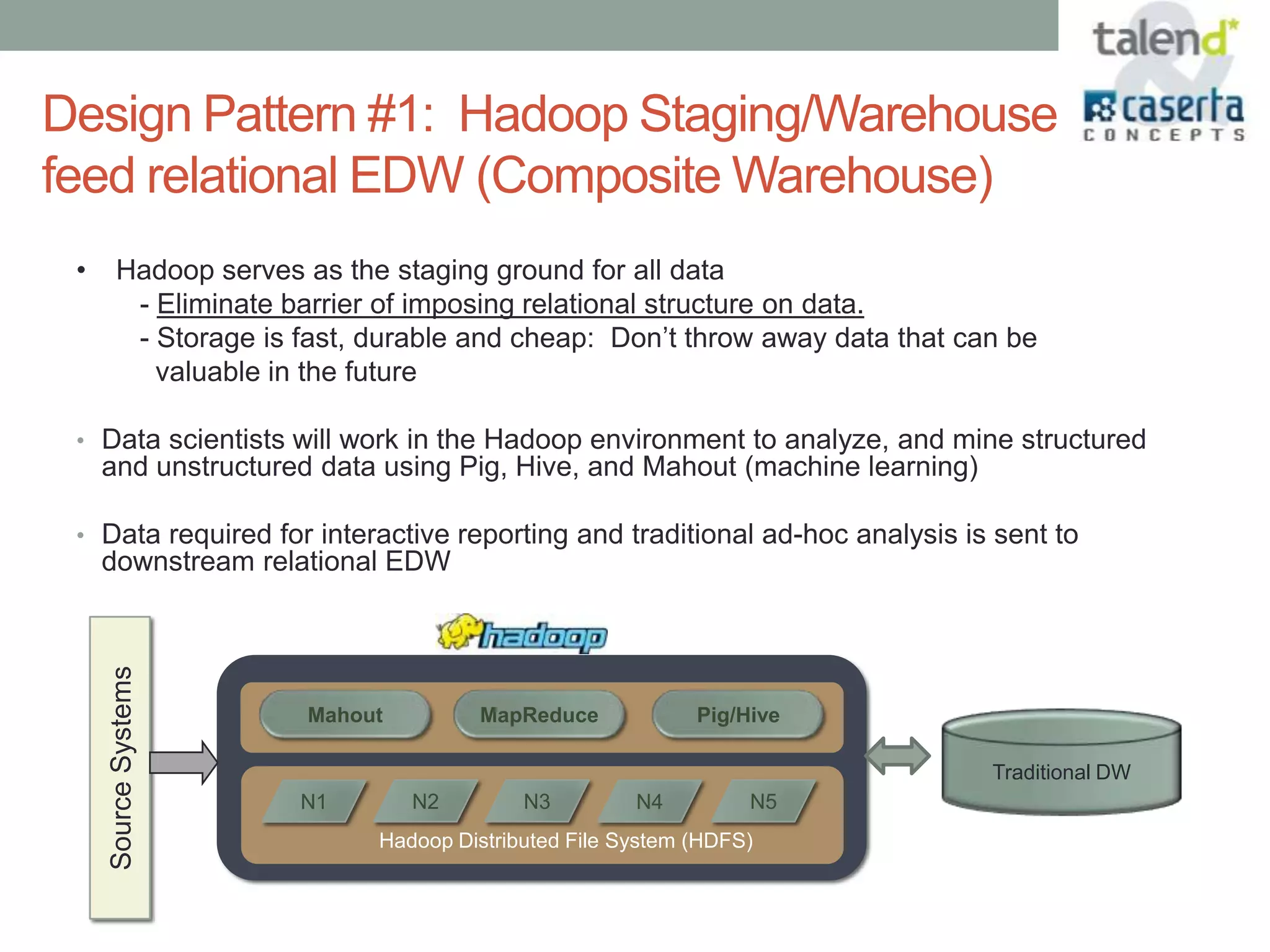
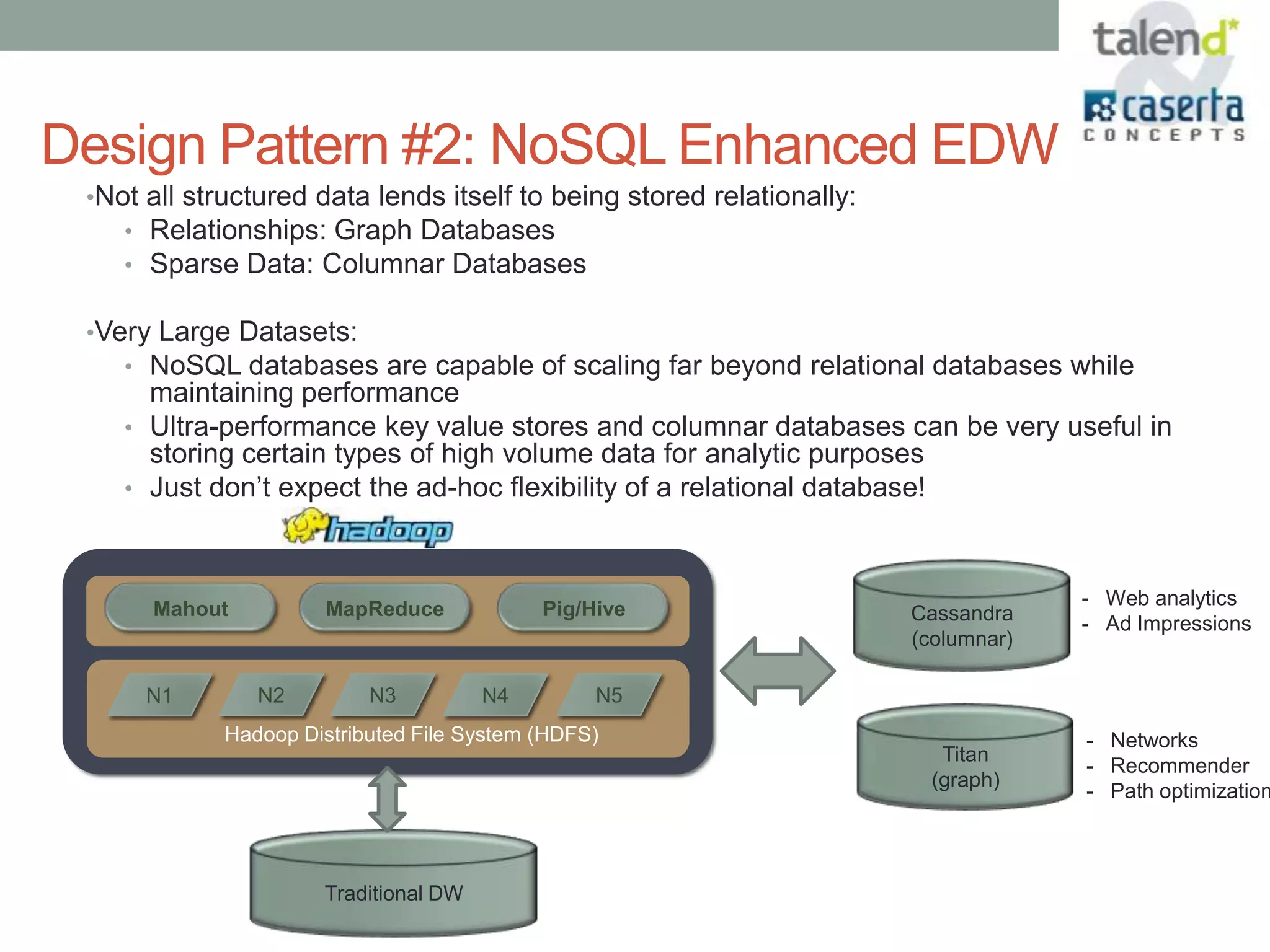
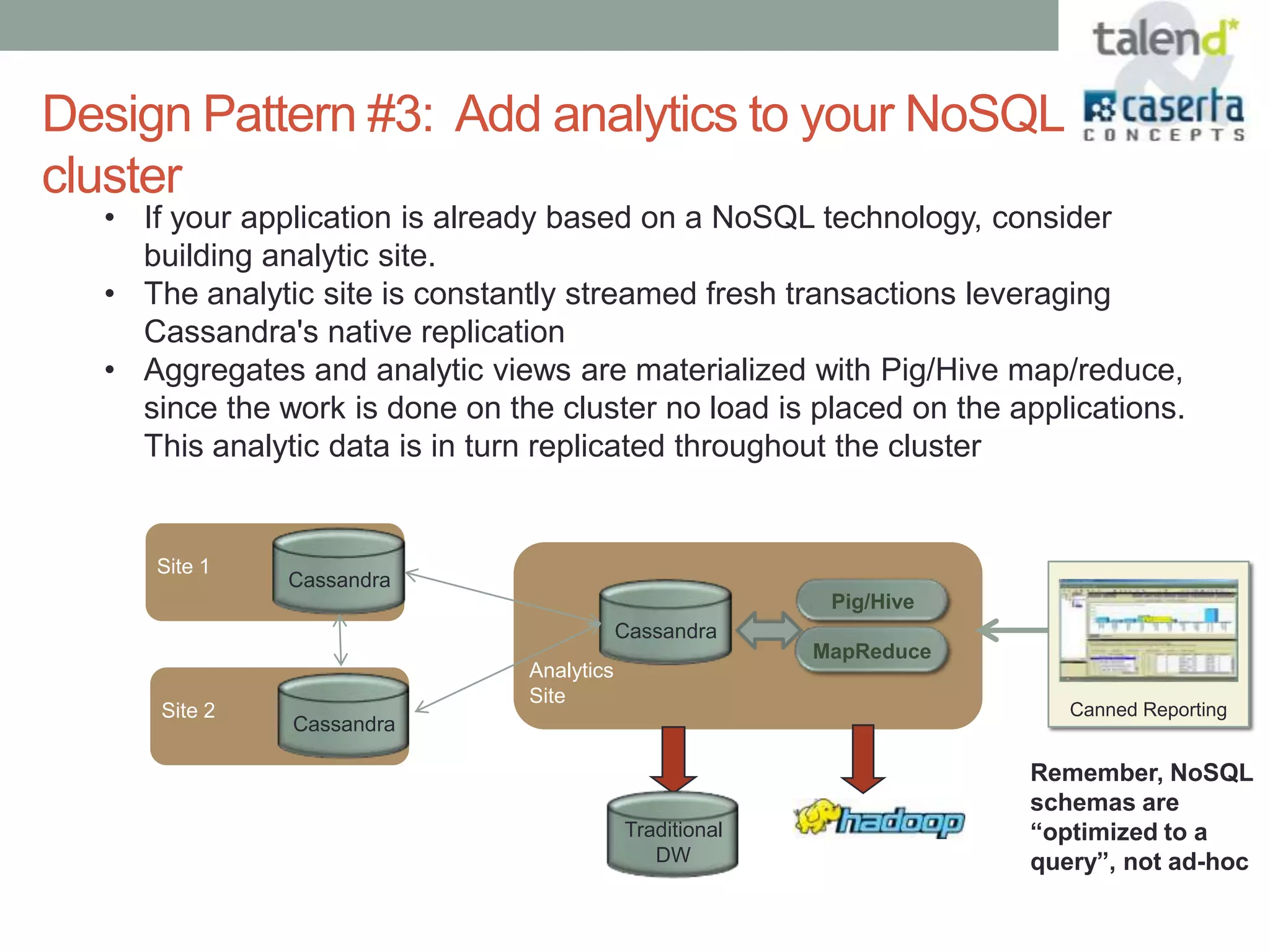
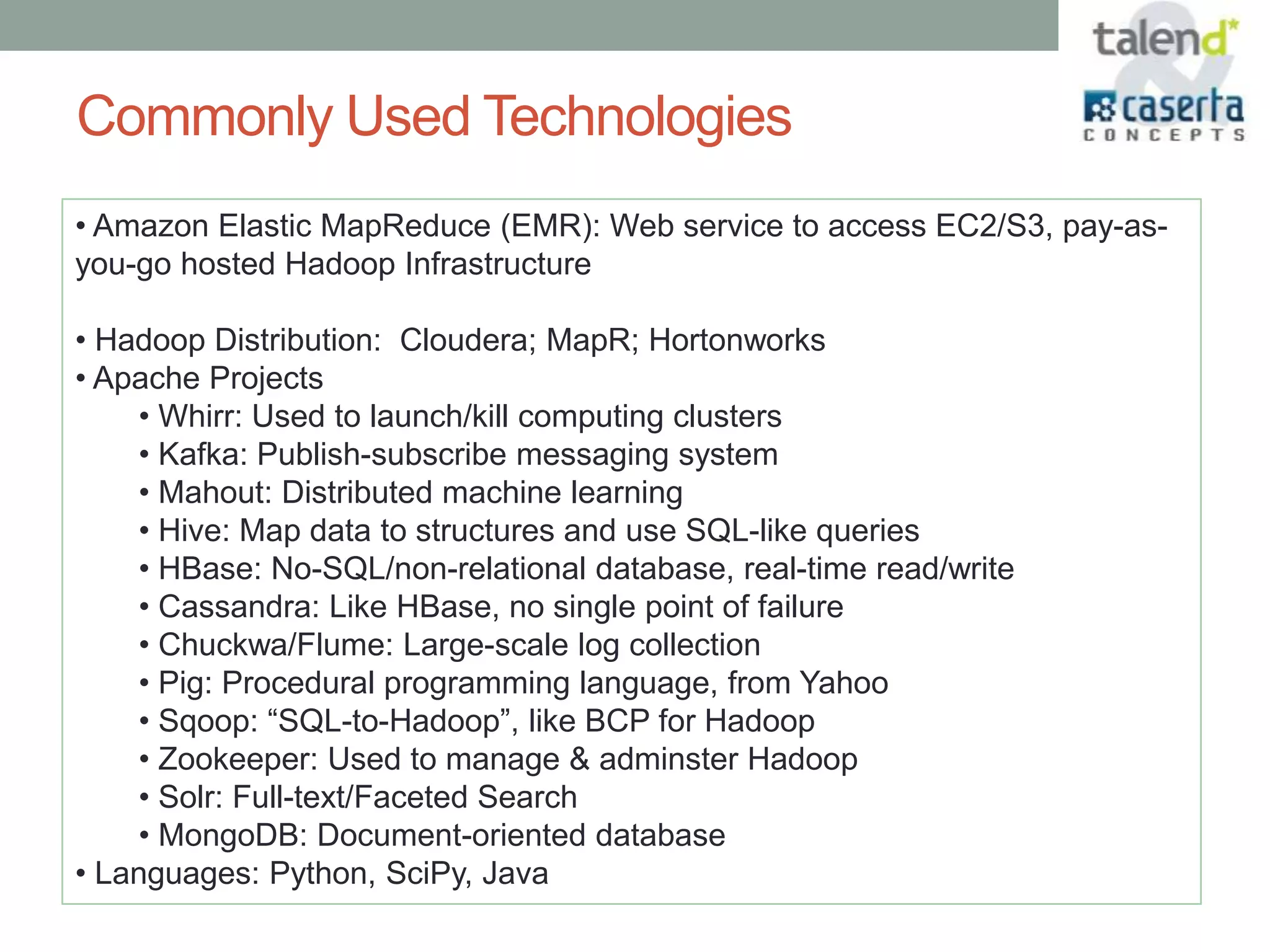
This document summarizes a webinar presented by Talend and Caserta Concepts on the big data ecosystem. The webinar discussed how Talend provides an open source integration platform that scales to handle large data volumes and complex processes. It also overviewed Caserta Concepts' expertise in data management, big data analytics, and industries like financial services. The webinar covered topics like traditional vs big data, Hadoop and NoSQL technologies, and common integration patterns between traditional data warehouses and big data platforms.